人工智能专家系统_外文翻译原文
人工智能伦理学英文

人工智能伦理学英文Ethical Considerations in Artificial IntelligenceThe rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have revolutionized various aspects of our lives, from healthcare to transportation, and have the potential to shape the future of humanity. As AI systems become more sophisticated and integrated into our daily lives, it is crucial to address the ethical implications of these technologies. The field of AI ethics explores the moral and philosophical considerations surrounding the development, deployment, and impact of artificial intelligence.One of the primary concerns in AI ethics is the issue of algorithmic bias. AI systems are trained on data that often reflects the biases inherent in human-generated information. This can lead to the perpetuation and amplification of societal biases based on factors such as race, gender, or socioeconomic status. For instance, facial recognition algorithms have been shown to perform less accurately for individuals with darker skin tones, potentially leading to discriminatory outcomes. Addressing algorithmic bias requires a concerted effort to diversify the data used to train AI systems and to implement rigorous testing and auditing procedures.Another critical aspect of AI ethics is the question of transparency and accountability. As AI algorithms become increasingly complex and opaque, it becomes challenging to understand the decision-making processes that underlie their outputs. This raises concerns about the ability to hold AI systems and their developers accountable for their actions. Proponents of AI ethics argue that there should be clear mechanisms in place to ensure that AI systems are transparent, explainable, and subject to human oversight and intervention.The issue of privacy and data protection is also a significant concern in the context of AI. The vast amounts of data required to train and operate AI systems can potentially infringe on individual privacy rights. AI-powered surveillance, targeted advertising, and automated decision-making can all raise privacy concerns. Ethical AI frameworks emphasize the importance of obtaining informed consent, protecting sensitive personal information, and ensuring that data collection and usage practices are aligned with individual privacy rights.Another crucial aspect of AI ethics is the impact of AI on employment and the workforce. As AI systems become more capable of performing tasks traditionally carried out by humans, there is a growing concern about job displacement and the need to address the societal and economic implications. Ethical considerations in thisdomain include ensuring fair and equitable transitions for workers, investing in reskilling and education programs, and exploring waysto distribute the benefits of AI-driven productivity gains more equitably.The development of autonomous systems, such as self-driving cars or autonomous weapons, also raises significant ethical concerns. These systems have the potential to make decisions that can have life-or-death consequences, and it is crucial to ensure that they are designed and deployed in a manner that prioritizes human safety and well-being. Ethical frameworks for autonomous systems often emphasize the need for robust safety measures, clear accountability, and the preservation of human agency and control.Finally, the existential risks posed by the potential development of superintelligent AI systems are a subject of intense debate within the field of AI ethics. The prospect of an AI system that surpasses human-level intelligence and capabilities raises concerns about the ability of humanity to maintain control and ensure that such systems are aligned with human values and interests. Addressing these risks requires a multifaceted approach that includes research into AI safety, the development of ethical guidelines for advanced AI systems, and ongoing collaboration between policymakers, researchers, and the AI industry.In conclusion, the ethical considerations surrounding artificial intelligence are complex and multifaceted. As AI technologies continue to evolve and become more ubiquitous, it is crucial that we address the moral and philosophical implications of these advancements. By developing robust ethical frameworks, promoting transparency and accountability, and ensuring that AI systems are designed with human values and well-being in mind, we can work towards the responsible and beneficial development of artificial intelligence.。
人工智能专家系统

人工智能专家系统人工智能(Artificial Intelligence,简称AI)专家系统是一种基于计算机技术和人类专家经验的智能化系统。
它能够模拟和实现人类专家在特定领域的问题解决能力,可以用于辅助决策、问题诊断和解决方案推荐等方面。
本文将从专家系统的定义、原理、组成和应用等四个方面进行论述。
一、专家系统的定义专家系统是一种基于知识工程的人工智能系统,它通过模拟和利用领域专家的经验和知识来解决特定领域的问题。
专家系统主要由知识库、推理机和用户界面三部分组成。
知识库存储了经验和知识,推理机则对知识进行推理和运算,用户界面则提供了用户与系统进行交互的接口。
二、专家系统的原理专家系统的原理可以概括为知识获取、知识表示、知识推理和知识应用四个步骤。
知识获取是指将专家的经验和知识进行提取和整理,并存储到系统的知识库中;知识表示是指将知识以适当的形式进行表达和组织,以便系统能够理解和推理;知识推理是指根据系统中的知识,通过推理机对问题进行分析和推理;知识应用是指将推理得到的结果转化为实际解决方案,供用户使用。
三、专家系统的组成专家系统主要由知识库、推理机和用户界面三部分组成。
知识库是专家系统存储知识和经验的地方,常见的形式包括规则库、案例库和模型库等。
推理机是专家系统进行推理和运算的核心组件,它能够根据知识库中的知识进行逻辑推理和问题求解。
用户界面则提供了用户与系统进行交互的接口,使用户能够方便地向系统提供问题并获取解决方案。
四、专家系统的应用专家系统在各个领域都有广泛的应用。
在医疗领域,专家系统可以用于辅助疾病诊断和治疗方案选择;在金融领域,专家系统可以用于风险评估和投资决策;在工业领域,专家系统可以用于故障诊断和维修指导。
此外,专家系统还可以应用于法律、教育、交通等领域,为人们提供更加智能化和便捷化的服务。
综上所述,人工智能专家系统是一种基于计算机技术和人类专家经验的智能化系统。
它能够模拟和实现人类专家在特定领域的问题解决能力,具有广泛的应用前景。
专业英语 人工智能 最终版

• 人工智能是计算机科学的前沿,充满机遇和挑战。 • “A student in physics might reasonably feel that all the good ideas have already been taken by Galileo,Newton,Einstein,and the rest,and that it takes many years of study before one can contribute new ideas,AI,on the other hand,still has openings for a full-time Einstein.” • _______《Artificial Intelligence:A modern Approach》 • (一位在物理学领域的学生会理所当然的认为所有的好点子已经 被伽利略,牛顿,爱因斯坦和其他人,它需要许多年前的研究能 做出贡献的新思路,另一方面,AI,仍然作为一个全职的爱因斯 坦。)
