最新微观经济学选择题100道答案

1. The scientific method is not applicable to the study of economics because economics is not a true science.
A) True
B) False
2. Hypotheses derived from economic analysis can be validated through empirical analysis, but hardly ever with absolute certainty.
A) True
B) False
3. Which of the following statements relates to the concept of efficiency?
A) The absence of waste.
B) Using resources as effectively as possible.
C) Being able to produce more of one good only by producing less of something else.
D) All the above.
E) b. and c. only.
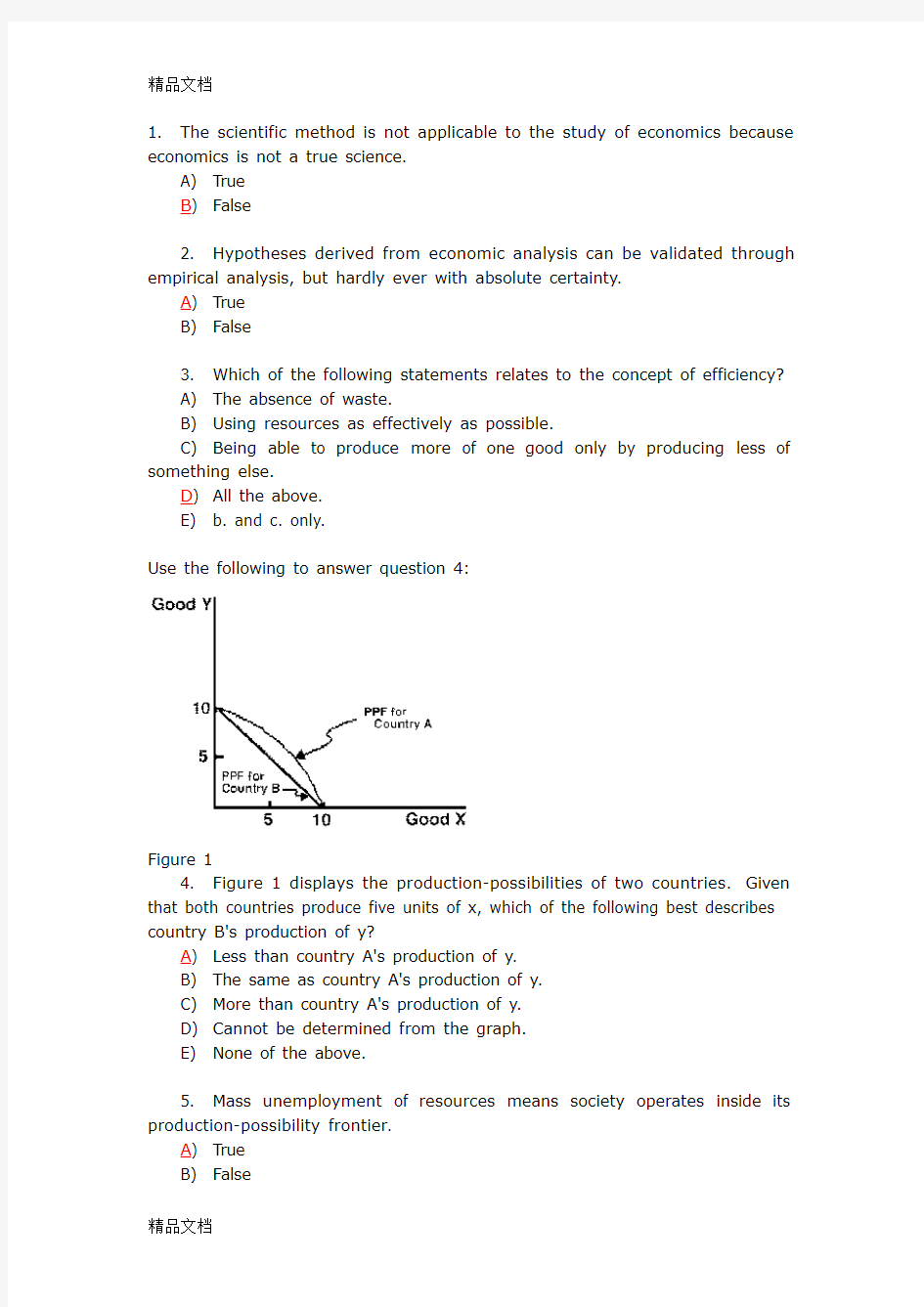
Use the following to answer question 4:
Figure 1
4. Figure 1 displays the production-possibilities of two countries. Given that both countries produce five units of x, which of the following best describes country B's production of y?
