初中八种基本时态讲解及练习
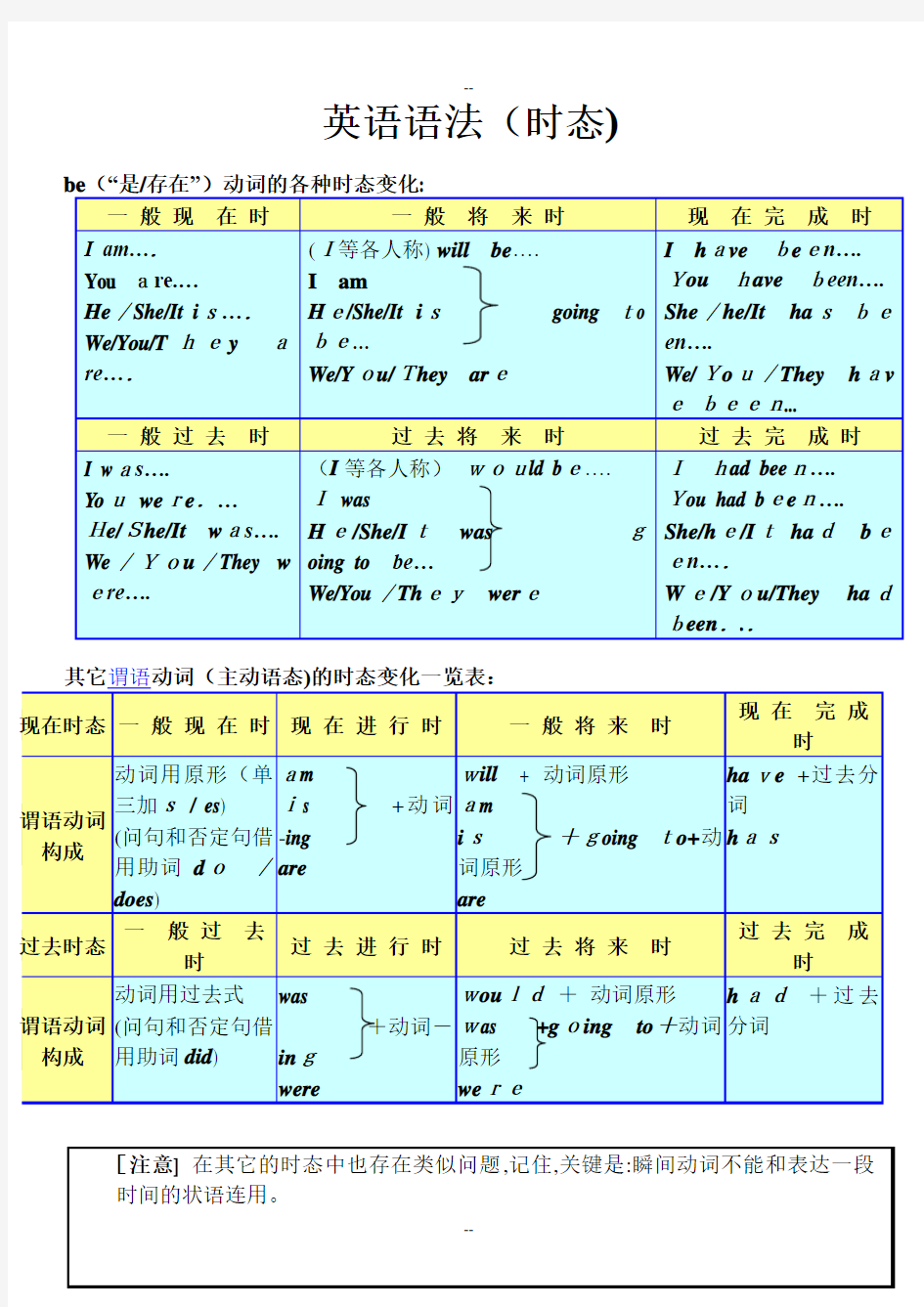

英语语法(时态)
[注意] 在其它的时态中也存在类似问题,记住,关键是:瞬间动词不能和表达一段时间的状语连用。
如:How long may Ikeep the book?(这本书我能借多久?)(句子中keep取代了borrow)
注意:句型变化时,
否定句在am /is /are/will/have/has/was /were /had/would 后面加not,而且not都可以缩写为n’t (am后面not不可以缩写);
疑问句将am/is/are /will /have /has /was/were/had/would 提前到句首。
八种时态的具体用法:
(1)一般现在时:表示现阶段经常或习惯发生的动作或存在的状态,或说明主语的特征。
①一般现在时句子中常有的时间状语:often,usually,sometimes,alwa
ys,every (day等), once/twice,a(week等), on (Sunday等),never,in th
e(morning等)。
如:They go to the Palace Museum once a year.(他们每年去一次故宫)/
They oftendiscuss business in the evening.(他们经常在晚上商谈生意)
②表示客观真理、事实、人的技能或现在的状态时句子里一般不用时间状语。
如:The earth turnsroundthesun.(地球绕着太阳转)/
Lighttravels faster than sound.(光传播比声音快)
③表示十分确定会发生(如安排好的事情)或按照时间表进行的事情,用一般现
在可以表达将来,句子中可以有将来时间。
如:The trainfor Haikouleavesat 8:00 in themorning.(开往海口的列车上午8点开车)
④在时间状语从句中(以when,after, before, while, until,as
soonas等引导)和条件状语从句中(以if,unless引导),用一般现在时代替
一般将来时,句子可以有将来时间。
如:Pleaseringme upas soon as youarrive inGermany.(你一到德国就给我打电话)/
If it rains tomorrow,we will havetostay at home.(如果明天下雨我们就只好呆在家)
⑤一般现在时用于倒装句中可以表示正在发生的动作,动词以come,go为
主。
如:Here comesthe bus.(车来了) /
There goes the bell.(铃响了)。
(2)一般过去时表示过去某时发生的动作或状态,这种动作或状态可能是一次性,也
可能经常发生。
①表示过去具体时刻发生的一次性动作时,时间状语有:at(eight) (yest
erdaymorning),(ten minutes) ago, when引导的时间状语从句。
如:I got upat 6:00thismorning.(我是早上六点钟起床的)/
Little Tom broke the window at half past ninethis mor
ning.(小汤姆今天早上九点半把窗子打破了)/
When he wentintotheroom,he saw a stranger talking with his father.(他走进房间时发现一个陌生人正和他父亲谈话)
②表示过去一段时间内不知何时发生的一次性动作时,时间状语有:yesterda
y,last(year等), in(1998 等)。
如:He came toourcity inthe year2000.(他2000年来
到我们市)
③表示过去一个阶段中经常发生的事情时,时间状语有:last…, in…,f
rom…to…,for(10years),often,usually, sometimes,always,
never等。
如:MrJackson usually went toevening schools when he wasyoung./
Every day he wentto therich manandborrowed
books fromhim.
