Input-Output Stability 输入输出稳定
Stability and stabilization of nonlinear system-Chapter 8非线性系统稳定性和稳定化

Chapter8Open ProblemsIn this chapter,we would like to give a list of open and unanswered problems in Mathematical Control Theory.The solutions of these open problems will be very important for the development of modern nonlinear control theory.Expectedly novel mathematical analysis and synthesis tools need to be developed to address these challenging problems.The interested reader should also consult the book[3]for other significant and important open problems in Mathematical Control Theory.Open Problem#1Under what conditions WIOS implies IOS?A qualitative characterization of the IOS property for abstract control systems as discussed in this book has not been available yet.For systems described by ODEs, many qualitative characterizations of the ISS and IOS properties are provided in [21–23].Moreover,Theorem4.1in Chap.4gives a complete qualitative character-ization of the WIOS property:“0-GAOS”+“RFC”+“the continuity with respect to initial conditions and external inputs”implies WIOSA similar qualitative characterization for the IOS property in a general context of abstract dynamical systems as discussed in this book will be very important for control designs and applications.Open Problem#2Development of small-gain techniques for dynamical systems described by Partial Differential Equations(PDEs).Small-gain results have been well studied forfinite-dimensional nonlinear sys-tems described by ordinary differential,or difference,equations(see,e.g.,[8–10] and references therein).However,as of today,there is little research devoted to the development of small-gain techniques for nonlinear systems described by Partial Differential Equations(PDEs).We believe that the small-gain results provided in the present book(Theorems5.1and5.2in Chap.5)will pave the road for the appli-cation of small-gain results to systems described by PDEs.I.Karafyllis,Z.-P.Jiang,Stability and Stabilization of Nonlinear Systems,381 Communications and Control Engineering,DOI10.1007/978-0-85729-513-2_8,©Springer-Verlag London Limited2011Open Problem#3Formulas for the Coron–Rosier methodology.Theorem6.1in Chap.6is an existence-type result.Although its proof is con-structive,it cannot be easily applied for feedback design purposes.The creation of formulas for the Coron–Rosier approach will be very significant for control pur-poses,since the Coron–Rosier approach can allow nonconvex control sets and does not require additional properties for the Control Lyapunov Function.The signifi-cance of the solution of this open problem is also noted in[5].Open Problem#4When is a nonlinear,time-varying,time-delay system stabiliz-able?We have recently provided a positive answer to the above question when the sys-tem only involves state-delay[13].A complete answer to the question of when the nonlinear time-varying system with both state and input delays is stabilizable re-mains open and requires deeper investigation.Nonetheless,it should be mentioned that sufficient,but not necessary,conditions for the solution of the stabilization prob-lem with input delays are proposed in the recent work of Krsti´c[14–16](also see [11]).To our knowledge,a necessary and sufficient condition for stabilizability is missing even for linear time-varying systems with input delays.Open Problem#5Application of small-gain results for distributed feedback design of large-scale nonlinear systems.Large-scale systems are abundant in variousfields of science and engineering and have gained increasing attention due