symmetric and asymmetric encryption
对称密码体制和非对称密码体制

对称密码体制和⾮对称密码体制⼀、对称加密 (Symmetric Key Encryption)对称加密是最快速、最简单的⼀种加密⽅式,加密(encryption)与解密(decryption)⽤的是同样的密钥(secret key)。
对称加密有很多种算法,由于它效率很⾼,所以被⼴泛使⽤在很多加密协议的核⼼当中。
⾃1977年美国颁布DES(Data Encryption Standard)密码算法作为美国数据加密标准以来,对称密码体制迅速发展,得到了世界各国的关注和普遍应⽤。
对称密码体制从⼯作⽅式上可以分为分组加密和序列密码两⼤类。
对称加密算法的优点:算法公开、计算量⼩、加密速度快、加密效率⾼。
对称加密算法的缺点:交易双⽅都使⽤同样钥匙,安全性得不到保证。
此外,每对⽤户每次使⽤对称加密算法时,都需要使⽤其他⼈不知道的惟⼀钥匙,这会使得发收信双⽅所拥有的钥匙数量呈⼏何级数增长,密钥管理成为⽤户的负担。
对称加密算法在分布式⽹络系统上使⽤较为困难,主要是因为密钥管理困难,使⽤成本较⾼。
⽽与公开密钥加密算法⽐起来,对称加密算法能够提供加密和认证却缺乏了签名功能,使得使⽤范围有所缩⼩。
对称加密通常使⽤的是相对较⼩的密钥,⼀般⼩于256 bit。
因为密钥越⼤,加密越强,但加密与解密的过程越慢。
如果你只⽤1 bit来做这个密钥,那⿊客们可以先试着⽤0来解密,不⾏的话就再⽤1解;但如果你的密钥有1 MB⼤,⿊客们可能永远也⽆法破解,但加密和解密的过程要花费很长的时间。
密钥的⼤⼩既要照顾到安全性,也要照顾到效率,是⼀个trade-off。
分组密码:也叫块加密(block cyphers),⼀次加密明⽂中的⼀个块。
是将明⽂按⼀定的位长分组,明⽂组经过加密运算得到密⽂组,密⽂组经过解密运算(加密运算的逆运算),还原成明⽂组,有 ECB、CBC、CFB、OFB 四种⼯作模式。
序列密码:也叫流加密(stream cyphers),⼀次加密明⽂中的⼀个位。
网络信息安全英语练习题

网络信息安全英语练习题### Network Information Security Practice Questions1. Understanding Network Security Basics- Question: What is the primary function of a firewall in network security?- Answer: A firewall's primary function is to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.2. Types of Network Attacks- Question: Differentiate between a DDoS attack and a phishing attack.- Answer: A DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack overwhelms a website or server with a flood of traffic, making it inaccessible. A phishing attack, on the other hand, involves tricking individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card numbers, through deceptive emails or websites.3. Cryptography- Question: Explain the difference between symmetric and asymmetric encryption.- Answer: Symmetric encryption uses the same key for both encryption and decryption, making it faster but requiring secure key distribution. Asymmetric encryption uses a pair of keys, a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption, which enhances security but is computationallyslower.4. Secure Communication Protocols- Question: What is SSL/TLS and why is it important for secure communication?- Answer: SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security) is a protocol used to provide secure communication over the internet. It is important because it encrypts data being transmitted, ensuring that it cannot be intercepted and read by unauthorized parties.5. Vulnerability Management- Question: How can organizations manage and mitigate software vulnerabilities?- Answer: Organizations can manage and mitigate software vulnerabilities by regularly updating and patching software, conducting vulnerability assessments, and implementing a strong patch management policy.6. Network Security Policies- Question: What are the key components of a network security policy?- Answer: Key components of a network security policy include access control, password policies, network segmentation, incident response plan, and user education on security practices.7. Wireless Security- Question: What is WPA2 and why is it preferred over WPA for wireless security?