A) Less than country A's production of y.
B) The same as country A's production of y.
C) More than country A's production of y.
D) Cannot be determined from the graph.
E) None of the above.
5. Mass unemployment of resources means society operates inside its production-possibility frontier.
A) True
B) False
6. If two goods use the same resources and the same technology, the production possibilities curve between the two goods will have a positive slope.
A) True
B) False
7. It is scarcity that makes goods economic goods.
A) True
B) False
8. Which of the following is the most basic of the subjects with which the study of economics must try to deal?
A) Markets.
B) Money.
C) Profit seeking.
D) The price mechanism.
E) Scarcity.
9. Poor money management by the government, aside from increasing the unemployment rate, will have a relatively small effect on the economy.
A) True
B) False
Use the following to answer question 10:
Figure 2
10. In Figure 2, what is Country B's cost of producing 1 unit of x in terms of y?
A) 10 units of y.
B) 1/2 units of y.
C) 5 units of y.
D) 2 units of y.
E) None of the above.
11. Barter is inconvenient because:
A) bargaining power is unequal between rich and poor.
B) without money, who can define "fair" values?
C) my wants and supplies do not match your supplies and wants.
D) it leads to imperfect competition.
E) all of the above.
12. The economic role of government in mixed economies can include:
A) provision of public goods.
B) tax collections.
C) income redistribution.
D) all of the above.
E) none of the above.
13. By the "invisible hand," Smith meant the influence and lobbying of the hidden interest groups.
A) True
B) False
14. A society which forgoes present consumption:
A) is forced to do so because of excessive consumption within the country in the past.
B) may be devoting new resources to new capital formation.
C) is merely devoting resources to the replacement of capital.
D) expects to consume only that amount tomorrow which was foregone today.
E) does none of the above.
15. An economic good is valued in part by its scarcity.
A) True
B) False
16. The statement that roundabout methods of production are often more efficient than more direct methods:
A) means that roundabout methods use the same inputs as more direct methods, except for time, which is not a scarce economic good.
B) means that consumers ought to choose those goods which most lend themselves to roundabout methods of production.
C) means that the most roundabout method is always the most efficient method of producing any output.
D) is false, for direct and indirect methods of production are usually the same in terms of efficiency.
E) suggests that foregone consumption devoted to investment sometimes increases future output in ways that more closely match individual and/or social desires.
17. Which of the following statements is true of specialization?
A) Specialization is inconsistent with the idea of individual freedom.
B) Economies that practice a division of labor are morally superior to those that do not.
C) In accepting specialization, a person sacrifices his or her own interests for the sake of society's interest.
D) While specialization has enormous advantages, the costs outweigh them.
E) Increased productivity is more likely to be achieved through specialization.
18. In an affluent modern society, businesses may have to offer workers more fulfilling jobs.
A) True
B) False
19. Consumers vote their dollars primarily in:
A) labor markets.
B) land markets.
C) capital markets.
D) goods markets .
E) none of the above.
20. An example of legal limitations on property rights is the prohibition of pollution.
A) True
B) False
21. Lower prices coax out higher quantities demanded along a downward-sloping demand curve.
A) True
B) False
22. An increase in price will lead to a lower quantity demanded because:
A) suppliers will supply only the smaller amount.
B) quality deteriorates.
C) people will purchase less of the good.