to emerging engineering and biomedical applications.Examples of these applications are from smart grids with green and re-newable energy sources,modern transportation networks,and biological networks. There has been some success with the use of decentralized control strategy for both linear and nonlinear large-scale systems;see[7,19]and many references therein. Clearly more remains to be accomplished in this excitingfield.We feel that small-gain is a very appropriate tool for addressing some of these modern-day challenges. The small-gain results of the present book(Theorems5.1and5.2in Chap.5)make a preliminary step forward toward studying some complex large-scale systems be-yond the past literature of decentralized systems and control.Open Problem#6Extension of the discretization approach for autonomous sys-tems.The discretization approach for Lyapunov functionals was described in Chap.2 (Propositions2.4and2.5).However,as remarked in Chap.2,the discretization ap-proach requires good knowledge of some approximation of the solution map,and its use has been restricted to time-varying systems with special structure(see[1,17, 18]).An extension of the discretization approach for autonomous systems wouldbe an important contribution in stability theory because such a result would al-low the use of positive definite functions with non sign-definite derivative.The re-quired extension of the discretization approach must utilize appropriate differential inequalities in the same spirit as the classical Lyapunov’s approach(without requir-ing knowledge of the solution map or a system with special structure).The recent work in[12]is an attempt in this research direction(see also references therein). However,the problem is still completely“untouched.”Open Problem#7Application of feedback design methodologies to other mathe-matical problems.In this book,we have seen the applications of certain tools of modern nonlinear control theory to problems arising from mathematics and economics.Particularly, we have seen•applications of small-gain results to game theory(see Sect.5.5in Chap.5),•applications to numerical analysis(see Sect.7.3).We believe that feedback design methodologies can be applied with success to other areas of mathematical sciences.Fixed Point Theory(see[6])and Optimization Theory can be benefited by the application of certain tools of modern nonlinear con-trol theory.Corollary5.4in Chap.5already shows that small-gain results can have serious consequences in Fixed Point Theory.Further connections between Fixed Point Theory and Stability Theory are provided by the work of Burton(see[4]and references therein)but are in the opposite direction from what we propose,that is, the work of Burton applies results from Fixed Point Theory to Stability Theory.The efforts for the solution of problems in Game Theory,Numerical Analysis, Fixed Point Theory,and Optimization Theory will necessarily demand the creation of novel results in stability theory and feedback stabilization theory.Therefore,the application of modern nonlinear control theory to other areas of applied mathe-matics will result to a“knowledge feedback mechanism”between Mathematical Control Theory and other areas in mathematics!Open Problem#8Integral input-to-state stability(for short,iISS)in complex dy-namical systems.The external stability results of this book are exclusively targeted at extensions of Sontag’s ISS property and its variants to a very general context of complex dynamic systems.That is,we want to address a wide class of dynamical systems which may not satisfy the semigroup