④讲故事、对过去经历的回忆、双方都明白的过去事件等一般用过去时,而且经
常省略时间状语。
如:I happenedto meetRoseinthestreet.(我正好在街上遇到露西)
(3)一般将来时表示将来某一时刻或经常发生的动作或状态。
①一般将来时的时间状语有:tomorrow,this(afternoon),next (year),one day,now,soon,someday,sometime, in the future, when引导的从句等。
②用will构成的将来时,表示动作与人的主观愿望无关。“shall”用于第一人称,“will”用于所有人称。
如:I will graduate from this schoolsoon.(我很快就要从这所中学毕业了)/
Youwill stay alone after Ileave.(我走了之后你就要一个人过了)
③“am/is/are goingto+动词原形”表示打算或准备要做的事情,或
者主观判断即将要发生的事情,而“am/is/are to+动词原形”表示安排或
计划中的动作。
如:Aman told themthatthe womanwasto give birth to thespecial baby.(有一个人告诉他们那个妇女就会生下那个特别的男孩)/
It’s going to rain soon.(天快要下雨了)
④表示一个人临时决定要做某事,可以用will表达。
如:I will go to thelab toget some chemicals(化学药剂).So pleasewaituntil I return.(我要到化学实验室去取些药品,请等我回来)
⑤现在进行时、一般现在时也可以表示将来。(见相应时态)
⑥shall和will在口语的一些疑问句中相当于情态动词。Shall一般与第一人
称连用,will与第二人称连用。如:Shallwego tothe zoo next S
aturday?(我们下周六去动物园好吗?)/ Will you pleaseopen th
edoor for me?(替我把门打开好吗?)
⑦“be to +动词原形”表示按照计划将要发生的事情。如:An angel came
totellher that shewasto havethisspecial boy.
(4)现在进行时现在进行时表示现在正在进行的动作或是现阶段正发生而此刻不一
定在进行的动作。
①现在进行时由“助动词be (amis are )+现在分词”构成。
②现在进行时的时间状语有:now, this…, these…等,但经常不用。
如:What areyou doing up inthe tree?(你在树上干什么?)/
I am writing a long novel thesedays.(我最近在写一本长篇小
说)
③表示即将发生的动作,一般指近期安排好的事情。常见的动词有:com
e, go,stay, leave,spend,do等。
如:I’m coming now.(我就来)/
What are you doing tomorrow?(你明天干什么?)/
He is leavingsoon.(他就要走了)
(5)过去进行时过去进行时表示过去某一时刻或某阶段正在进行的动作。
①过去进行时由“was(第一、三人称单数)或were(第二人称单数和各人称
的复数)+现在分词”构成。
②过去进行时的时间状语有:then, at that time, this time yesterda
y, at (eight) yesterday(morning),(a year) ago,以及由whe
n引出的时间状语从句。
如:He wascookingsupper this timeyesterday.(昨天这个时候他正在做晚饭)/
The littlegirlwasplaying with her toy when I sawher.(我
看到小女孩的时候她正在玩玩具)
③用于宾语从句或时间状语从句中,表示与主句动作同时进行而且是延续时
间较长。句子中通常不用时间状语。
如:Shesaw ithappen when she waswalking past.(她路过时看到事情的发生)/
They sang a lot of songswhile theywere walkingin
the darkforest.(他们在黑暗的森林里走时唱了很多歌)
(6)现在完成时现在完成时表示一个发生在过去的、对现在仍有影响的动作,或
表示开始在过去,并且一直延续到现在,甚至还可能延续下去的动
作。
①在完成时由“助动词have (has)+动词的过去分词”构成。
②表示发生在过去的对现在仍有影响的动作时,时间状语有:already,yet,
just,once,twice,ever, never,threetimes,before等。
如:I have never seen suchfinepicturesbefore. (我以前从来没有看过这么好的画)/
Hehas justgoneto England.(他刚去英国)
③表示在过去开始一直延续到现在(可能延续下去)的动作或状态时,时间状语有:
for(two years),since1990,since (two weeks ago)和since 引导的状语从句。如:I have been away from my hometown for thirty years.(我离开家乡有30年了)/
Uncle Wanghas worked in thefactorysince it opened.(自从这家工厂开张,王叔叔一直在那儿工作)
④口语中have got往往表示have(有)的意思。
如:They have got thousandsof booksin their library.(他们图书馆有上万本书)
⑤have beento与have goneto的区别:havegone to(“已经去了”)表示
人不在这里,have beento(“去过”)表示人在这里。
如:--Whereis Mr Li? –He hasgoneto theUK.(李先生在哪里?他去了英国。)/
--Doyou know something aboutBeijing?