Definition 定义
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the intelligence of machines and the branch of computer science that aims to create it. Definition in AI textbook :”the study and design of intelligent agents” 人工智能(AI)是机器智能与计算机科学,旨 在创建它的分支。在AI教科书的定义:“学习 的智能代理的设计。”
在解决问题方面:1960纽厄尔编译一个普遍的问题解决者 (GPS),可以解决11个不同类型的问题; 在专家系统:1968的结果费根鲍姆开发DENDRAL“专家系 统”并投入使用;
专家系统(Expert System,简称ES)
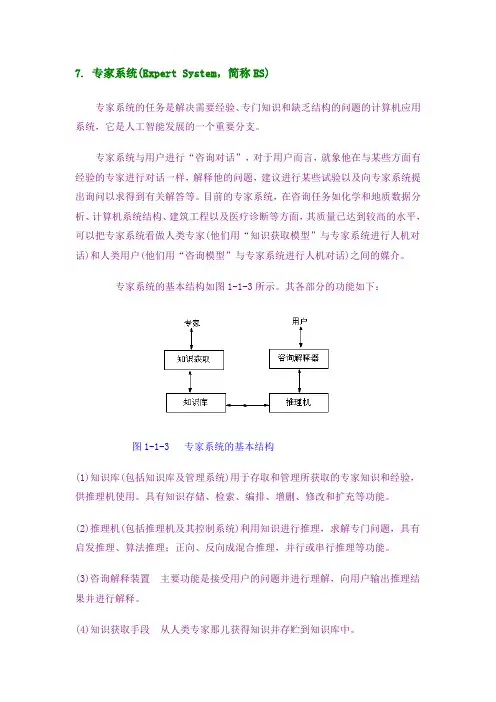
7. 专家系统(Expert System,简称ES)专家系统的任务是解决需要经验、专门知识和缺乏结构的问题的计算机应用系统,它是人工智能发展的一个重要分支。
专家系统与用户进行“咨询对话”,对于用户而言,就象他在与某些方面有经验的专家进行对话一样,解释他的问题,建议进行某些试验以及向专家系统提出询问以求得到有关解答等。
目前的专家系统,在咨询任务如化学和地质数据分析、计算机系统结构、建筑工程以及医疗诊断等方面,其质量已达到较高的水平,可以把专家系统看做人类专家(他们用“知识获取模型”与专家系统进行人机对话)和人类用户(他们用“咨询模型”与专家系统进行人机对话)之间的媒介。
专家系统的基本结构如图1-1-3所示。
其各部分的功能如下:图1-1-3 专家系统的基本结构(1)知识库(包括知识库及管理系统)用于存取和管理所获取的专家知识和经验,供推理机使用。
具有知识存储、检索、编排、增删、修改和扩充等功能。
(2)推理机(包括推理机及其控制系统)利用知识进行推理,求解专门问题,具有启发推理、算法推理;正向、反向成混合推理,并行或串行推理等功能。
(3)咨询解释装置主要功能是接受用户的问题并进行理解,向用户输出推理结果并进行解释。
(4)知识获取手段从人类专家那儿获得知识并存贮到知识库中。
专家系统可以解决的问题通常包括解释预测、诊断、设计、规划、监视、修理、指导和控制等。
管理决策可以分为:程序性决策(结构性决策):是指可以利用一定的规章或公式来解决的决策。
非程序性决策:是指一般没有公式可算,无章可循的决策问题。
半结构化决策:是介于程序性和非程序性决策之间,有的决策问题有一定的决策规律,有的则无章可循。
MIS是解决程序性决策的现代方式。
应用MIS支持决策,就要研究如何使非程序性的、非数量化的、单次性的、不确定性的决策数量化,程序化,如何把人的经验和智慧吸收进来,把计算机和人结合起来。
在人机决策系统中,计算机的长处是:(1)可储存大量数据,能对保存收集的数据进行筛选、分析和提炼。
人工智能英文文献原文及译文

附件四英文文献原文Artificial Intelligence"Artificial intelligence" is a word was originally Dartmouth in 1956 to put forward. From then on, researchers have developed many theories and principles, the concept of artificial intelligence is also expands. Artificial intelligence is a challenging job of science, the person must know computer knowledge, psychology and philosophy. Artificial intelligence is included a wide range of science, it is composed of different fields, such as machine learning, computer vision, etc, on the whole, the research on artificial intelligence is one of the main goals of the machine can do some usually need to perform complex human intelligence. But in different times and different people in the "complex" understanding is different. Such as heavy science and engineering calculation was supposed to be the brain to undertake, now computer can not only complete this calculation, and faster than the human brain can more accurately, and thus the people no longer put this calculation is regarded as "the need to perform complex human intelligence, complex tasks" work is defined as the development of The Times and the progress of technology, artificial intelligence is the science of specific target and nature as The Times change and development. On the one hand it continues to gain new progress on the one hand, and turning to more meaningful, the more difficult the target. Current can be used to study the main material of artificial intelligence and artificial intelligence technology to realize the machine is a computer, the development history of artificial intelligence is computer science and technology and the development together. Besides the computer science and artificial intelligence also involves information, cybernetics, automation, bionics, biology, psychology, logic, linguistics, medicine and philosophy and multi-discipline. Artificial intelligence research include: knowledge representation, automatic reasoning and search method, machine learning and knowledge acquisition and processing of knowledge system, natural language processing, computer vision, intelligent robot, automatic program design, etc.Practical application of machine vision: fingerprint identification,face recognition, retina identification, iris identification, palm, expert system, intelligent identification, search, theorem proving game, automatic programming, and aerospace applications.Artificial intelligence is a subject categories, belong to the door edge discipline of natural science and social science.Involving scientific philosophy and cognitive science, mathematics, neurophysiological, psychology, computer science, information theory, cybernetics, not qualitative theory, bionics.The research category of natural language processing, knowledge representation, intelligent search, reasoning, planning, machine learning, knowledge acquisition, combined scheduling problem, perception, pattern recognition, logic design program, soft calculation, inaccurate and uncertainty, the management of artificial life, neural network, and complex system, human thinking mode of genetic algorithm.Applications of intelligent control, robotics, language and image understanding, genetic programming robot factory.Safety problemsArtificial intelligence is currently in the study, but some scholars think that letting computers have IQ is very dangerous, it may be against humanity. The hidden danger in many movie happened.The definition of artificial intelligenceDefinition of artificial intelligence can be divided into two parts, namely "artificial" or "intelligent". "Artificial" better understanding, also is controversial. Sometimes we will consider what people can make, or people have high degree of intelligence to create artificial intelligence, etc. But generally speaking, "artificial system" is usually significance of artificial system.What is the "smart", with many problems. This involves other such as consciousness, ego, thinking (including the unconscious thoughts etc. People only know of intelligence is one intelligent, this is the