property,motivated by important examples of hybrid sys-tems,switched systems,and time-delay systems.It remains an open and important, but interesting,question to know how much we could do with the iISS property introduced in[2,20].References1.Aeyels,D.,Peuteman,J.:A new asymptotic stability criterion for nonlinear time-variant dif-ferential equations.IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control43(7),968–971(1998)2.Angeli,D.,Sontag,E.D.,Wang,Y.:A characterization of integral input-to-state stability.IEEETransactions on Automatic Control45(6),1082–1097(2000)3.Blondel,V.D.,Megretski,A.(eds.):Unsolved Problems in Mathematical Systems and ControlTheory.Princeton University Press,Princeton(2004)4.Burton,T.A.:Stability by Fixed Point Theory for Functional Differential Equations.Dover,Mineola(2006)5.Coron,J.-M.:Control and Nonlinearity.Mathematical Surveys and Monographs,vol.136.AMS,Providence(2007)6.Granas,A.,Dugundji,J.:Fixed Point Theory.Springer Monographs in Mathematics.Springer,New York(2003)7.Jiang,Z.P.:Decentralized control for large-scale nonlinear systems:A review of recent results.Dynamics of Continuous,Discrete and Impulsive Systems11,537–552(2004).Special Issue in honor of Prof.Siljak’s70th birthday8.Jiang,Z.P.:Control of interconnected nonlinear systems:a small-gain viewpoint.In:deQueiroz,M.,Malisoff,M.,Wolenski,P.(eds.)Optimal Control,Stabilization,and Nonsmooth Analysis.Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences,vol.301,pp.183–195.Springer, Heidelberg(2004)9.Jiang,Z.P.,Mareels,I.M.Y.:A small-gain control method for nonlinear cascaded systems withdynamic uncertainties.IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control42,292–308(1997)10.Jiang,Z.P.,Teel,A.,Praly,L.:Small-gain theorems for ISS systems and applications.Mathe-matics of Control,Signals,and Systems7,95–120(1994)11.Karafyllis,I.:Stabilization by means of approximate predictors for systems with delayed in-put.To appear in SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization12.Karafyllis,I.:Can we prove stability by using a positive definite function with non sign-definite derivative?Submitted to Nonlinear Analysis Theory,Methods and Applications 13.Karafyllis,I.,Jiang,Z.P.:Necessary and sufficient Lyapunov-like conditions for robustnonlinear stabilization.ESAIM:Control,Optimization and Calculus of Variations(2009).doi:10.1051/cocv/2009029,pp.1–42,August200914.Krsti´c,M.:Delay Compensation for Nonlinear,Adaptive,and PDE Systems.Systems&Con-trol:Foundations&Applications.Birkhäuser,Boston(2009)15.Krsti´c,M.:Input delay compensation for forward complete and feedforward nonlinear sys-tems.IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control55,287–303(2010)16.Krsti´c,M.:Lyapunov stability of linear predictor feedback for time-varying input delay.IEEETransactions on Automatic Control55,554–559(2010)17.Peuteman,J.,Aeyels,D.:Exponential stability of slowly time-varying nonlinear systems.Mathematics of Control,Signals and Systems15,42–70(2002)18.Peuteman,J.,Aeyels,D.:Exponential stability of nonlinear time-varying differential equationsand partial averaging.Mathematics of Control,Signals and Systems15,202–228(2002)19.Siljak,D.:Decentralized Control of Complex Systems.Academic Press,New York(1991)20.Sontag,E.D.:Comments on integral variants of ISS.Systems Control Letters3(1–2),93–100(1998)21.Sontag,E.D.,Wang,Y.:On characterizations of the input-to-state stability property.Systemsand Control Letters24,351–359(1995)22.Sontag,E.D.,Wang,Y.:New characterizations of the input-to-state stability.IEEE Transac-tions on Automatic Control41,1283–1294(1996)23.Sontag,E.D.,Wang,Y.:Lyapunov characterizations of input to output stability.SIAM Journalon Control and Optimization39,226–249(2001)。