- Answer: WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access II) is a securityprotocol for wireless networks that provides stronger encryption and is more secure than WPA. It is preferred dueto its use of the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), whichis more resistant to hacking attempts.8. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)- Question: What is the role of an IDS in network security? - Answer: An IDS monitors network traffic for suspicious activity or policy violations. It can detect and alert administrators to potential intrusions or attacks, allowingfor a timely response to mitigate threats.9. Social Engineering- Question: How can social engineering attacks be prevented?- Answer: Social engineering attacks can be prevented by educating employees about the tactics used in such attacks, implementing strict security policies, and encouraging a culture of skepticism towards unsolicited communications.10. Incident Response- Question: What steps should be taken when a security incident is detected?- Answer: Upon detecting a security incident, stepsshould include isolating the affected system, collecting evidence, analyzing the incident, eradicating the threat, restoring affected systems, and reviewing the incident to improve security measures.11. Data Protection- Question: What measures can be taken to protectsensitive data?- Answer: Measures to protect sensitive data include data encryption, access controls, regular backups, and secure data disposal practices.12. Compliance and Regulations- Question: Why is compliance with data protection regulations important?- Answer: Compliance with data protection regulations is important to protect the privacy of individuals, maintain trust with customers, and avoid legal penalties and reputational damage.Remember, these practice questions are designed to test your understanding of network information security concepts and practices. It is essential to stay updated with the latest security trends and technologies to effectively protect your networks and data.。
《高级宏观经济学》教学大纲(硕士研究生)-RonaldoCarpio

《高级宏观经济学》教学大纲(硕士研究生) - RonaldoCarpio《高级微观经济分析》教学大纲(博士研究生)课程代码:(按本专业或方向培养方案填写)课程名称:(按本专业或方向培养方案填写)英文名称:Advanced Microeconomic Analysis课程性质:(按本专业或方向培养方案填写)学分学时:3学分,48学时授课对象:金融学院一年级博士研究生课程简介:Based on Microeconomics I (for master students), the course will discuss thecontemporary development in microeconomics. This course is also designed to develop andextend the students’ analytical and reading skills in modern microeconomics. A student who haspassed the course should be able to read typical articles in the mainline journals, understand theanalytical derivations and arguments commonly used in the literature, and know how to solve themore widely used models.先修课程:Microeconomics for master students选用教材:1、 Mas-Colell, A., M. D. Whinston, and J. Green, Microeconomic Theory. (MWG)2、 Jehle, Geoffrey A. and Philip J. Reny, Advanced Microeconomic Theory. (JR)考核方式与成绩评定:Final Exam %; Midterm Exam %; Class Participation % 主讲教师:Carpio Ronaldo、颜建晔所属院系:金融学院联系方式:******************、*******************答疑时间及地点:求索楼123,Wednesday 13:30-14:30 (Carpio),Tuesday 15:00-17:00(颜)第一章:Consumer Theory教学目标和要求:Understand the consumer’s problem and consumer demand.