–Yes,Ihave beento Beijing threetimes.(你知道北京的情况吗?是的,我去过那里三次。)
(7)过去完成时过去完成时表示过去某一时间或某一动作发生之前已经完成的动作。简言之, 过去完成时所表示的时间是“过去的过去”。
①过去完成时由“助动词had+动词的过去分词”构成。
②过去完成时时间状语有:by (yesterday), by then, bythe end
of (last…)或者由when,before等引出状语从句。有时句子中会有already, just,once, ever,never等词语,也会有for…或since…构成的时间状语。
如:They had already finished cleaning the classroom when their teacher came.(当老师来的时候他们已经打扫完了教室)/
The woman had leftbefore he realized she was acheat.(在他发觉那个妇女是个骗子时她已经走掉了)
③过去完成时常用于宾语从句中、after引导的从句中,或者从句是before
引导的主句中。
如:After I had put on my shoes andhat,Iwalkedinto the dar kness.(我穿上鞋子戴上帽子走进了黑暗之中)/
He said thathe hadnever seen a kangaroobefore.(他说他以前从来没有见过袋鼠)
(8)过去将来时过去将来时表示在过去预计将要发生的动作或存在的状态。
①过去将来时由“助动词should(第一人称)或would(第二、三人称)+动词
原形”构成。在美国英语中,过去将来时的助动词一律用“would +动词原形”。
②过去将来时常由于宾语从句中,时间状语有:later, soon,the next (day).
③在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中不可以使用过去将来时,而应该使用一般过
去时。
如:He promisedthat hewould pay me a lotifIhelpedhim with the project.(他答应付给我许多钱如果我帮助他搞那个项目)/
Every time when hewasfree,he would sitdown andrea dsome books.(以前每次只要他有空他就会坐下来看看书)
④表示纯粹的将来时用would或should,表示打算或主观认为的事情用was/wer
egoing to(+动词原形)。
如:Shetold meshe wouldbe 18the next month.(她告诉我她下个月就18岁了)/
Shetoldme that she was going to have a walk with h er pet dog.(她告诉我她打算带她的宠物狗去散步)
⑤过去将来时还可以表示一个过去经常性的动作。如:When itrained i
nthe day,he would bring an umbrellawith him.(白天下雨时
他会随身带一把雨伞)
(9)现在完成进行时:现在完成进行时指一个从过去就开始一直延续到现在并由可能继续下去的动作,它具有现在完成时和现在进行时双重特征,结构是:“have/has +been +动词的现在分词”。
如:I have been swimmingin the cold waterforabouttwo hours.(我已经在冰冷的水里游了将近两个小时)/
How long haveyou been waiting here?(你在这里一直等了多
久?)
时态综合练习(一)
1. Sales of CDs have greatly increased since the early 1990s, when people ________toenjoy theadvantages ofthisnew technology.
A.begin B. Began C. have begun D. had beg un
2.Turnon thetelevision or open amagazine andyou ________advertisements showinghappy families.
A.will often see B. oftensee C. are often seeing D. have often seen
3. —I hear Jane has goneto the Holy Island for her holiday.
—Oh, hownice!Doyou know whenshe ________?
A.wasleaving B. had left C.hasleft D. Left
4.—What were you doing when Tonyphoned you?
—I had just finished myworkand________ to take a shower.
A. hadstarted B.Started C. have started D.wasstart ing
5.I ________ you notto movemydictionary—nowI can’t find it.
A. asked
B. AskC. was asking D. hadasked
6. —HasSam finished his homework today?
—I havenoidea. He________ it this morning.
A. did B.hasdone C. was doingD. had done
7. —What’s that terriblenoise?
—The neighbors ________ for aparty.
A.haveprepared B. are preparing C. prepare D. will prepare
8.Now that she is out of a job, Lucy________ going back to school, butshe hasn’tdecidedyet.
A.hadconsidered B. hasbeen consideringC.considered D. i sgoingtoconsider
9.The teacher, with6 girlsand 8boys of herclass, ________ visiting a museum when the earthquake struck.
A. was
B. were
C. hadbeen D. would be
10. The discussion ________ alive whenan interestingtopic was brought in.
A.wascoming B. had come C. has come D. came
11. Because the shop ________,allthe T-shirtsare sold at half price.
A. has closed down B. closed down C. is closing down D. had cl osed down
12. Let’s keep to the point or we ________ any decisions.
A. willnever reach B.have never reachedC.neverre
ach D. never reached
13. My mind wasn’t on what he was saying so I’m afraidI ________half ofit.
A. wasmissing B. had missedC.will
miss D.missed
14. —You were outwhen I dropped inat your house.
—Oh,I ________ forafriend fromEnglandat theairport.
A. was waiting
B. had waited C.amwaitingD.has waited
时态综合练习(二)
1. She has set a new record, thatis,the sales of herlatest book ________ 50 million.
A. have reached B. has reached C. are reaching D.had r eached
2. He keptlooking at her, wondering whether he________ her somewhere.
A. sawB. has seen C.sees D. had se en
3.Thecrazy fans ________patiently for two hours and they would wait t ill the movie star arrived.
A.werewaiting B.had been waiting C. hadwaite
d D. would wait
4. She________ her hairstyle in her hometown before shecame toChongqing for a better job.
A. would change B. has changed C. changed D.was changing
5. The first useof atomic weapons was in 1945, and their power________ increasedenormously ever since.
A. is
B. was
C. has been
D. had been
6.—You haven’tsaid aword about my newcoat,Brenda. Do you like it?
—I’m sorry I ________ anything about it sooner. I certainlythinkit’s pretty on you.
A. wasn’tsaying
B. don’t say
C. won’t say
D. didn’t s ay
7.Why don’t youput themeat in the fridge? It will________ fresh for several days.
A. be stayed B. stay C. be stayin
gD.have stayed
8.How can youpossibly miss thenews? It ________on TVall day long.
A. has beenB. had been C.was D.will b e
9. -Sorryto have interrupted you. Please go on.
-WherewasI?
-You________you didn’tlikeyourfather’s job.
A. had said
B. said C. were saying D. had been saying
10.I arrived late; I ________theroad to be so icy.