自动化专业英语常用词汇

自动化专业英语常用词汇acceleration transducer 加速度传感器accumulated error 累积误差AC-DC-AC frequency converter交-直-交变频器AC (alternating current) electric drive 交流电子传动active attitude stabilization 主动姿态稳定adjoint operator 伴随算子admissible error 容许误差amplifying element 放大环节analog-digital conversion 模数转换operational amplifiers运算放大器aperiodic decomposition 非周期分解approximate reasoning 近似推理a priori estimate 先验估计articulated robot 关节型机器人asymptotic stability 渐进稳定性attained pose drift 实际位姿漂移attitude acquisition 姿态捕获AOCS (attitude and orbit control system) 姿态轨道控制系统attitude angular velocity 姿态角速度attitude disturbance 姿态扰动automatic manual station 自动-手动操作器automaton 自动机base coordinate system 基座坐标系bellows pressure gauge 波纹管压力表 gauge测量仪器black box testing approach 黑箱测试法bottom-up development 自下而上开发boundary value analysis 边界值分析brainstorming method 头脑风暴法CAE (computer aided engineering) 计算机辅助工程CAM (computer aided manufacturing) 计算机辅助制造capacitive displacement transducer 电容式位移传感器capacity电容 displacement 位移capsule pressure gauge 膜盒压力表rectangular coordinate system直角坐标系cascade compensation 串联补偿using series or parallel capacitors用串联或者并联的电容chaos 混沌calrity 清晰性classical information pattern 经典信息模式classifier 分类器clinical control system 临床控制系统closed loop pole 闭环极点 open loop 开环closed loop transfer function 闭环传递函数c ombined pressure and vacuum gauge 压力真空表command pose 指令位姿companion matrix 相伴矩阵compatibility 相容性,兼容性compensating network 补偿网络Energy is conserved in all of its forms能量是守恒的compensation 补偿,矫正conditionally instability 条件不稳定性configuration 组态connectivity 连接性conservative system 守恒系统consistency 一致性constraint condition 约束条件control accuracy 控制精度Gyroscope陀螺仪control panel 控制屏,控制盘control system synthesis 控制系统综合corner frequency 转折频率coupling of orbit and attitude 轨道和姿态耦合critical damping 临界阻尼临界criticalDamper阻尼器critical stability 临界稳定性cross-over frequency 穿越频率,交越频率cut-off frequency 截止频率cybernetics 控制论cyclic remote control 循环遥控 cycle 循环 cycliccylindrical robot 圆柱坐标型机器人damped oscillation 阻尼振荡oscillation 振荡;振动;摆动damper 阻尼器damping ratio 阻尼比 ratio 比data acquisition 数据采集data preprocessing 数据预处理data processor 数据处理器D controller 微分控制器微分控制:Differential control 积分控制:integral control 比例控制:proportional controldescribing function 描述函数desired value 希望值真值:truth values 参考值:reference value destination 目的站detector 检出器deviation 偏差deviation alarm 偏差报警器differential dynamical system 微differential pressure level meter 差压液位计 meter=gauge 仪表 differential 差别的微分的differential pressure transmitter 差压变送器differential transformer displacement transducer 差动变压器式位移传感器differentiation element 微分环节digital filer 数字滤波器 filter 滤波器digital signal processing 数字信号处理dimension transducer 尺度传感器discrete system simulation language 离散系统仿真语言 discrete离散的不连续的displacement vibration amplitude transducer 位移振幅传感器幅度:amplitudedistrubance 扰动disturbance compensation 扰动补偿diversity 多样性divisibility 可分性domain knowledge 领域知识dominant pole 主导极点零点zero调制:modulation ;modulate 解调:demodulationcountermodulationduty ratio负载比dynamic characteristics 动态特性dynamic deviation 动态偏差dynamic error coefficient 动态误差系数dynamic input-output model 动态投入产出模型Index指数eddy current thickness meter 电涡流厚度计 meter 翻译成计 gauge 翻译成表electric conductance level meter 电导液位计electromagnetic flow transducer 电磁流量传感器electronic batching scale 电子配料秤 scale 秤electronic belt conveyor scale 电子皮带秤electronic hopper scale 电子料斗秤elevation 仰角 depression 俯角equilibrium point 平衡点error 误差estimate 估计量estimation theory 估计理论expected characteristics 希望特性failure