universal view of our own. But we are very limited understanding of the intelligence of the intelligent people constitute elements are necessary to find, so it is difficult to define what is "artificial" manufacturing "intelligent". So the artificial intelligence research often involved in the study of intelligent itself. Other about animal or other artificial intelligence system is widely considered to be related to the study of artificial intelligence.Artificial intelligence is currently in the computer field, the moreextensive attention. And in the robot, economic and political decisions, control system, simulation system application. In other areas, it also played an indispensable role.The famous American Stanford university professor nelson artificial intelligence research center of artificial intelligence under such a definition: "artificial intelligence about the knowledge of the subject is and how to represent knowledge -- how to gain knowledge and use of scientific knowledge. But another American MIT professor Winston thought: "artificial intelligence is how to make the computer to do what only can do intelligent work." These comments reflect the artificial intelligence discipline basic ideas and basic content. Namely artificial intelligence is the study of human intelligence activities, has certain law, research of artificial intelligence system, how to make the computer to complete before the intelligence needs to do work, also is to study how the application of computer hardware and software to simulate human some intelligent behavior of the basic theory, methods and techniques.Artificial intelligence is a branch of computer science, since the 1970s, known as one of the three technologies (space technology, energy technology, artificial intelligence). Also considered the 21st century (genetic engineering, nano science, artificial intelligence) is one of the three technologies. It is nearly three years it has been developed rapidly, and in many fields are widely applied, and have made great achievements, artificial intelligence has gradually become an independent branch, both in theory and practice are already becomes a system. Its research results are gradually integrated into people's lives, and create more happiness for mankind.Artificial intelligence is that the computer simulation research of some thinking process and intelligent behavior (such as study, reasoning, thinking, planning, etc.), including computer to realize intelligent principle, make similar to that of human intelligence, computer can achieve higher level of computer application. Artificial intelligence will involve the computer science, philosophy and linguistics, psychology, etc. That was almost natural science and social science disciplines, the scope of all already far beyond the scope of computer science and artificial intelligence and thinking science is the relationship between theory and practice, artificial intelligence is in the mode of thinking science technology application level, is one of its application. From the view of thinking, artificial intelligence is not limited to logicalthinking, want to consider the thinking in image, the inspiration of thought of artificial intelligence can promote the development of the breakthrough, mathematics are often thought of as a variety of basic science, mathematics and language, thought into fields, artificial intelligence subject also must not use mathematical tool, mathematical logic, the fuzzy mathematics in standard etc, mathematics into the scope of artificial intelligence discipline, they will promote each other and develop faster.A brief history of artificial intelligenceArtificial intelligence can be traced back to ancient Egypt's legend, but with 1941, since the development of computer technology has finally can create machine intelligence, "artificial intelligence" is a word in 1956 was first proposed, Dartmouth learned since then, researchers have developed many theories and principles, the concept of artificial intelligence, it expands and not in the long history of the development of artificial intelligence, the slower than expected, but has been in advance, from 40 years ago, now appears to have many AI programs, and they also affected the development of other technologies. The emergence of AI programs, creating immeasurable wealth for the community, promoting the development of human civilization.The computer era1941 an invention that information storage and handling all aspects of the revolution happened. This also appeared in the U.S. and Germany's invention is the first electronic computer. Take a few big pack of air conditioning room, the programmer's nightmare: just run a program for thousands of lines to set the 1949. After improvement can be stored procedure computer programs that make it easier to input, and the development of the theory of computer science, and ultimately computer ai. This in electronic computer processing methods of data, for the invention of artificial intelligence could provide a kind of media.The beginning of AIAlthough the computer AI provides necessary for technical basis, but until the early 1950s, people noticed between machine and human intelligence. Norbert Wiener is the study of the theory of American feedback. Most familiar feedback control example is the thermostat. It will be collected room temperature and hope, and reaction temperature compared to open or close small heater, thus controlling environmental temperature. The importance of the study lies in the feedback loop Wiener:all theoretically the intelligence activities