初中英语八大时态语态总复习时态讲解
初中英语八大时态语态总复习时态讲解 一般现在时态 【展示平台】 1 一般现在时态用来表示经常,反复,习惯性发生的动作或存在的状态,常与表示频率的副词sometimes(有时), often(经常), usually(通常), always (总是)等连用。时间状语in the morning/ afternoon/ evening(在上午/下午/晚上), every day/ week/ month/ year(每天/周/月/年, at noon/night (在中午/夜里), on Monday/Tuesday(在星期一/二)等也可用在一般现在时态中。如: Bruce usually walks to school. 布鲁斯通常步行去上学。 We have two P.E classes every week. 我们每周上两节体育课。 2 表示现在的特征或状态。如: She is always ready to help others. 她总是乐于助人。 He is 13 years old. 他13岁了。 3 表示事实或客观真理,或在谚语中,也用一般现在时。如: The sun rises in the east and sets in the west every day. 太阳每天东升西落。 When there is a will, there is a way. 有志者,事竟成。 4 一般现在时的基本句型 1)肯定句:① 主语+动词原形+其他②主语(第三人称单数)+ 动词-s+ 其他如:They live in China. 他们住在中国。 He likes eating apples. 他喜欢吃苹果。 2)否定句:① 主语+don’t+ 动词原形+其他 ② 主语(第三人称单数)+doesn’t+ 动词原形+其他 如:They don’t live in China. 他们不住在中国。 He doesn’t like eating apples. 他不喜欢吃苹果。 3)一般疑问句:① Do+主语+动词原形+其他? ② Does+主语(第三人称单数)+ 动词原形+其他? 如:Do they live in China? 他们住在中国吗? Does he like eating apples? 他喜欢吃苹果吗? 【相关链接】 当主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词用第三人称的单数形式。谓语动词的第三人称单数形式的变化规则如下: 1)一般在动词后直接加s。如:talk –talks, live –lives。 2)以s, x., ch, sh或o结尾的动词在其后加es。如: watch –watches, wash –washes, go –goes。 3)以辅音字母加y结尾的动词,把y变成i再加es。如: carry – carries, fly –flies。 4)特殊的,如:have的第三人称单数为has。 【牵手中考】 1. Bob often ______his mother with the housework on Sundays A. help B. helping C. helps D. helped
高中英语八大时态全套精讲
基础课程教学资料祝福您及家人身体健康、万事如意、阖家欢乐!祝福同学们快乐成长,能够取得好成绩,为祖国奉献力量 高中英语八大时态全套精讲 英语共有十六种时态,其表现形式如下(以study为例): 祝福您及家人身体健康、万事如意、阖家欢乐!祝福同学们快乐成长,能够取得好成绩,为祖国奉献力量祝福您及家人身体健康、万事如意、阖家欢乐!祝福同学们快乐成长,能够取得好成绩,为祖国奉献力量 时态 一般时进行时完成时完成进行时 现在祝福您及家人身体健康、万事如意、阖家欢乐!祝福同学们快乐成长, 能够取得好成绩,为祖国奉献力量祝福您及家人身体健康、万事如意、阖家欢乐!祝福同学们快乐成长,能够取得好成 绩,为祖国奉献力量 study be studying have studied have been studying 过去祝福您及家人身体健康、万事如意、阖家欢乐!祝福同学们快乐成长, 能够取得好成绩,为祖国奉献力量祝福您及家人身体健康、万事如意、阖家欢乐!祝福同学们快乐成长,能够取得好成 绩,为祖国奉献力量 studied be studying had studied had been studying 将来will study will be studying will have studied will have been studying 过去将来would study would be studying would have studied would have been studying .1 一般现在时的用法 1) 经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频腮度的时间状语连用。时间状语:every…, sometimes, at…, on Sunday I leave home for school at 7 every morning.
初中英语八大时态讲解及练习(全)
概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。 时间状语:always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays, etc. 基本结构:①be动词; ②行为动词 否定形式:①am/is/are+not; ②此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。 一般疑问句: ①把be动词放于句首; ②用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。在一般现在时中,当主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词要用第三人称单数形式,即常在动词原形后加-s或-es。 一、人称代词he, she, it是第三人称单数。如: He likes watching TV. 他喜欢看电视。 She has lunch at twelve. 她十二点吃午餐。 It looks like a cat. 它看起来像只猫。(口诀:I用am,you用are,is用于她他它,单数名词用is,复数名词都用are) 二、单个人名、地名或称呼作主语;是第三人称单数。如: ①Han Mei looks like her mother. 韩梅看起来像她的母亲。 ②Beijing is in China. 北京在中国。③Uncle Wang often makes cakes. 王叔叔经常做蛋糕。 三、单数可数名词或"this / that / the+单数可数名词"作主语时,是第三人称单数。如: ①A horse is a useful animal. 马是有用的动物。 ②This book is yours. 这本书是你的。 四、不定代词someone, somebody, nobody, everything, something等及指示代词this, that 作主语时,是第三人称单数。如: ①Everyone is here. 大家到齐了。 ②There is something wrong with the watch. 这块手表有毛病。 五、不可数名词作主语时为第三人称单数。如: ①The milk is in the glass. 牛奶在玻璃杯里。 ②The bread is very small. 那面包很小。 六、当数字或字母作主语时,看作第三人称单数。如: ①"6" is a lucky number. "6"是个吉利数字。 【练习】 一、单选 1 Jenny ____ in an office. Her parents ____in a hospital. A work works B works work C work are working D is working work 2 One of the boys_____ a black hat. A have B there is C there are D has 3 We will go shopping if it____ tomorrow. A don't rain B didn't rain C doesn't rain D isn't rain
初中英语八种时态详解及习题
初中英语八种时态详解及 习题 Written by Peter at 2021 in January
智学教育学科教师讲义讲义编号:组长签字:_____________ 签字日期:__________ 初中英语八种时态归纳 一、一般现在时: 概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。 时间状语: a lways, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays, etc. 基本结构:①be动词;②行为动词 否定形式:①am/is/are+not;②此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。 一般疑问句:①把be动词放于句首;②用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。