diagnosis 故障诊断feasibility study 可行性研究feasible 可行的feasible region 可行域feature detection 特征检测feature extraction 特征抽取feedback compensation 反馈补偿Feed forward path 前馈通路前馈:feed forward 反馈feedbackFMS (flexible manufacturing system) 柔性制造系统柔性:flexible 刚性:rigidity bending deflection 弯曲挠度 deflect 偏向偏离flow sensor/transducer 流量传感器flow transmitter 流量变送器forward path 正向通路frequency converter 变频器frequency domain model reduction me thod 频域模型降阶法频域frequency response 频域响应functional decomposition 功能分解FES (functional electrical stimulation) 功能电刺激stimulate 刺激functional simularity 功能相似fuzzy logic模糊逻辑generalized least squares estimation 广义最小二乘估计geometric similarity 几何相似global optimum 全局最优goal coordination method 目标协调法graphic search 图搜索guidance system 制导系统gyro drift rate 陀螺漂移率gyrostat 陀螺体Hall displacement transducer 霍尔式位移传感器horizontal decomposition横向分解hydraulic step motor 液压步进马达I controller 积分控制器 integral 积分identifiability 可辨识性image recognition 图像识别impulse 冲量impulse function 冲击函数,脉冲函数index of merit 品质因数 index 指数inductive force transducer 电感式位移传感器感应的inductive 电感:inductance industrial automation 工业自动化inertial attitude sensor 惯性姿态敏感器inertial coordinate system 惯性坐标系information acquisition 信息采集infrared gas analyzer 红外线气体分析器 infrared 红外线红外线的ultraviolet ray紫外线的 visible light可见光inherent nonlinearity 固有非线性inherent regulation 固有调节initial deviation 初始偏差input-output model 投入产出模型instability 不稳定性integrity 整体性intelligent terminal 智能终端internal disturbance 内扰invariant embedding principle 不变嵌入原理inverse Nyquist diagram 逆奈奎斯特图investment decision 投资决策joint 关节knowledge acquisition 知识获取knowledge assimilation 知识同化knowledge representation 知识表达lag-lead compensation 滞后超前补偿Laplace transform 拉普拉斯变换large scale system 大系统least squares criterion 最小二乘准则 criterion 准则linearization technique 线性化方法linear motion electric drive 直线运动电气传动linear motion valve 直行程阀linear programming 线性规划load cell 称重传感器local optimum 局部最优local 局部log magnitude-phase diagram 对数幅相图magnitude大小的程度amplitude振幅long term memory 长期记忆Lyapunov theorem of asymptotic stability 李雅普诺夫渐近稳定性定理magnetoelastic weighing cell 磁致弹性称重传感器magnitude-frequency characteristic 幅频特性magnitude margin 幅值裕度 margin 边缘magnitude scale factor 幅值比例尺manipulator 机械手man-machine coordination 人机协调MAP (manufacturing automation protocol) 制造自动化协议 protocol 协议marginal effectiveness 边际效益Mason‘‘s gain formula 梅森增益公式matching criterion 匹配准则maximum likelihood estimation 最大似然估计maximum overshoot 最大超调量maximum principle 极大值原理mean-square error criterion 均方误差准则minimal realization 最小实现minimum phase system 最小相位系统minimum variance estimation 最小方差估计model reference adaptive control system 模型参考适应控制系统model verification 模型验证modularization 模块化MTBF (mean time between failures) 平均故障间隔时间 mean 平均MTTF (mean time to failures) 平均无故障时间multiloop control 多回路控制multi-objective decision 多目标决策Nash optimality 纳什最优性nearest-neighbor 最近邻necessity measure 必然性侧度negative feedback 负反馈neural assembly 神经集合neural network computer 神经网络计算机Nichols chart 尼科尔斯图Nyquist stability criterion 奈奎斯特稳定判据objective function 目标函数on-line assistance 在线帮助on-off control 通断控制optic fiber tachometer 光纤式转速表optimal trajectory 最优轨迹optimization technique 最优化技术order parameter 序参数orientation control 定向控制oscillating period 振荡周期周期:period cycleoutput prediction method 输出预估法oval wheel flowmeter 椭圆齿轮流量计Over damping 过阻尼underdamping 欠阻尼PR (pattern recognition) 模式识别P control 比例控制器peak time 峰值时间penalty function method 罚函数法perceptron 感知器phase lead 相位超前 phase lag相位滞后Photoelectri c光电 tachometric transducer 光电式转速传感器piezoelectric force transducer 压电式力传感器PLC (programmable logic controller) 可编程序逻辑控制器plug braking 反接制动pole assignment 极点配置pole-zero cancellation 