are a result of feedback mechanism and feedback mechanism is. Can use machine. The findings of the simulation of early development of AI.1955, Simon and end Newell called "a logical experts" program. This program is considered by many to be the first AI programs. It will each problem is expressed as a tree, then choose the model may be correct conclusion that a problem to solve. "logic" to the public and the AI expert research field effect makes it AI developing an important milestone in 1956, is considered to be the father of artificial intelligence of John McCarthy organized a society, will be a lot of interest machine intelligence experts and scholars together for a month. He asked them to Vermont Dartmouth in "artificial intelligence research in summer." since then, this area was named "artificial intelligence" although Dartmouth learn not very successful, but it was the founder of the centralized and AI AI research for later laid a foundation.After the meeting of Dartmouth, AI research started seven years. Although the rapid development of field haven't define some of the ideas, meeting has been reconsidered and Carnegie Mellon university. And MIT began to build AI research center is confronted with new challenges. Research needs to establish the: more effective to solve the problem of the system, such as "logic" in reducing search; expert There is the establishment of the system can be self learning.In 1957, "a new program general problem-solving machine" first version was tested. This program is by the same logic "experts" group development. The GPS expanded Wiener feedback principle, can solve many common problem. Two years later, IBM has established a grind investigate group Herbert AI. Gelerneter spent three years to make a geometric theorem of solutions of the program. This achievement was a sensation.When more and more programs, McCarthy busy emerge in the history of an AI. 1958 McCarthy announced his new fruit: LISP until today still LISP language. In. "" mean" LISP list processing ", it quickly adopted for most AI developers.In 1963 MIT from the United States government got a pen is 22millions dollars funding for research funding. The machine auxiliary recognition from the defense advanced research program, have guaranteed in the technological progress on this plan ahead of the Soviet union. Attracted worldwide computer scientists, accelerate the pace of development of AI research.Large programAfter years of program. It appeared a famous called "SHRDLU." SHRDLU "is" the tiny part of the world "project, including the world (for example, only limited quantity of geometrical form of research and programming). In the MIT leadership of Minsky Marvin by researchers found, facing the object, the small computer programs can solve the problem space and logic. Other as in the late 1960's STUDENT", "can solve algebraic problems," SIR "can understand the simple English sentence. These procedures for handling the language understanding and logic.In the 1970s another expert system. An expert system is a intelligent computer program system, and its internal contains a lot of certain areas of experience and knowledge with expert level, can use the human experts' knowledge and methods to solve the problems to deal with this problem domain. That is, the expert system is a specialized knowledge and experience of the program system. Progress is the expert system could predict under certain conditions, the probability of a solution for the computer already has. Great capacity, expert systems possible from the data of expert system. It is widely used in the market. Ten years, expert system used in stock, advance help doctors diagnose diseases, and determine the position of mineral instructions miners. All of this because of expert system of law and information storage capacity and become possible.In the 1970s, a new method was used for many developing, famous as AI Minsky tectonic theory put forward David Marr. Another new theory of machine vision square, for example, how a pair of image by shadow, shape, color, texture and basic information border. Through the analysis of these images distinguish letter, can infer what might be the image in the same period. PROLOGE result is another language, in 1972. In the 1980s, the more rapid progress during the AI, and more to go into business. 1986, the AI related software and hardware sales $4.25 billion dollars. Expert system for its utility, especially by demand. Like digital electric company with such company XCON expert system for the VAX mainframe programming. Dupont, general motors and Boeing has lots of dependence of expert system for computer expert. Some production expert system of manufacture software auxiliary, such as Teknowledge and Intellicorp established. In order to find and correct the mistakes, existing expert system and some other experts system was designed,such as teach users learn TVC expert system of the operating system.From the lab to daily lifePeople began to feel the computer technique and artificial intelligence. No influence of computer technology belong to a group of researchers in the lab. Personal computers and computer technology to numerous technical magazine now before a people. Like the United States artificial intelligence association foundation. Because of the need to develop, AI had a private company researchers into the boom. More than 150 a DEC (it employs more than 700 employees engaged in AI research) that have spent 10 billion dollars in internal AI team.Some other AI areas in the 1980s to enter the market. One is the machine vision Marr and achievements of Minsky. Now use the camera and production, quality control computer. Although still very humble, these systems have been able to distinguish the objects and through the different shape. Until 1985 America has more than 100 companies producing machine vision systems, sales were us $8 million.But the 1980s to AI and industrial all is not a good year for years. 