D) all of the above.
E) none of the above.
Use the following to answer question 23:
Figure 3
23.Let P* and Q* represent market clearing price and quantity, respectively. Given the supply and demand curves drawn in Figure 3, a reduction in the price of an input used in the production of Q can be expected to cause:
A) P* and Q* to climb.
B) P* to climb while Q* falls.
C) P* to climb while Q* holds steady.
D) P* to fall while Q* climbs.
E) P* and Q* to fall.
Use the following to answer question 24:
Table 1
The Market for Potato Chips
(quantities measured in bags per week)
Price Quantity Supplied Quantity Demanded
$1.00 500 2000
2.00 1000 1750
3.00 1500 1500
4.00 2000 1250
5.00 2500 1000
24. According to T able 1, the equilibrium price for potato chips is:
A) $1.00.
B) $2.00.
C) $2.50.
D) $3.00.
E) $4.00.
25. Upward-sloping supply curves are the result of:
A) increasing returns to scale.
B) increasing costs of production.
C) changes in government policies.
D) changes in technology.
E) none of the above
26. To say that a price "clears the market" is to say that everyone who wants that commodity is getting all they want.
A) True
B) False
27. The position of the supply schedule for American-made cars will not be directly affected by which of the following?
A) Union wage rates.
B) Car prices.
C) The possibility of strikes.
D) A change in assembly technology.
E) All of the above will affect supply.
28. The demand curve for a normal good will shift to the right if:
A) income increases.
B) population increases.
C) the price of a substitute good increases.
D) all the above.
E) none of the above.
29. Given a fixed supply of lamb chops, a reduction in the price of pork chops (close substitutes) will tend to: (这类题比容易出)
A) shift the demand curve for lamb chops to the right.
B) shift the demand curve for pork chops to the right.
C) shift the demand curve for pork chops to the left.
D) raise the price of lamb chops.
E) lower the price of lamb chops.
30. One reason that supply curves display positive slope is that:
A) expanded production may require the use of superior resources.
B) people are not willing to pay a higher price for more goods.
C) expanded industry output might cause a labor shortage and subsequently increase the wage rate included in the cost of production.
D) extra production brings in the more efficient, lower-cost producers.
E) the law of diminishing returns is important to producers.
31. If a 1 percent change in price causes a 5 percent change in quantity demanded, then demand is price inelastic.
A) True
B) False
32. Whenever total expenditure (i.e., total revenue) remains the same after
a change in price, the elasticity of demand is:
A) greater than 1.
B) less than 1.
C) equal to 0.
D) equal to 1.
E) equal to infinity.
33. If price and quantity sold both decrease from one period to another, we may infer that the law of downward-sloping demand does not operate in that market.
A) True
B) False
(重要)34. In "tight" housing markets, rent controls are often applied to hold the price of housing to a "reasonable" level. What is the immediate effect of this price policy with respect to the allocative functions of prices, and the relative incomes of tenants and landlords?
A) The allocative function of prices is impaired, but the tenants are prevented from gaining at the expense of the landlords.
B) The allocative function of prices is not impaired, and the tenants are prevented from gaining at the expense of landlords.
C) The allocative function of prices is impaired, and the tenants who find housing gain at the expense of landlords.
D) The allocative function of prices is not impaired, but the landlords gain at the expense of tenants who do not find housing.
E) None of the above.
35. Which of the following inefficiencies might be the result of monopoly power's destroying a competitive equilibrium?
A) Prices too high.
B) Output too low.
C) Wages distorted across the economy.
D) Input prices distorted across the economy.
E) All of the above.
36. Dollar receipts for sellers of some commodities will be lower at higher prices.
A) True
B) False
37. The quantity of a good which a person will purchase will not depend on which one of the following items? x
A) The price of the good.
B) His or her tastes.
C) The prices of substitute goods.
D) His or her income.
E) The elasticity of supply.