零极点相消polynomial input 多项式输入portfolio theory 投资搭配理论pose overshoot 位姿过调量position measuring instrument 位置测量仪posentiometric displacement transducer 电位器式位移传感器positive feedback 正反馈power system automation 电力系统自动化pressure transmitter 压力变送器primary frequency zone 主频区priority 优先级process-oriented simulation 面向过程的仿真proportional control 比例控制proportional plus derivative controller 比例微分控制器pulse duration 脉冲持续时间pulse frequency modulation control system 脉冲调频控制系统:frequency modulation 频率调制调频pulse width modulation control system 脉冲调宽控制系统PWM inverter 脉宽调制逆变器QC (quality control) 质量管理quantized noise 量化噪声ramp function 斜坡函数random disturbance 随机扰动random process 随机过程rate integrating gyro 速率积分陀螺real time telemetry 实时遥测receptive field 感受野rectangular robot 直角坐标型机器人redundant information 冗余信息regional planning model 区域规划模型regulating device 调节装载regulation 调节relational algebra 关系代数remote regulating 遥调reproducibility 再现性resistance thermometer sensor 热电阻电阻温度计传感器response curve 响应曲线return difference matrix 回差矩阵return ratio matrix 回比矩阵revolute robot 关节型机器人revolution speed transducer 转速传感器rewriting rule 重写规则rigid spacecraft dynamics 刚性航天动力学 dynamics 动力学robotics 机器人学robot programming language 机器人编程语言robust control 鲁棒控制robustness 鲁棒性root locus 根轨迹roots flowmeter 腰轮流量计rotameter 浮子流量计,转子流量计sampled-data control system 采样控制系统sampling control system 采样控制系统saturation characteristics 饱和特性scalar Lyapunov function 标量李雅普诺夫函数s-domain s域self-operated controller 自力式控制器self-organizing system 自组织系统self-reproducing system 自繁殖系统self-tuning control 自校正控制sensing element 敏感元件sensitivity analysis 灵敏度分析sensory control 感觉控制sequential decomposition 顺序分解sequential least squares estimation 序贯最小二乘估计servo control 伺服控制,随动控制servomotor 伺服马达settling time 过渡时间sextant 六分仪short term planning 短期计划short time horizon coordination 短时程协调signal detection and estimation 信号检测和估计signal reconstruction 信号重构similarity 相似性simulated interrupt 仿真中断simulation block diagram 仿真框图simulation experiment 仿真实验simulation velocity 仿真速度simulator 仿真器single axle table 单轴转台single degree of freedom gyro 单自由度陀螺翻译顺序呵呵spin axis 自旋轴spinner 自旋体stability criterion 稳定性判据stability limit 稳定极限stabilization 镇定,稳定state equation model 状态方程模型state space description 状态空间描述static characteristics curve 静态特性曲线station accuracy 定点精度stationary random process 平稳随机过程statistical analysis 统计分析statistic pattern recognition 统计模式识别steady state deviation 稳态偏差顺序翻译即可steady state error coefficient 稳态误差系数step-by-step control 步进控制step function 阶跃函数strain gauge load cell 应变式称重传感器subjective probability 主观频率supervisory computer control system 计算机监控系统sustained oscillation 自持振荡swirlmeter 旋进流量计switching point 切换点systematology 系统学system homomorphism 系统同态system isomorphism 系统同构system engineering 系统工程tachometer 转速表target flow transmitter 靶式流量变送器task cycle 作业周期temperature transducer 温度传感器tensiometer 张力计texture 纹理theorem proving 定理证明therapy model 治疗模型thermocouple 热电偶thermometer 温度计thickness meter 厚度计three-axis attitude stabilization 三轴姿态稳定three state controller 三位控制器thrust vector control system 推力矢量控制系统thruster 推力器time constant 时间常数time-invariant system 定常系统,非时变系统 invariant不变的time schedule controller 时序控制器time-sharing control 分时控制time-varying parameter 时变参数top-down testing 自上而下测试TQC (total quality control) 全面质量管理tracking error 跟踪误差trade-off analysis 权衡分析transfer function matrix 传递函数矩阵transformation grammar 转换文法transient deviation 瞬态偏差短暂的瞬间的transient process 过渡过程transition diagram 转移图transmissible pressure gauge 电远传压力表transmitter 变送器trend analysis 趋势分析triple modulation telemetering system 三重调制遥测系统turbine flowmeter 涡轮流量计Turing machine 图灵机two-time scale system 双时标系统ultrasonic levelmeter 