1986-87 AI system requirements, the loss of industry nearly five hundred million dollars. Teknowledge like Intellicorp and two loss of more than $6 million, about one-third of the profits of the huge losses forced many research funding cuts the guide led. Another disappointing is the defense advanced research programme support of so-called "intelligent" this project truck purpose is to develop a can finish the task in many battlefield robot. Since the defects and successful hopeless, Pentagon stopped project funding.Despite these setbacks, AI is still in development of new technology slowly. In Japan were developed in the United States, such as the fuzzy logic, it can never determine the conditions of decision making, And neural network, regarded as the possible approaches to realizing artificial intelligence. Anyhow, the eighties was introduced into the market, the AI and shows the practical value. Sure, it will be the key to the 21st century. "artificial intelligence technology acceptance inspection in desert storm" action of military intelligence test equipment through war. Artificial intelligence technology is used to display the missile system and warning and other advanced weapons. AI technology has also entered family. Intelligent computer increase attracting public interest. The emergence of network game, enriching people's life.Some of the main Macintosh and IBM for application software such as voice and character recognition has can buy, Using fuzzy logic,AI technology to simplify the camera equipment. The artificial intelligence technology related to promote greater demand for new progress appear constantly. In a word ,Artificial intelligence has and will continue to inevitably changed our life.附件三英文文献译文人工智能“人工智能”一词最初是在1956 年Dartmouth在学会上提出来的。
第7章专家系统人工智能

知识库 以一套规则建立人的长期存储器模型 工作存储器 建立人的短期存储器模型,存放问题事实和由规则激发而推断出的新事实。 推理机 借助于把存放在工作存储器内的问题事实和存放在知识库内的规则结合起来,建立人的 推理模型,以推断出新的信息 。
2. 基于规则专家系统的结构 推理机
工作存储器
解释器
知识库
用户界面
基于框架专家系统的主要设计步骤与基于规则的专家系统相似,主要差别在于如何看待和使用知识 在设计基于框架的专家系统时,把整个问题和每件事想像为编织起来的事物 在辨识事物之后,寻找把这些事物组织起来的方法 对于任何类型的专家系统,其设计是个高度交互的过程
开发基于框架专家系统的主要任务
定义问题,包括对问题和结论考察与综述 分析领域,包括定义事物、事物特征、事件和框架结构 定义类及其特征 定义例及其框架结构 确定模式匹配规则 规定事物通信方法 设计系统界面 对系统进行评价 对系统进行扩展,深化和扩宽知识
6.4.1 基于模型专家系统的提出
❖ 关于人工智能的一个观点 ❖ 综合各种模型的专家系统比基于逻辑心理模型的系统具有更强的功能,从而有可能显著改
进专家系统的设计 ❖ 在诸多模型中,人工神经网络模型的应用最为广泛
6.4 Model-based Expert System 基于模型的专家系统
The contribution & limitation of Rule-based ES Use various qualitative models to AI An expert system integrated with various models
人工智能 中英文翻译(升序排列)
B 规则B-ruleF 规则F-ruleNP 完全问题 NP-complete problem本原问题primitive problem博弈game不可解标示过程unsolvable-labeling procedure不可解节点unsolvable node不可满足集unsatisfiable set不确定性uncertainty差别difference产生式production产生式规则production rule冲突解决conflict resolution存在量词existential quantifier代换substitution代换例substitution instance倒退值backed-up value等价equivalence定理证明theorem-proving动作action反演refutation反演树refutation tree费用cost估计费用estimated cost 估值函数evaluation function归结resolution归结反演resolution refutation归结式resolvent归结原理resolution principle归约reduction合取conjunction合取范式conjunctive normal form合取式conjunct合适公式、合式公式well-formed formula (wff)合一unifier回答语句answer statement回溯backtracking机器学习machine learning节点的扩展expansion of node解释器interpreter解树solution tree解图solution graph句子sentence可解标示过程solvable labeling procedure可解节点solvable node 可满足性satisfiability 空子句empty clause控制策略control strategy宽度优先搜索breadth-first search扩展节点expendingnode连词,连接词connective量词quantifier量词辖域scope ofquantifier论域,文字域domainof discourse逻辑logic逻辑连词logicconnective逻辑推理logicreasoning盲目搜索,无信息搜blind search模式匹配match pattern模式识别Patternrecognition母式matrix逆向推理backwardreasoning匹配match启发函数heuristicfunction启发式搜索Heuristicsearch启发搜索heuristicsearch启发信息heuristicinformation前缀prefix全称量词universalquantifier全局数据库Globaldatabase人工神经网络artificialneural network人工智能artificialintelligence,AI人工智能语言AIlanguage深度优先搜索depth-first search事实fact搜索search, searching搜索策略searchingstrategy搜索树searching tree搜索算法searchingalgorithm搜索算法的效率efficiency of searchalgorithm搜索图searching graph算符、算子、操作符operator图graph图表示法graph notation图搜索graph search图搜索控制策略graph-search controlstrategy推导表,引导图derivation graph推理inference推理reasoning推理机reasoning machine谓词predicate谓词逻辑predicatelogic谓词演算predicatecalculus谓词演算公式wffs ofpredicate calculus谓词演算辖域domainin predicate calculus文字literal问题归约problem-reduction问题求解problemsolving析取disjunction析取式disjunct线形输入形策略linear-input formstrategy项term学习learning演绎deduction一阶谓词演算firstorder predicate calculus一致解图consistantsolution graph遗传算法geneticalgorithm永真式validity有向图directed graph有序搜索orderedsearch与或树AND/OR tree与或图AND/OR graph与节点AND node原子公式atomicformula蕴涵,蕴涵式implication正向推理forwardreasoning知识knowledge知识工程knowledgeengineering知识获取knowledgeacquisition知识库knowledge base智能intelligence重言式tautology专家系统Expert system状态state状态空间state space子句clause自动定理证明automatic theoremproving组合爆炸combinatorialexplosion祖先过滤形策略ancestry-filtered formstrategy最一般合一most generalunifier最一般合一者mostgeneral unifier最优解树optimalsolution treeaction 动作AI language 人工智能语言ancestry-filtered form strategy 祖先过滤形策略AND node 与节点AND/OR graph 与或图AND/OR tree 与或树answer statement 回答语句artificial intelligence,AI 人工智能artificial neural network 人工神经网络atomic formula 原子公式automatic theorem proving 自动定理证明backed-up value 倒退值backtracking 回溯backward reasoning 