教学时数:6学时教学方式:讲授准备知识:calculus教学内容:Preferences, Utility, and Consumer’s Problem第一节:Consumer’s Problem第二节:Indirect Utility, Demand作业与思考题:JR Ch 1.6参考资料:JR Ch 1, Appendix A1, A21第二章: Topics in Consumer Theory教学目标和要求:Understand duality, integrability, and uncertainty.教学时数:6 学时教学方式:讲授准备知识:statistics教学内容:Duality, Integrability, and Uncertainty 第一节:Duality of Consumer’s Problem第二节:Revealed Preferences & Uncertainty 作业与思考题:JR Ch 2.5 参考资料:JR Ch 2第三章: Theory of the Firm教学目标和要求:Understand the firm’s profit maximization problem.教学时数:6 学时教学方式:讲授准备知识:Chapter 1,2教学内容:Production, Cost, Profit Maximization 第一节:Production Functions & Cost第二节:Duality in Production, Competitive Firms 作业与思考题:JR Ch 3.6参考资料:JR Ch 3第四章: Partial Equilibrium教学目标和要求:Understand partial equilibrium markets. 教学时数:3学时教学方式:讲授准备知识:Chapter 3教学内容:Perfect & Imperfect Competition, Welfare 第一节:Competition 第二节:Equilibrium & Welfare作业与思考题:JR Ch 4.4参考资料:JR Ch 4第五章: Walras’/competitive equilibrium2教学目标和要求:competitive market economies from a Walrasian (general) equilibrium perspective.Let students understand “why the competitive market/equilibrium may work or fail?”教学时数:6学时方式:讲授教学准备知识:consumer theory, production theory教学内容:第一节:Walrasian economy and mathematical language of microeconomics 第二节:competitive equilibria of pure exchange and with production 作业与思考题:JR5.5, exercises of MWG Ch15, 18, 教师自编习题集参考资料:MWG Mathematical Appendix, Ch15, 18; JR5.4第六章: Social choice function/theory and social welfare: normative aspect of microeconomics教学目标和要求:When we judge some situation, such as a market equilibrium, as “good”or “bad”, or “better” or “worse” than another, we necessarily make at least implicit appeal to some underlying ethical standard. Welfare economics helps to inform the debate on social issues by forcingus to confront the ethical premises underlying our arguments as well as helping us to seetheir logical implications.Let students have a systematic framework for thinking about normative and social welfare topics.教学时数:3学时教学方式:讲授准备知识:Walrasian equilibrium教学内容:第一节:social choice, comparability, and some possibilities第二节:Rawlsian, Utiliterian, and flexible forms作业与思考题:JR6.5, exercises of MWG Ch21, 22, 教师自编习题集参考资料:MWG Ch21.A, Ch21.E, Ch22.C; JR Ch6第七章: Strategic Behavior and Asymmetric Information教学目标和要求:A central feature of contemporary microeconomicsafter Walrasian economy is the multi-agent interaction which represents the potential for the presence of strategicinterdependence. Let students grasp classic models of imperfect competition under symmetric and asymmetric information.3教学时数:3学时教学方式:讲授准备知识:perfect competition教学内容:第一节:monopoly and oligopoly under symmetric information第二节:oligopoly under asymmetric information作业与思考题:教师自编习题集参考资料:MWG Ch12; JR Ch4第八章: Theory of Incentives教学目标和要求:The strategic opportunities that arise in the presence of asymmetricinformation typically lead to inefficient market outcomes, a form of market failure. Underasymmetric information, the first welfare theorem no longer holds generally. Thus, the main themeto be explored is to stimulate different agents’ optimal/efficient behaviors in differentinformational settings to achieve the “second-best” market outcomes.教学时数:9学时教学方式:讲授准备知识:Strategic Behavior and Asymmetric Information教学内容:第一节:Adverse selection第二节:Moral hazard*第三节:Task separation/integration,第三节:Career concern作业与思考题:exercises of MWG Ch13, 14, 教师自编习题集参考资料:JR Ch8; MWG Ch13, 14第九章前沿研究讲座:待定邀请校外老师(待定)给学生们讲演最新研究,引导学生讨论;在学生掌握现代微观经济学基本模型之后能够接触到前沿研究。