注:当主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词需加-s或-es: 注意:动词have的第三人称单数是has. 写出下列动词的单数第三人称形式。 1. cook _______ 2. watch________ 3. build_________ 4. have________ 5. wash________ 6. enjoy ______ 7. go _________ 8. receive ______ 9. cry______ 10. close ________ 11. drive _______ 12. choose ______ 13. play ________ 14. reach ________ ________ 一般现在时的用法: 1)表示经常的或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的副词连用。常用的频度副词有:always、often、 usually、seldom、never。频度副词在句中通常放在行为动词之前,系动词、助动词之后。 例如: He often goes swimming in summer.他夏天经常游泳。 I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 每天早上我七点离开家。 2)表示现在的状态。 例如:My father is at is very busy. 我父亲在工作,他很忙。 The boy is twelve. 这男孩十二岁。 3)表示主语具备的性格、特征和能力等。 例如:All my family love football .我全家人都喜欢足球。My sister is always ready to help others . 我妹妹总是乐于助人。
初中英语八大时态讲解及练习(全)
一、一般现在时: 概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。 时间状语:always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays, etc. 基本结构:①be动词; ②行为动词 否定形式:①am/is/are+not; ②此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。 一般疑问句: ①把be动词放于句首; ②用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。在一般现在时中,当主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词要用第三人称单数形式,即常在动词原形后加-s或-es。 一、人称代词he, she, it是第三人称单数。如: He likes watching TV. 他喜欢看电视。 She has lunch at twelve. 她十二点吃午餐。 It looks like a cat. 它看起来像只猫。(口诀:I用am,you用are,is用于她他它,单数名词用is,复数名词都用are)
二、单个人名、地名或称呼作主语;是第三人称单数。如: ①Han Mei looks like her mother. 韩梅看起来像她的母亲。 ②Beijing is in China. 北京在中国。 ③Uncle Wang often makes cakes. 王叔叔经常做蛋糕。 三、单数可数名词或"this / that / the+单数可数名词"作主语时,是第三人称单数。如: ①A horse is a useful animal. 马是有用的动物。 ②This book is yours. 这本书是你的。 四、不定代词someone, somebody, nobody, everything, something等及指示代词this, that 作主语时,是第三人称单数。如: ①Everyone is here. 大家到齐了。 ②There is something wrong with the watch. 这块手表有毛病。 五、不可数名词作主语时为第三人称单数。如: ①The milk is in the g lass. 牛奶在玻璃杯里。 ②The bread is very small. 那面包很小。 六、当数字或字母作主语时,看作第三人称单数。如: ①"6" is a lucky number. "6"是个吉利数字。 【练习】
初中英语八种时态详解及练习讲解学习
初中英语语法:动词八种时态、被动语态详解练习及答案: 一、初中英语被动语态用法小结 [1]一、语态概述 英语的语态是通过动词形式的变化表现出来的。英语中有两种语态:主动语态和被动语态。 主动语态表示主语是动作的执行者。 例如:Many people speak Chinese. 谓语:speak的动作是由主语many people来执行的。 被动语态表示主语是动作的承受者,即行为动作的对象。例如:Chinese is spoken by many people. 英语English是动词speak的承受者。 二、被动语态的构成 被动语态由“助动词be+及物动词的过去分词”构成。人称、数和时态的变化是通过be的变化表现出来的。现以speak为例说明被动语态在各种时态中的构成。 一般现在时:am/is/are+spoken 一般过去时:was/were+spoken 一般将来时:will/shall be+spoken 现在进行时:am/is/are being+spoken 过去进行时:was/were being+spoken 现在完成时:have/has been+spoken 过去完成时:had been + spoken 三、被动语态的用法 (1)不知道或没有必要说明动作的执行者是谁。 例如:Some new computers were stolen last night.一些新电脑在昨晚被盗了。(不知道电脑是谁偷的) This bridge was founded in 1981.这座桥竣工于1981年。 (2)强调动作的承受者,而不强调动作的执行者。 例如:The glass was broken by Mike.玻璃杯是迈克打破的。
最新整理初中英语语法八大时态总结
初中英语语法八大时态总结 初中英语时态是英语学习中一个至关重要的内容,同学们在实际运用时,往往对时态总是倍感棘手,为了让大家能更深刻地记住英语语法中的各种时态,下面是小编为您收集整理的初中英语语法八大时态总结,供大家参考! 初中英语语法八大时态总结 一、一般现在时: 概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。 时间状语:a l w a y s,u s u a l l y,o f t e n,s o m e t i m e s,e v e r y w e e k(d a y,y e a r,m o n t h),o n c e a w e e k,o n S u n d a y s,e t c. 基本结构:①b e动词;②行为动词 否定形式:①a m/i s/a r e+n o t;②此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加d o n t,如主语为第三人称单数,则用d o e s n t,同时还原行为动词。 一般疑问句:①把b e动词放于句首;②用助动词d o 提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用d o e s,同时,还原行为动词。
二、一般过去时: 概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。 时间状语:a g o,y e s t e r d a y, t h e d a y b e f o r e y e s t e r d a y,l a s t w e e k(y e a r,n i g h t, m o n t h),i n1989,j u s t n o w,a t t h e a g e o f5,o n e d a y, l o n g l o n g a g o,o n c e u p o n a t i m e,e t c. 基本结构:①b e动词;②行为动词 否定形式:①w a s/w e r e+n o t;②在行为动词前加 d i d n t,同时还原行为动词。 一般疑问句:①w a s或w e r e放于句首;②用助动词 d o的过去式d i d提问,同时还原行为动词。 三、现在进行时: 概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。 时间状语:n o w,a t t h i s t i m e,t h e s e d a y s,e t c. 基本结构:a m/i s/a r e+d o i n g 否定形式:a m/i s/a r e+n o t+d o i n g. 一般疑问句:把b e动词放于句首。 四、过去进行时: 概念:表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进
初中英语八种时态归纳复习 详解
Ⅰ. 初中英语八种时态归纳复习 英语时态是一种表示动作或状态发生的时间的动词形式,而汉语动词没有时态形式。 一、一般现在时: 1. 概念:表示经常性的习惯动作,现在的特征或状态,和普遍真理的时候,谓语动词用一般现在时。 2. 构成:一般现在时主要由动词原形构成,但第三人称单数后要加词尾-s , 另外 动词be 和 have 有特殊的人称变化形式。 列表如下: 3.在词尾加-s 时要注意: 4.词尾-s 的读音, 与名词复数词尾-s 读音一样: always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays, etc. 例句:I go to school every day. 7. 否定形式:①动词be: am/is/are+not;②行为动词:在其前加don't, 如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't ,助动词后动词一概用原形。 例句:Jerry is not a student. Sally doesn ’t like animals. 8. 一般疑问句:①把be 动词放于句首;②用助动词do 提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does ,同时,还原行为动词。 例句: Is Jerry a student? Does sally like animals?