逆向推理blind search 盲目搜索,无信息搜breadth-first search 宽度优先搜索B-rule B 规则clause 子句combinatorial explosion 组合爆炸conflict resolution 冲突解决conjunct 合取式conjunction 合取conjunctive normal form 合取范式connective 连词,连接词consistant solution graph一致解图control strategy 控制策略cost 费用deduction 演绎depth-first search 深度优先搜索derivation graph 推导表,引导图difference 差别directed graph 有向图disjunct 析取式disjunction 析取domain in predicate calculus 谓词演算辖域domain of discourse 论域,文字域efficiency of search algorithm 搜索算法的效率empty clause 空子句equivalence 等价estimated cost 估计费用evaluation function 估值函数existential quantifier 存在量词expansion of node 节点的扩展expending node 扩展节点Expert system 专家系统fact 事实first order predicate calculus一阶谓词演算forward reasoning 正向推理F-rule F 规则game 博弈genetic algorithm 遗传算法Global database 全局数据库graph 图graph notation 图表示法graph search 图搜索graph-search control strategy图搜索控制策略heuristic function 启发函数heuristic information 启发信息Heuristic search 启发式搜索heuristic search 启发搜索implication 蕴涵,蕴涵式inference 推理intelligence 智能interpreter 解释器knowledge 知识knowledge acquisition 知识获取knowledge base 知识库knowledge engineering 知识工程learning 学习linear-input form strategy线形输入形策略literal 文字logic逻辑logic connective 逻辑连词logic reasoning 逻辑推理machine learning 机器学习match 匹配match pattern 模式匹配matrix 母式most general unifier 最一般合一most general unifier 最一般合一者NP-complete problem NP完全问题operator 算符、算子、操作符optimal solution tree 最优解树ordered search 有序搜索Pattern recognition 模式识别predicate 谓词predicate calculus 谓词演算predicate logic 谓词逻辑prefix 前缀primitive problem 本原问题problem solving 问题求解problem-reduction 问题归约production 产生式production rule 产生式规则quantifier 量词reasoning 推理reasoning machine 推理机reduction 归约refutation 反演refutation tree 反演树resolution归结resolution principle 归结原理resolution refutation 归结反演resolvent 归结式satisfiability 可满足性scope of quantifier 量词辖域search, searching 搜索searching algorithm 搜索算法searching graph 搜索图searching strategy 搜索策略searching tree 搜索树sentence 句子solution graph 解图solution tree 解树solvable labeling procedure可解标示过程solvable node 可解节点state 状态state space 状态空间substitution 代换substitution instance 代换例tautology 重言式term 项theorem-proving 定理证明uncertainty 不确定性unifier 合一universal quantifier 全称量词unsatisfiable set 不可满足集unsolvable node 不可解节点unsolvable-labelingprocedure不可解标示过程validity 永真式well-formed formula (wff)合适公式、合式公式wffs of predicate calculus谓词演算公式。
英语论文素材(人工智能)
摘要:人工智能(Artificial Intelligence) ,英文缩写为AI。
它是研究、开发用于模拟、延伸和扩展人的智能的理论、方法、技术及应用系统的一门新的技术科学。
人工智能是计算机科学的一个分支,它企图了解智能的实质,并生产出一种新的能以人类智能相似的方式做出反应的智能机器,该领域的研究包括机器人、语言识别、图像识别、自然语言处理和专家系统等。
专家系统是人工智能应用研究的主要领域。
70年代中期,专家系统的开发获得成功。
正如专家系统的先驱费根鲍姆(Feigenbaum)所说:专家系统的力量是从它处理的知识中产生的,而不是从某种形式主义及其使用的参考模式中产生的。
这正符合一句名言:知识就是力量。
80年代,专家系统在全世界得到迅速发展和广泛应用。
本文中介绍了人工智能的概念,分类,特点以及人工智能的研究的发展及其现状。
由此引出专家系统的基本概念及主要特点。
最后,通过查阅各种资料以及自己的理解分析,对专家系统的主要应用做具体分析。
阐述了将计算机人工智能的专家系统理念与审计实务相结合并提出审计工具智能化的设想,同时,具体分析了构建审计专家系统可供利用的计算机应用技术,并初步建立了审计专家系统的模块体系。
关键词:人工智能,专家系统,审计专家系统Expert system outline and applicationAbstract :The artificial intelligence (Artificial Intelligence), English abbreviation is AI.It is the research, the development uses in simulating, extending and expands human's intelligence theory, the method, technical and an application system new technical science. The artificial intelligence is a computer science branch, it attempts the understanding intelligence the essence, the parallel intergrowth delivers one kind newly to be able to make the response by the human intelligence similar way the intelligent machine, this domain research including robot, language recognition, pattern recognition, natural language processing and expert system and so on.The expert system is the artificial intelligence applied research main domain.The 70's intermediate stages, the expert system development obtains successfully.Just like expert system pioneer Fei Genbao mho (Feigenbaum) said that,The expert system strength is in the knowledge which processes from it produces, but is not produces from some formalism and in the use reference pattern.This is conforming to a famous saying: The knowledge is a strength.The 80's, the expert system obtains the rapid development and the widespread application in the world.In this article introduced the artificial intelligence concept, the classification, the characteristic as well as the artificial intelligence research development and the present situation.From this draws out the expert system the basic concept and the main characteristic.Finally, through consults each kind of material as well as own understanding analysis, makes the concrete elaboration to the expert system main application.Introduced unifies the computer artificial intelligence expert system idea and the audit practice and proposed the audit tool intellectualization tentative plan, simultaneously, analyzed the construction to audit the expert system specifically to be possible to supply the use the computer application technology, and established initially has audited the expert system the module system.Key word: Artificial intelligence,Expert system,Auditing Expert System人工智能的发展作者XXX南京XXX大学XXX学院南京摘要计算机科学和人工智能将是21世纪逻辑学发展的主要动力源泉,并且在很大程度上将决定21世纪逻辑学的面貌。
人工智能与专家系统-1(1)
表1-2、三种产品的边际贡献率
单位边际贡献 边际贡献率 销售额 销售比重
I型 7
20% 35000
35%
II 型 4
40% 15000
15%
III型 9
36% 50000
50%
单位:元
合计
— — 100000 100%
根据表1-2,计算加权平均边际贡献率和综合保本销
售额。
24
加权平均边际贡献率= 10 7 0 10 5 4 0 20 0 9 0 1% 0 0 3 0 % 1
因此,本例中三种产品的保本点分别为: I型产品保本销售额=50000×35%=17500元, I型产品保本销售量=17500÷35=500件;
26
II 型产品保本销售额 = 50000×15%=7500元, 保本销售量 = 7500÷10=750件;
III型产品保本销售额 = 50000×50%=25000元, 保本销售量 = 25000÷25=1000件。
方案二:采用高速公路运输,平均每吨每公里运 费为0.6元,损坏率为 2%,售出价格也为每吨2200 元;
19
考虑到还有加工等费用的存在,企业决定只有当销售 收入扣除原材料的采购成本和运输成本后的总收益超过 20000 元时才可以采购。在销售不成问题的情况下,该 企业是否应采购这批原材料?若采购,应采用哪种运输 方式?