信息安全的英文

Apply regular firewall updates to patch vulnerability and ensure optimal performance
Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS)
Real time Monitoring
Threats
Any circulation or event with the potential to cause harm to information systems through unauthorized access, destruction, disclosure, modification of data, or denial of service
Regular updates of antivirus software to ensure protection against the latest threats
Integration of antivirus software with other security tools for comprehensive protection
03
Key Management: Implement robust key management practices to securely generate, store, distribute, and revoke encryption keys
04
Compliance with Standards: Adhere to industry standards and regulations for encryption technologies to ensure interoperability and security
(完整版)信息安全与保密技术复习试题与答案
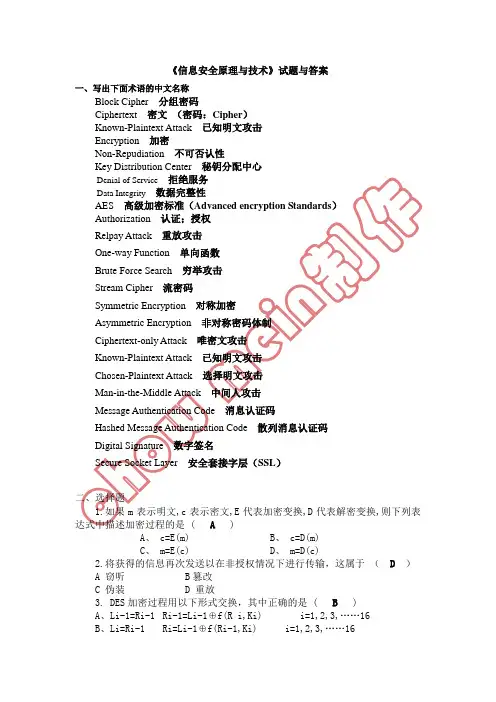
《信息安全原理与技术》试题与答案一、写出下面术语的中文名称Block Cipher 分组密码Ciphertext 密文(密码:Cipher)Known-Plaintext Attack 已知明文攻击Encryption 加密Non-Repudiation 不可否认性Key Distribution Center 秘钥分配中心Denial of Service拒绝服务Data Integrity数据完整性AES 高级加密标准(Advanced encryption Standards)Authorization 认证;授权Relpay Attack 重放攻击One-way Function 单向函数Brute Force Search 穷举攻击Stream Cipher 流密码Symmetric Encryption 对称加密Asymmetric Encryption 非对称密码体制Ciphertext-only Attack 唯密文攻击Known-Plaintext Attack 已知明文攻击Chosen-Plaintext Attack 选择明文攻击Man-in-the-Middle Attack 中间人攻击Message Authentication Code 消息认证码Hashed Message Authentication Code 散列消息认证码Digital Signature 数字签名Secure Socket Layer 安全套接字层(SSL)二、选择题1.如果m表示明文,c表示密文,E代表加密变换,D代表解密变换,则下列表达式中描述加密过程的是 ( A )A、 c=E(m)B、 c=D(m)C、 m=E(c)D、 m=D(c)2.将获得的信息再次发送以在非授权情况下进行传输,这属于( D )A 窃听 B篡改C 伪装D 重放3. DES加密过程用以下形式交换,其中正确的是 ( B )A、Li-1=Ri-1 Ri-1=Li-1⊕f(R i,Ki) i=1,2,3, (16)B、Li=Ri-1 Ri=Li-1⊕f(Ri-1,Ki) i=1,2,3, (16)C、Li-1=Ri+1 Ri=Li+1⊕f(Ri-1,Ki) i=1,2,3, (16)D、Li-1=Ri-1 Ri=Li+1⊕f(Ri-1,Ki) i=0,1,2,3, (15)4. 在不知道密钥的情况下,通过获取密文而恢复明文的方法是。
对称加密与非对称加密

对称加密与非对称加密IntroductionEncryption is a method to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of data, that is, to keep it safe from unauthorized access. There are two types of encryption: symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption. Symmetric encryption uses the same key to encrypt and decrypt data, while asymmetric encryption uses a pair of public and private keys to encrypt and decrypt data. These two types of encryption have their advantages and disadvantages, and they are usedfor different purposes. This paper will discuss thedifference between symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption, their strengths and weaknesses, and their application in different fields.Symmetric EncryptionSymmetric encryption, also known as secret-key encryption, uses the same key to encrypt and decrypt data. This meansthat both the sender and receiver of the data have to sharethe same secret key, which they use to encrypt and decryptthe data. Symmetric encryption is fast and efficient, as it requires less computational power compared to asymmetric encryption. It is commonly used