Use the following to answer question 38:
Figure 4
38. Refer to Figure 4 once again. Suppose that now the demand curve has shifted to D'D'. At what point along D'D' is price elasticity equal to 1?
A) G
B) between G and H.
C) H.
D) between H and I.
E) I.
39. Rank the supply curves in the figure below in order of greatest to least price elasticity at the common intersection point.
A) C, A, B.
B) B, A, C.
C) B, C, A.
D) A, B, C.
E) None of the above.
40. A price subsidy of 20 cents per gallon on milk (which does not have a totally inelastic demand curve) will result in a:
A) change in consumer tastes.
B) drop in the equilibrium price of 20 cents per gallon.
C) drop in the equilibrium price of less than 20 cents per gallon.
D) drop in the equilibrium price of more than 20 cents per gallon.
41. The law of diminishing marginal utility states that the:
A) ratio of MU to P for luxuries is lower than that for necessities.
B) utility derived from the last unit of the good consumed falls as the consumption of the good increases.
C) ratio of MU to P will be the same for all goods.
D) utility derived from total consumption of a good falls as consumption increases.
E) none of the above.
42. A consumer is said to be in equilibrium in his or her choice between two goods A and B when:
A) the purchase of good A gives the same satisfaction as the purchase of good B.
B) the last purchase of good A gives the same addition to satisfaction as the last purchase of good B.
C) each penny spent on good A gives the same satisfaction as each penny spent on good B.
D) the last penny spent on good A gives the same addition to satisfaction as the last penny spent on good B.
E) the last pennies spent on goods A and B generate no additions to satisfaction.
43. A consumer spends all of her income on two goods, coffee and doughnuts. She purchases coffee at 25 cents a unit with a total utility of 800 and a marginal utility of 12. Doughnuts are purchase at 75 cents a unit with a total utility of 200 and a marginal utility of 24. In order to reach consumer equilibrium, she should consume:
A) less doughnuts and more coffee.
B) more doughnuts but the same amount of coffee.
C) more coffee but the same amount of doughnuts.
D) more doughnuts and less coffee.
E) the same amount of coffee and doughnuts.
44. If a person only consumes pickles and peanut butter, he will consume peanut butter up to the point where the:
A) marginal utility of the last unit of peanut butter consumed equals that of the last unit of pickles consumed.
B) total utility of peanut butter consumed equals the total utility of pickles consumed.
C) consumer surplus of peanut butter consumption equals the consumer surplus of pickle consumption.
D) last dollar spent on peanut butter consumption provides the same
marginal utility as the last dollar spent on pickle consumption.
E) none of the above.
45. Water tends to have a low marginal utility because substitutes for it are widely available.
A) True
B) False
46. A good which sells for a higher price than one which is more important for welfare reflects the concept of:
A) complementarity in demand.
B) substitution.
C) marginal or total utility.
D) the paradox of value.
E) law of diminishing marginal utility.
47. The price of good X is $1.50 and that of good Y, $1. A particular consumer who evaluates the marginal utility of Y to be 30 units, and is in equilibrium with respect to purchases of X and Y, must consider the marginal utility of X to be:
A) 15 units.
B) 20 units.
C) 30 units.
D) 45 units.
E) none of the above.
48. It is possible to sum individual demand curves to get the market demand curve only when all consumers are exactly alike in their demands.
A) True
B) False
49. The paradox of value is not the result of declining marginal utility.
A) True
B) False
50. In the figure below, which area represents consumer surplus at a price of 5?
A) OADC.
B) OBEC.
C) CEH.
D) OBEH.
E) CEGF.
51. Both in number and in dollar value of sales, the individual proprietorship is the dominant form of American enterprise.
A) True
B) False
Use the following to answer question 52:
Figure 5
52. Suppose that two inputs, K and L, are variable and increase at the same rate. Which one of the panels in Figure 5 represents Increasing Return to Scale (IRS)?
A) Panel a.
B) Panel b.
C) Panel c.
D) Panel d.
E) None of the above.