100000
综合保本销售额=固定成本总额÷加权平均边际贡 献率=15500÷31%=50000(元)。
综合保本销售额确定后,可按各种产品的销售比 重和单位售价计算各产品的保本点:
某种产品保本销售额 = 各产品综合保本销售额 ×该种产品销售比重;
25
某种产品保本销售量 = 某种产品的保本销售额 ÷某种产品单位售价。
人工智能与专家系统外文文献译文和原文
人工智能与专家系统外文文献译文和原文AI研究仍在继续,但与MIS和DDS等计算机应用相比,研究热情的减弱使人工智能的研究相对落后。
然而,在研究方面的不断努力一定会推动计算机向人工智能化方向发展。
2.AI领域AI现在已经以知识系统的形式应用于商业领域,既利用人类知识来解决问题。
专家系统是最流行的基于知识的系统,他是应用计算机程序以启发方式替代专家知识。
Heuritic术语来自希腊eureka,意思是“探索”。
因此,启发方式是一种良好猜想的规则。
启发式方法并不能保证其结果如同DSS系统中传统的算法那样绝对化。
但是启发式方法提供的结果非常具体,以至于能适应于大部分情况启发式方法允许专家系统能像专家那样工作,建议用户如何解决问题。
因为专家系统被当作顾问,所以,应用专家系统就可以被称为咨询。
除了专家系统外,AI还包括以下领域:神经网络系统、感知系统、学习系统、机器人、AI硬件、自然语言处理。
注意这些领域有交叉,交叉部分也就意味着这个领域可以从另一个领域中收益。
3.专家系统的吸引力专家系统的概念是建立在专家知识能够存储在计算机中并能被其他人应用这一假设的基础上的。
专家系统作为一种决策支持系统提供了独无二的能力。
首先,专家系统为管理者提供了超出其能力的决策机会。
比如,一家新的银行投资公司可以应用先进的专家系统帮助他们进行选择、决策。
其次,专家系统在得到一个解决方案的同时给出一步步的推理。
在很多情况下,推理本身比决策的结果重要的多。
4.专家系统模型专家系统模型主要由4个部分组成:用户界面使得用户能与专家系统对话;推理引擎提供了解释知识库的能力;专家和工程师利用开发引擎建立专家系统。
1.用户界面用户界面能够方便管理者向专家系统中输入命令、信息,并接受专家系统的输出。
命令中有具体化的参数设置,引导专家系统的推理过程。
信息以参数形式赋予某些变量。
(1)专家系统输入现在流行的界面格式是图形化用户界面格式,这种界面与Window有些相同的特征。
- 1、下载文档前请自行甄别文档内容的完整性,平台不提供额外的编辑、内容补充、找答案等附加服务。
- 2、"仅部分预览"的文档,不可在线预览部分如存在完整性等问题,可反馈申请退款(可完整预览的文档不适用该条件!)。
- 3、如文档侵犯您的权益,请联系客服反馈,我们会尽快为您处理(人工客服工作时间:9:00-18:30)。
附件毕业生毕业论文(设计)翻译原文论文题目远程农作物病虫害诊断专家系统的设计与实现系别_____ ______ _年级______ _ _ _ _ _专业_____ ___ ___学生姓名______ _____学号 ___ __ _指导教师______ ___ _ __ _职称______ __ ___系主任 _________________ _ _ ___2012年 04月22 日EXPERT SYSTEMS AND ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCEExpert Systemsare computer programs that are derived from a branch of computer science research called Artificial Intelligence (AI). AI's scientific goal is to understand intelligence by building computer programs that exhibit intelligent behavior. It is concerned with the concepts and methods of symbolic inference, or reasoning, by a computer, and how the knowledge used to make those inferences will be represented inside the machine.Of course, the term intelligence covers many cognitive skills, including the ability to solve problems, learn, and understand language; AI addresses all of those. But most progress to date in AI has been made in the area of problem solving -- concepts and methods for building programs that reason about problems rather than calculate a solution.AI programs that achieve expert-level competence in solving problems in task areas by bringing to bear a body of knowledge about specific tasks are called knowledge-based or expert systems. Often, the term expert systems is reserved for programs whose knowledge base contains the knowledge used by human experts, in contrast to knowledge gathered from textbooks or non-experts. More often than not, the two terms, expert systems (ES) and knowledge-based systems (KBS), are used synonymously. Taken together, they represent the most widespread type of AI application. The area of human intellectual endeavor to be captured in an expert system is called the task domain. Task refers to some goal-oriented, problem-solving activity. Domain refers to the area within which the task is being performed. Typical tasks are diagnosis, planning, scheduling, configuration and design. An example of a task domain is aircraft crew scheduling, discussed in Chapter 2.Building an expert system is known as knowledge engineering and its practitioners are called knowledge engineers. The knowledge engineer must make sure that the computer has all the knowledge needed to solve a problem. The knowledge engineer must choose one or more forms in which to represent the required knowledge as symbol patterns in the memory of the computer -- that is, he (or she) must choose a knowledge representation. He must also ensure that the computer can use the knowledge efficiently by selecting from a handful of reasoning methods. The practice of knowledge engineering is described later. We first describe the components of expert systems.The Building Blocks of Expert SystemsEvery expert system consists of two principal parts: the knowledge base; and the reasoning, or inference, engine.The knowledge base of expert systems contains both factual and heuristic knowledge. Factual knowledge is that knowledge of the task domain that is widely shared, typically found in textbooks or journals, and commonly agreed upon by those knowledgeable in the particular field.Heuristic knowledge is the less rigorous, more experiential, more judgmental knowledge of performance. In contrast to factual knowledge, heuristic knowledge is rarely discussed, and is largely individualistic. It is the knowledge of good practice, good judgment, and plausible reasoning in the field. It is the knowledge that underlies the "art of good guessing."Knowledge representation formalizes and organizes the knowledge. One widely used representation is the production rule, or simply rule. A rule consists of an IF part and a THEN part (also called a condition and an action). The IF part lists a set of conditions in some logical combination. The piece of knowledge represented by the production rule is relevant to the line of reasoning being developed if the IF part of the rule is satisfied; consequently, the THEN part can be concluded, or its problem-solving action taken. Expert systems whose knowledge is represented in rule form are called rule-based systems.Another widely used representation, called the unit (also known as frame, schema, or list structure) is based upon a more passive view of knowledge. The unit is an assemblage of associated symbolic knowledge about an entity to be represented. Typically, a unit consists of a list of properties of the entity and associated values for those properties.Since every task domain consists of many entities that stand in various relations, the properties can also be used to specify relations, and the values of these properties are the names of other units that are linked according to the relations. One unit can also represent knowledge that is a "special case" of another unit, or some units can be "parts of" another unit.The problem-solving model,or paradigm, organizes and controls the steps taken to solve the problem. One common but powerful paradigm involves chaining of IF-THEN rules to form a line of reasoning. If the chaining starts from a set of conditions and moves toward some conclusion, the method is called forward chaining. If the conclusion is known (for example, a goal to be achieved) but the path to that conclusion is not known, then reasoning backwards is called for, and the method is backward chaining. These problem-solving methods are built into program modules called inference engines or inference procedures that manipulate and use knowledge in the knowledge base to form a line of reasoning.The knowledge base an expert uses is what he learned at school, from colleagues, and from years of experience. Presumably the more experience he has, the larger his storeof knowledge. Knowledge allows him to interpret the information in his databases to advantage in diagnosis, design, and analysis.Though an expert system consists primarily of a knowledge base and an inference engine, a couple of other features are worth mentioning: reasoning with uncertainty, and explanation of the line of reasoning.Knowledge is almost always incomplete and uncertain. To deal with uncertain knowledge, a rule may have associated with it a confidence factor or a weight. The set of methods for