in applications such as data encryption, file encryption, and encryption of communication between devices.Advantages of Symmetric EncryptionSpeed: Symmetric encryption is very fast because it usesa single key to encrypt and decrypt data. This makes it ideal for applications that require quick data encryption, such as large-scale file transfers.Less Computational Power: Symmetric encryption requires less computational power than asymmetric encryption. This isbecause the algorithms used in symmetric encryption are simpler and more efficient.Disadvantages of Symmetric EncryptionKey Management: Keys used in symmetric encryption need to be shared between the sender and receiver of data. This creates a key management problem, as it is difficult to distribute and manage secret keys securely.Single Point of Failure: The use of a single key to encrypt and decrypt data makes it easier for an attacker to breach the system. If the key is compromised, it can be used to decrypt all the encrypted data.Asymmetric EncryptionAsymmetric encryption, also known as public-key encryption, uses a pair of keys to encrypt and decrypt data. This means that there are two keys: a public key and aprivate key. The public key is used for encryption, while theprivate key is used for decryption. The public key is freely available to anyone who wants to send encrypted data, while the private key is kept secret by the receiver of the data. Asymmetric encryption is commonly used to secure communication channels, such as email, and to ensure the authenticity of digital signatures.Advantages of Asymmetric EncryptionSecurity: Asymmetric encryption provides better security than symmetric encryption. This is because the private key is kept secret and is not shared with anyone else. This means that even if an attacker gets hold of the public key, they cannot decrypt the data without the private key.Key Management: Asymmetric encryption does not require a shared secret key. This makes it easier to distribute and manage keys securely. It also eliminates the need for a secure key exchange channel, which is required in symmetric encryption.Disadvantages of Asymmetric EncryptionComputational Power: Asymmetric encryption requires more computational power than symmetric encryption. This is because the algorithms used in asymmetric encryption are more complex.Speed: Asymmetric encryption is slower than symmetric encryption. This makes it unsuitable for applications that require quick data encryption, such as large-scale file transfers.Application of Symmetric and Asymmetric EncryptionSymmetric encryption is commonly used in applicationsthat require quick data encryption, such as large-scale file transfers. It is also used in applications where the data is not sensitive, such as internal communications within an organization.Asymmetric encryption is commonly used in applications where security is a top priority, such as secure communication channels like email, and to ensure the authenticity of digital signatures. It is also used in applications where the data is sensitive, such as online banking and e-commerce.ConclusionIn conclusion, symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption are two different encryption methods, each withits own strengths and weaknesses. Symmetric encryption isfast and efficient, but requires a secure key distribution mechanism. Asymmetric encryption provides better security, but requires more computational power. The choice between symmetric and asymmetric encryption depends on theapplication requirements, and the level of security required.。