二、一般过去时 1.概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态,现在已经不再继续;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。 2.构成:一般过去时由动词的过去式表示, 1) 动词be有 was, were 两个过去式,was 用于第一、第三人称, were 用于第二人称和第一、二、三人称的复数形式。 动词表。 读音规则: 3. 与一般过去式经常搭配的时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week(year, night, month…), in 1989, just now, at the age of 5, one day, long long ago, once upon a time, etc. 4.否定形式:①was/were+not;②在行为动词前加助动词didn't,助动词后加动词原形。 5.一般疑问句:①was或were放于句首;②用助动词do的过去式did 提问,助动词后用动词原形。
初中英语八大时态讲解及练习(全)之欧阳家百创编
一、一般现在时: 欧阳家百(2021.03.07) 概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。 时间状语:always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays, etc. 基本结构:①be动词; ②行为动词 否定形式:①am/is/are+not; ②此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。 一般疑问句: ①把be动词放于句首; ②用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。 在一般现在时中,当主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词要用第三人称单数形式,即常在动词原形后加-s或-es。 一、人称代词he, she, it是第三人称单数。如:He likes watching TV. 他喜欢看电视。She has lunch at twelve. 她十二点吃午餐。It looks like a cat. 它看起来像只猫。(口诀:I用am,you用are,is用于她他它,单数名词用is,复数名词都用are) 二、单个人名、地名或称呼作主语;是第三人称单数。如: ①Han Mei looks like her mother. 韩梅看起来像她的母亲。 ②Beijing is in China. 北京在中国。 ③Uncle Wang often makes cakes. 王叔叔经常做蛋糕。 三、单数可数名词或"this / that / the+单数可数名词"作主语时,是第三人称单数。如: ①A horse is a useful animal. 马是有用的动物。 ②This book is yours. 这本书是你的。 四、不定代词someone, somebody, nobody, everything, something 等及指示代词this, that作主语时,是第三人称单数。如: ①Everyone is here. 大家到齐了。 ②There is something wrong with the watch. 这块手表有毛病。 五、不可数名词作主语时为第三人称单数。如: ①The milk is in the glass. 牛奶在玻璃杯里。 ②The bread is very small. 那面包很小。 六、当数字或字母作主语时,看作第三人称单数。如:
初中英语的八大时态教学教材
英语中的八大时态
定义:表示主语反复、经常、习惯性的动作。 句型结构 1.S+V 1.be 2.实义动词(行为动词) (在肯定句中,在实义动词前加do/does 用来表示强调,以加强句子的语气) 2.否定句主语+don’t / doesn't+动词原形+其他 3.一般疑问句 Do / Does+主语+动词原形+其他 4.肯定回答 Yes,主语+do / does 5.否定回答 No,主语+don’t / doesn't 用法 1.表示主语的特征或状态。 2.表示客观真理和客观事实。 3.在以when+句子,as soon as+句子,not…until, if+句子的句型中,用主将从现。 4.在以here , there 开头引导的倒装句中,通常采用一般现在时表示正在发生的动作。时间状语(标志词) 1. every+表时间n. on +星期 2. 频率副词always usually often sometimes seldom never 3. in the moring / afternoon / evening 形式 1一般情况下,在动词末尾+s。 2以s x sh ch结尾的动词+es。 3以辅音字母加y结尾的动词,把y改为i 加es。 4以o结尾的单词有生命的+s没生命的加es。 5特殊的be 改为am is are。
定义表示主语的动作正在进行的句子 用法 1.表示此时此刻正在进行的动作 2.表示现阶段正在进行的动作或持续的状态 句型结构 1.肯定句:S + am/is/are + Ving 2.否定句:S+ am/is/are + not + Ving 3.一般疑问句:Am/Is/Are + S + Ving 4.肯定回答Yes,S+ am/is/are 5.否定回答NO,S + am/is/are + not 形式 1如果动词以不发音字母e结尾ie,应先去e加ing 2如果动词时只有一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节结尾,应双写该辅音字母再加ing 3一般情况下,直接加ing 时间状语(标志词) Look! Listen! now, at the mome nt, these days, can you see, can’t you see 注意事项: 1.arrive, come, get, go, have, leave, meet, play, return, see, spend, start, stay, wear, work等词用现在进行时表示将来。 2.并不是所有动词都有进行时,一些动词一般在句中不能用现在进行时态,而应用一般现在时。这些动词往往是等表示情感状态、知觉认识、愿望或短暂性的动词。 例如:see(明白), know, want, would like, like, love, hear, have(有), hope, hate等。
英语中考八大时态讲解及习题
Ⅰ. 初中英语八种时态归纳复习 1.一般现在时 2.一般过去时 3.现在进行时 4.过去进行时 5.现在完成时 6.过去完成时 7.一般将来时 8.过去将来时 一、一般现在时: 概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。 时间状语: always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays, etc. 基本结构:①be动词;②行为动词
否定形式:①am/is/are+not;②此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。 一般疑问句:①把be动词放于句首;②用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。 二、一般过去时: 概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。 时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week(year, night, month…), in 1989, just now, at the age of 5, one day, long long ago, once upon a time, etc. 基本结构:①be动词;②行为动词 否定形式:①was/were+not;②在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词。 一般疑问句:①was或were放于句首;②用助动词do的过去式did 提问,同时还原行为动词。 三、现在进行时: 概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。