using uncertain knowledge in combination with uncertain data in the reasoning process is called reasoning with uncertainty. An important subclass of methods for reasoning with uncertainty is called "fuzzy logic," and the systems that use them are known as "fuzzy systems."Because an expert system uses uncertain or heuristic knowledge (as we humans do) its credibility is often in question (as is the case with humans). When an answer to a problem is questionable, we tend to want to know the rationale. If the rationale seems plausible, we tend to believe the answer. So it is with expert systems. Most expert systems have the ability to answer questions of the form: "Why is the answer X?" Explanations can be generated by tracing the line of reasoning used by the inference engine (Feigenbaum, McCorduck et al. 1988).The most important ingredient in any expert system is knowledge. The power of expert systems resides in the specific, high-quality knowledge they contain about task domains. AI researchers will continue to explore and add to the current repertoire of knowledge representation and reasoning methods. But in knowledge resides the power. Because of the importance of knowledge in expert systems and because the current knowledge acquisition method is slow and tedious, much of the future of expert systems depends on breaking the knowledge acquisition bottleneck and in codifying and representing a large knowledge infrastructure.Knowledge engineeringis the art of designing and building expert systems, and knowledge engineers are its practitioners. Gerald M. Weinberg said of programming in The Psychology of Programming: "'Programming,' -- like 'loving,' -- is a single word that encompasses an infinitude of activities" (Weinberg 1971). Knowledge engineering is the same, perhaps more so. We stated earlier that knowledge engineering is an applied part of the science of artificial intelligence which, in turn, is a part of computer science. Theoretically, then, a knowledge engineer is a computer scientist who knows how to design and implement programs that incorporate artificial intelligence techniques. The nature of knowledge engineering is changing, however, and a new breed of knowledge engineers is emerging. We'll discuss the evolving nature of knowledge engineering later.Today there are two ways to build an expert system. They can be built from scratch, or built using a piece of development software known as a "tool" or a "shell." Before we discuss these tools, let's briefly discuss what knowledge engineers do. Though different styles and methods of knowledge engineering exist, the basic approach is the same: a knowledge engineer interviews and observes a human expert or a group of experts and learns what the experts know, and how they reason with their knowledge. The engineer then translates the knowledge into a computer-usable language, and designs an inference engine, a reasoning structure, that uses the knowledge appropriately. He also determines how to integrate the use of uncertain knowledge in the reasoning process, and what kinds of explanation would be useful to the end user. Next, the inference engine and facilities for representing knowledge and for explaining are programmed, and the domain knowledge is entered into the program piece by piece. It may be that the inference engine is not just right; the form of knowledge representation is awkward for the kind of knowledge needed for the task; and the expert might decide the pieces of knowledge are wrong. All these are discovered and modified as the expert system gradually gains competence.The discovery and cumulation of techniques of machine reasoning and knowledge representation is generally the work of artificial intelligence research. The discovery and cumulation of knowledge of a task domain is the province of domain experts. Domain knowledge consists of both formal, textbook knowledge, and experiential knowledge -- the expertise of the experts.Tools, Shells, and SkeletonsCompared to the wide variation in domain knowledge, only a small number of AI methods are known that are useful in expert systems. That is, currently there are only a handful of ways in which to represent knowledge, or to make inferences, or to generate explanations. Thus, systems can be built that contain these useful methods without any domain-specific knowledge. Such systems are known as skeletal systems, shells, or simply AI tools.Building expert systems by using shells offers significant advantages. A system can be built to perform a unique task by entering into a shell all the necessary knowledge about a task domain. The inference engine that applies the knowledge to the task at hand is built into the shell. If the program is not very complicated and if an expert has had some training in the use of a shell, the expert can enter the knowledge himself. Many commercial shells are available today, ranging in size from shells on PCs, to shells on workstations, to shells on large mainframe computers. They range in price from hundreds to tens of thousands of dollars, and range in complexity from simple, forward-chained, rule-based systems requiring two days of training to those so complex that only highly trained knowledge engineers can use them to advantage.They range from general-purpose shells to shells custom-tailored to a class of tasks, such as financial planning or real-time process control.Although shells simplify programming, in general they don't help with knowledge acquisition. Knowledge acquisition refers to the task of endowing expert systems with knowledge, a task currently performed by knowledge engineers. The choice of reasoning method, or a shell, is important, but it isn't as important as the accumulation of high-quality knowledge. The power of an expert system lies in its store of knowledge about the task domain -- the more knowledge a system is given, the more competent it becomes.Bricks and MortarThe fundamental working hypothesis of AI is that intelligent behavior can be precisely described as symbol manipulation and can be modeled with the symbol processing capabilities of the computer.In the late 1950s, special programming languages were invented that facilitate symbol manipulation. The most prominent is called LISP (LISt Processing). Because of its simple elegance and flexibility, most AI research programs are written in LISP, but commercial applications have moved away from LISP.In the early 1970s another AI programming language was invented in France. It is called PROLOG (PROgramming in LOGic). LISP has its roots in one area of mathematics (lambda calculus), PROLOG in another (first-order predicate calculus).PROLOG consists of English-like statements which are facts (assertions), rules (of inference), and questions. Here is an inference rule: "If object-x is part-of object-y then a component-of object-y is object-x."Programs written in PROLOG have behavior similar to rule-based systems written in LISP. PROLOG, however, did not immediately become a language of choice for AI programmers. In the early 1980s it was given impetus with the announcement by the Japanese that they would use a logic programming language for the Fifth Generation Computing Systems (FGCS) Project. A variety of logic-based programming languages have since arisen, and the term prolog has become generic.。