Crack软件破解脱壳入门术语简介
SMC : (self-modifying code) 意思是自我修改的代码,使程序在运行时自我修改,用途包括:
- 使一些重要的跳转位置爆破无效化 (以 smc 对重要位置进行覆写)
- 使一些重要代码隐藏 (在必要时才实时产生重要代码段,防止程序被人静态分析,也防止一些透过搜寻的破解方法)
RSA : 是一套加密技术 (public key infrastructure),它被广泛应用于各种层面,由一对密钥 (public key 和 private key) 的组合,提供安全的资料加密
Symmetric encryption : 对称加密,意思是加密和解密的 secret key 是相同的,例如 DES, AES, Blowfish
VA : (Virtual Address) 内存虚拟空间中的一个位置,在 PE 描述中的意思是 : PE 被载入后,区块在内存的确实位置
Offset : 意思是偏移值,通常用于指明一个位置,它的用法是把一个基底位置加上 offset 值 (offset 可以是负数)。 例如我们说 : 一个资料结构在内存中的位置是 0x125000,它的 offset 0x10 处是用户名字, offset 0x14 是用户序号。在 PE 结构中, offset 通常用于指明在 exe 档案中的实际位置
【入门术语简介】
(更详尽的资料,请Байду номын сангаас考看雪论坛精华,或看雪的书籍)
加壳 : 表示程序的 exe 被一层外壳保护,这层外壳是一些软件保护公司 (或一些高手) 设计出来的,可以把 exe包裹起来,在 exe 执行时提供保护,对抗破解者
爆破 : 意思是透过修改程序,来达到破解目的,主要方法包括,修改重要跳转指令 (jmp, jz, jzn, 等等)
简述密码学的分类
简述密码学的分类
密码学可以分为以下几个主要分类:
1. 对称加密(Symmetric Encryption):也称为共享密钥加密,使用相同的密钥用于加密和解密信息。
常见的对称加密算法包括DES、AES和IDEA等。
2. 非对称加密(Asymmetric Encryption):也称为公钥加密,
使用一对非对称密钥,即公钥和私钥,其中公钥用于加密信息,私钥用于解密信息。
常见的非对称加密算法包括RSA和ECC 等。
3. 哈希函数(Hash Function):哈希函数将输入数据映射为固
定长度的输出值,常用于验证数据完整性。
常见的哈希函数包括MD5、SHA-1和SHA-256等。
4. 消息认证码(Message Authentication Code,MAC):MAC
是一种通过在信息中添加一个附加的认证标签来验证信息的完整性和真实性的技术。
常见的MAC算法包括HMAC和
CMAC等。
5. 数字签名(Digital Signature):数字签名是利用非对称加密
算法,对文档或数据进行签名,以验证发送者的身份和确保数据的完整性和非抵赖性。
常见的数字签名算法包括RSA和
DSA等。
6. 随机数生成器(Random Number Generator,RNG):RNG
生成随机数,常用于密码学中的密钥生成和加密算法中的初始化向量。
常见的RNG包括伪随机数生成器(PRNG)和真随机数生成器(TRNG)。
7. 公钥基础设施(Public Key Infrastructure,PKI):PKI是建立在非对称加密基础之上的一套加密系统、解决方案和设施,用于管理公钥和数字证书等。
密码学术语
BDK Base Derivation Key 基础导出密钥CS Configure Security 安全配置CSC Card Security Codes 卡安全码CSCK Card Security Codes Key 卡安全码密钥CVK Card Validation Key 卡校验密钥CVV Card Validatoin Value 卡校验值HSM H ost Security Module 主机加密模块KCV Key Check Value 密钥校验值IV Initialisation Vector 初始化向量LMK Local Master Key 本地主密钥MAC M essenge Authentication Code 信息认证码KSN Key serial number 密钥序列号PIN Personal Identification Number 个人身份号码PK Public Key 公钥PVK PIN Verification Key P IN校验密钥PVKI PIN Verification Key Indicator PIN校验密钥索引PVV PIN Verification Value PIN校验值TAK Terminal Authentication Key 终端认证密钥TMK Terminal Master Key 终端主密钥TPK Terminal PIN Key 终端PIN密钥WWK Watchword Key 口令密钥ZAK Zone Authentication Key 区域认证密钥ZEK Zone Encryption Key 区域加密密钥ZMK Zone Master Key 区域主密钥ZPK Zone PIN Key 区域PIN密钥AES 旨在替代DES 的高级加密标准(Advanced Encryption Standard)。
由NIST 组织的竞赛获胜者是Rijndael。
操作系统第六版第一章答案
⏹ 1. What are the three main purposes of an operating system?答:管理计算机硬件;提供应用程序的基础;充当用户和计算机硬件之间的媒介⏹ 2. What is the main advantage of multiprogramming?答:可以使CPU总有一个作业可以执行,提高CPU的利用率⏹ 3. In a multiprogramming and time-sharing environment, several users sharethe system simultaneously. This situation can result in various security problems.⏹ a. What are two such problems?答:用户之间相互窃取或者复制彼此的程序或数据;可能会没有合理的预算来使用资源⏹ b. Can we ensure the same degree of security in a time-sharedmachine as we have in a dedicated machine? Explain your answer.答:不能,虽然分时系统有相应的保护措施,但不能完全确保其安全和不被破解⏹ 4. Define the essential properties of the following types of operating systems:⏹ a. Batch答:具有相似需求的作业被成批的集合起来,并把它们作为一个整体通过一个操作员或自动作业程序装置运行通过计算机。