(完整word版)初中英语八种时态讲解
时态列表比较及具体运用
一般现在时 一.要点提示 一般现在时主要用动词原形表示,但是当主语是第三人称单数或者单数名词时,动词的形式要发生变化,其变化规律是: 1. 一般动词后加-s, 如:wears, reads, plays, likes 2.以s, x, ch, sh结尾,后加-es, 如:watches, brushes 3.以辅音字母+o结尾,一般加-es, 如:goes, does 4.辅音字母+y结尾,变y为i,再加-es, 如:worries, carries. 5.Be动词一般现在时的特殊形态是:am, is, are 6.Have的第三人称单数是has。 二.用法指南 一般现在时的用法 1) 表示经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的时间状语连用。 时间状语:always总是, often经常,usually通常, seldom很少, never从不, sometimes有时(以上频度副词位置放于行为动词之前), every…每…(放于句首或者句末均可) I leave home for school at 7 every morning. It often snows here. 2) 表示现在的状态、特征、能力、性格等。 I know him very well. Ann Wang writes good English but does not speak well. 3) 表示格言或警句中。 Pride goes before a fall. 骄者必败。 Failure is the mother of success. 失败是成功之母。 4) 表示客观真理,客观存在,科学事实。 The earth moves around the sun. Shanghai lies in the east of China. 三. 一般现在时态的肯定形式,否定形式及疑问形式 1.肯定形式是用动词原形,be动词用am, is, are, (注:动词的第三人称单数形式的变化;) 2.否定形式是在be动词后加否定词not(缩写成isn’t, aren’t, am与not不能缩写),或者添加助动词do/does加not再加动词原形(缩写成don’t/doesn’t). 3.疑问形式是把be动词或助动词do/does提置句首, 动词还原,句末问号,人称上第一人称变第二人称,第二人称变第一人称,第三人称不变。 一般将来时 一.要点提示
初中英语必考-八大时态结构及用法详解
初中英语必考八大时态结构及用法详解 一.一般现在时 1. 概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。 2. 基本结构:①is/am/are;②do/does 否定形式:①am/is/are+not; ②此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语 为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。 3. 一般疑问句: ①把is/am/are 动词放于句首; ②用助动词do 提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。 4. 用法
1)经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的时间状语连用。 例如:I leave home for school at 7 every morning. 每天早上我七点离开家。 2)客观真理,客观存在,科学事实。 例如:The earth moves around the sun. 地球绕太阳转动。 Shanghai lies in the east ofChina. 上海位于中国东部。 3)表示格言或警句。 例如:Pride goes before a fall 骄者必败。 注意:此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。 例如:Columbus proved that the earth is round. 哥伦布证实了地球是圆的。 4)现在时刻的状态、能力、性格、个性。 例如:I don't want so much. 我不要那么多。
Ann writes good English but does not speak well.安英语写得不错,讲的可不行。 5)一般现在时表示将来含义。 a. 下列动词come, go, arrive, leave, start, begin, return 的一般现在时可以表示将来,主要用 来表示在时间上已确定或安排好的事情。 例如:The train leaves at six tomorrow morning. 火车明天上午六点开。 When does the bus star? It stars in ten minutes. 汽车什么时候开?十分钟后。 b. 在时间或条件句中。 例如:When Bill comes (不是will come), ask him to wait for me. 比尔来后,让他等我。 I'll write to you as soon as I arrive there. 我到了那里,就写信给你。
【精品】初中英语语法八大时态总结(完整版)
初中英语语法八大时态 一.一般现在时 1.结构 肯定句式: 主语+动词原形/动词的第三人称单数+其他 否定句式: 主语+(助动词)don't/doesn't +动词原形+其他 一般疑问句式: Do/Does+主语+动词原形+其他 简略回答: (肯)Yes,主语+do/does (否)No,主语+do/does not 缩写形式: don't = do not doesn't = does not 例句:He often goes swimming in summer. I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2.用法 1)表示经常的、习惯性的动作或存在的状态,常与表示频度的副词连用。 常用的频度副词有:always、often、usually、seldom、never、sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays.频度副词在句中通常放在行为动词之前,系动词、助动词之后。 例如: He often goes swimming in summer. I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2)表示主语具备的性格、特征和能力等。 例如:All my family love football . My sister is always ready to help others . Ann writes good English but does not speak well. 3)表示客观真理、客观存在、自然现象。 例如:The earth moves around the sun. Shanghai lies in the east of China. 4)表示按计划或安排好的,或将要发生的动作,可用一般现在时表将来。 但只限于start,begin,leave,go,come,arrive,return,take place等。 例如:The train leaves at six tomorrow morning. He comes back tonight. 5)在复合句中,当主句是一般将来时,时间或条件状语从句的谓语动词只能用一般现在时来表示将 来要发生的动作。 例如:I'll tell him the news when he comes back. If you take the job , they will talk with you in greater details. 二.一般过去时态 1.结构 肯定句式: 主语+动词过去式+其他 否定句式: 主语+(助动词)didn’t +动词原形+其他 一般疑问句式: Did+主语+动词原形+其他 简略回答: (肯)Yes,主语+did (否)No,主语+did not 基本结构否定句一般疑问句
英语八大时态详细讲解