通过缓冲区,线下操作,后台和多道程序,运用尝试保持CPU和I/O一直繁忙,从而使得性能被提高。
批处理系统对于运行那些需要较少互动的大型作业十分适用⏹ b. Interactive答:提供用户与系统之间的直接通信;用户通过键盘和鼠标向操作系统和程序直接发出指令,并等待响应结果,响应时间比较短,通常为1s左右⏹ c. Time sharing答:使用CPU调度和多道程序控制提供给每个用户一小部分的分时计算机;允许许多用户同时共享计算机,系统快速的从一个用户切换到另一个用户,使每个用户感觉整个系统都为自己所用⏹ d. Real time答:常用于控制特定应用的设备;有明确的和固定的时间约束,处理必须在确定的时间约束内完成否则系统就会失败;含有硬实时系统和软实时系统两种:硬实时系统保证关键任务按时完成,约束比较强对系统的所有延迟都有限制;而软实时系统则限制较弱一些⏹ e. Network答:提供给操作体统一个特征使得其进入网络,比如文件共享等⏹ f. Distributed答:通过网络提供功能,分布式系统能够共享计算机任务,并向用户提供丰富的功能⏹ 5. Describe the differences between symmetric and asymmetricmultiprocessing. What are three advantages and one disadvantage of multiprocessor systems?答:对称对处理的所有处理器都对等,处理器之间没有主从关系,每个处理器都并发运行一个操作系统的拷贝,这些拷贝根据需要相互通信;非对称处理每个处理器都有各自特定的任务,一个主处理器控制系统,其他处理器或者想主处理器要任务或做预先固定的任务,主处理器为从处理器调度和安排工作多处理系统的优点:增加计算量;规模经济;增加可靠性多处理系统的缺点:软硬件更加复杂。
- 1、下载文档前请自行甄别文档内容的完整性,平台不提供额外的编辑、内容补充、找答案等附加服务。
- 2、"仅部分预览"的文档,不可在线预览部分如存在完整性等问题,可反馈申请退款(可完整预览的文档不适用该条件!)。
- 3、如文档侵犯您的权益,请联系客服反馈,我们会尽快为您处理(人工客服工作时间:9:00-18:30)。
Advantages of using digital signature:
authenticity
Integrity and Non-repudiation(不可抵赖性)
THANK YOU FOR LISTENING.
Those classes, contained on the same namespace of the SymmetricAlgorithm class
∟ Aes ∟ AesCryptoServiceProvider ∟ AesManaged ∟ Rjindael ∟ RjindaelManaged ∟ TripleDES ∟ TripleDESCryptoServiceProvider ∟ DES ∟ DESCryptoServiceProvider ∟ RC2 ∟ RC2CryptoServiceProvider
A digital signature is a mathematical scheme for demonstrating the authenticity of a digital message or document. A valid digital signature gives a recipient reason to believe that the message was created by a known sender, and that it was not altered in transit.
RSA asymmetric encryption (Rivest, Shamir and
Adleman): uses public and private keys that are functions of a pair of
large prime numbers
DSA (Digital Signature Algorithm) PGP (Pretty Good Privacy )
Process
Assume that there are two person:
Alice
Bob
Private key Public key
Public key
Private key
Public key
Private key
Private key
Asymmetric Encryption algorithms
Symmetric Encryption and Asymmetric encryption
Symmetric Encryption
What is symmetric encryption?
A
secret key mathematical algorithm
A
They are same.
Symmetric algorithms
Stream
algorithms (Stream ciphers)
Block
algorithms (Block ciphers)
Symmetric Encryption .NET Framework
&
The .NET Framework rationalizes the block symmetric algorithms implemented on it by defining the base abstract class Symmetric Algorithm. Symmetric Algorithm that you can find under the System.Security.Cryptography namespace.
What are symmetric encryption Advantages & Vulnerabilities?
Advantages
——Security & High Speed Vulnerabilities ——Brute force & Cryptanalysis
Asymmetric encryption
Definition:
Asymmetric encryption uses different keys for encryption and decryption.
Plaintext Encryption algorithm Public and private key Ciphertext Decryption algorithm源自Advantages
Complex algorithm Secure
Disadvantages
Slow Requires more processing power
An application of asymmetric encryption – digital signature