英语八大时态 一、一般现在时 1.构成:①肯定结构:主语+ 动词/be 或者情态动词+动词原形+ 宾语 ②否定结构:主语+ 情/助否定+动词或者be动词否定+ 宾语 ③疑问结构:(特殊疑问词)+ 情/助/be + 主语+ 动词原形+ 宾语? Eg. He is a worker. He works hard. He can do his work well. I can?t drive a car. She doesn?t like football. Jim is not a good student. Are you a English teacher? What can I do for you? May I have your attentions, please? Does he go to school by bike? Who is that? 2.用法:①现阶段习惯性动作或者存在的状态。 Eg. He is a worker. They have English classes every day. You always make fun of me. What do you think of the book? ②表示客观真理,科学事实。 Eg. Where there is a will, there is a way. The earth moves round the sun. Time and tide wait for no man. ③表将来A. 按时间表进行的,飞机、火车、巴士的出发 Eg. The train for Guangzhou leaves at 7:00. B. 时间状语从句(till, until, when, as soon as等引导),条件状语从句(unless, if引导)中表将来。主将从现 Eg. If it rains tomorrow, we will have to stay at home. 3.标志词:always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month...), once a week, on Sundays 4.三单动词变化规则:1) 一般情况下,动词后面直接加-s. 例如:works gets says reads 2) 以ch, sh, s, x 或o 结尾的动词,在后面加-es。如: go-goes teach-,teacher wash-washes brush-brushes ,catch-catches ,do-does ,fix -fixes 3) 以辅音字母+ y结尾的动词,把y变为i 再加-es. 如:study- studies try-tries carry-carries ,fly-flies cry-cries 二、一般过去时 1.构成:①肯定结构:主语+ 动词过去式/be过去式+ 宾语 ②否定结构:主语+助动词过去式否定+动词或者be动词过去式否定+ 宾语 ③疑问结构:(特殊疑问词)+ 助过去式/be过去式+ 主语+ 动词原形+ 宾语? Eg. I attended a meeting yesterday. He was often late for school. She didn?t go h ome last night. They were not good students before. Was he late for work yesterday? What did you do last morning? Where was he last afternoon? Did you go to the cinema last week? 2.用法:①表示过去某个时间完成的动作或一度存在的状态,也可以表示过去习惯性的动作。 Eg. I attended a meeting yesterday. I graduated from college in 1988. ②表示过去连续发生或者反复发生的动作。
初中英语动词八种时态
初中英语动词八种时态讲解 1、一般现在时 主要用于下面几情况: 1) 描述当前时间内经常出现、反复发生的动作或存在的状态。 在这种情景中,句子常带有表示频率的时间状语:always , everyday , often , once a week (month , year , etc.) , sometimes , seldom , usually等等,以表示句中的动作或状态是习惯性的、经常性的。例如:They raise ducks as a sideline .他们以养鸭为副业。 She doesn't often write to her family, only once a month. 她不常给家里写信,仅一月一封而已。 I cycle to work every day .我每天骑自行车上班。 It seldom rains here .这儿很少下雨。 2)仅为了描述状态、性质、特征、能力等等。 这里的目的是为了"描述现阶段的动作或状态",其重点"不是强调动作发生的时间、或进行的状态"。例如:He can speak five foreign languages .他能说五种外语。 That is a beautiful city .那是座美丽的城市。 Changjiang River is one of the longest rivers in the world. 长江是世界上最长的河流之一。 She majors in music .她主修音乐。 All my family love football .我全家人都喜欢足球。 My sister is always ready to help others . 我妹妹总是乐于助人。 3) 陈述客观事实、客观真理。 顾名思义,客观的情况是"没有时间概念"的;也"不会在意动作进行的状态"。例如: The sun rises in the east .日出东方。 The earth goes around the sun .地球绕着太阳转。 Ten minus two is eight.十减二等于八。 Light travels faster than sound .光的速度比声音的速度快。 The United States lies by the west coast of the Pacific Ocean. 美国位于太平洋西岸。 4) 根据英文语法规定,当主句的谓语动词是一般将来时,那么时间或条件状语从句的谓语动词只能用一般现在时来表示将来要发生的动作。例如: I'll tell him the news when he comes back. 他回来时,我将告诉他这个消息。 If you take the job, they will talk with you in greater details. 如果你接受这份工作,他们将和你谈谈细节。 用于一般现在时的副词,除了上面提到的一些表示频率的以外,常见的还有:now, today , nowadays等等。 2、一般过去时 主要是用来描述在过去某个时候发生的动作或存在的状态。它也可以用来表示在过去某段时间里经常发生的习惯性动作。这一点在表达意义上与一般现在时相同,只是所在的时间区域不同而已。由于它的主要作用如此,所以在使用一般过去时的句子里常常有一个意义较具体的过去时间状语。这也是它与现在完成时的最大区别之一。 一般过去时由谓语动词的过去式表示,也就是说动词词末要加-ed(除不规则动词外)。常和一般过去时连用的过去时间状语有:last night (week , month , year , century , etc.) , yesterday , the day before yesterday , yesterday morning ( afternoon , evening ) , in 1999 , two hours ago ( one week ago , tree years ago , …)等等。 使用一般过去时,在某种意义上说就是要强调动作或状态发生或存在于过去的某个时候。"过去"的时间概念有两层意思:一是指"现在某个时间"以前的时间;二是指"说话、写文章的那个时间点"以前的时间,在这个意义上,"现在的那个时间点"是很小很小的,甚至于小到无法量化的程度。例如: He got his driving license last month. 他上个月拿到了驾照。 --Where's Jim? 吉姆在哪里? --He just went out.他刚刚出去。 3、一般将来时 主要用来描述将要发生的动作或存在于未来的情况。这里所说的"将来时间"是指"说话、写文章那一刻以后