超声物位计unadjustable speed electric drive 非调速电气传动unbiased estimation 无偏估计underdamping 欠阻尼uniformly asymptotic stability 一致渐近稳定性uninterrupted duty 不间断工作制,长期工作制unit circle 单位圆unit testing 单元测试unsupervised learing 非监督学习upper level problem 上级问题urban planning 城市规划value engineering 价值工程variable gain 可变增益,可变放大系数variable structure control system 变结构控制vector Lyapunov function 向量李雅普诺夫函数function 函数velocity error coefficient 速度误差系数velocity transducer 速度传感器vertical decomposition 纵向分解vibrating wire force transducer 振弦式力传感器vibrometer 振动计 vibrationVibrate振动viscous damping 粘性阻尼voltage source inverter 电压源型逆变器vortex precession flowmeter 旋进流量计vortex shedding flowmeter 涡街流量计WB (way base) 方法库weighing cell 称重传感器weighting factor 权因子weighting method 加权法Whittaker-Shannon sampling theorem 惠特克-香农采样定理Wiener filtering 维纳滤波w-plane w平面zero-based budget 零基预算zero-input response 零输入响应zero-state response 零状态响应z-transform z变换《信号与系统》专业术语中英文对照表第 1 章绪论信号(signal)系统(system)电压(voltage)电流(current)信息(information)电路(circuit)确定性信号(determinate signal)随机信号(random signal)一维信号(one–dimensional signal)多维信号(multi–dimensional signal)连续时间信号(continuous time signal)离散时间信号(discrete time signal)取样信号(sampling signal)数字信号(digital signal)周期信号(periodic signal)非周期信号(nonperiodic(aperiodic) signal)能量(energy)功率(power)能量信号(energy signal)功率信号(power signal)平均功率(average power)平均能量(average energy)指数信号(exponential signal)时间常数(time constant)正弦信号(sine signal)余弦信号(cosine signal)振幅(amplitude)角频率(angular frequency)初相位(initial phase)频率(frequency)欧拉公式(Euler’s formula)复指数信号(complex exponential signal)复频率(complex frequency)实部(real part)虚部(imaginary part)抽样函数 Sa(t)(sampling(Sa) function)偶函数(even function)奇异函数(singularity function)奇异信号(singularity signal)单位斜变信号(unit ramp signal)斜率(slope)单位阶跃信号(unit step signal)符号函数(signum function)单位冲激信号(unit impulse signal)广义函数(generalized function)取样特性(sampling property)冲激偶信号(impulse doublet signal)奇函数(odd function)偶分量(even component)偶数 even 奇数 odd 奇分量(odd component)正交函数(orthogonal function)正交函数集(set of orthogonal function)数学模型(mathematics model)电压源(voltage source)基尔霍夫电压定律(Kirchhoff’s voltage law(KVL))电流源(current source)连续时间系统(continuous time system)离散时间系统(discrete time system)微分方程(differential function)差分方程(difference function)线性系统(linear system)非线性系统(nonlinear system)时变系统(time–varying system)时不变系统(time–invariant system)集总参数系统(lumped–parameter system)分布参数系统(distributed–parameter system)偏微分方程(partial differential function)因果系统(causal system)非因果系统(noncausal system)因果信号(causal signal)叠加性(superposition property)均匀性(homogeneity)积分(integral)输入–输出描述法(input–output analysis)状态变量描述法(state variable analysis)单输入单输出系统(single–input and single–output system)状态方程(state equation)输出方程(output equation)多输入多输出系统(multi–input and multi–output system)时域分析法(time domain method)变换域分析法(transform domain method)卷积(convolution)傅里叶变换(Fourier transform)拉普拉斯变换(Laplace transform)第 2 章连续时间系统的时域分析齐次解(homogeneous solution)特解(particular solution)特征方程(characteristic function)特征根(characteristic root)固有(自由)解(natural solution)强迫解(forced solution)起始条件(original condition)初始条件(initial condition)自由响应(natural response)强迫响应(forced response)零输入响应(zero-input response)零状态响应(zero-state response)冲激响应(impulse response)阶跃响应(step response)卷积积分(convolution integral)交换律(exchange law)分配律(distribute law)结合律(combine law)第3 章傅里叶变换频谱(frequency spectrum)频域(frequency domain)三角形式的傅里叶级数(trigonomitric Fourier series)指数形式的傅里叶级数(exponential Fourier series)傅里叶系数(Fourier coefficient)直流分量(direct component)基波分量(fundamental component) component 分量n 次谐波分量(n th harmonic component)复振幅(complex amplitude)频谱图(spectrum plot(diagram))幅度谱(amplitude spectrum)相位谱(phase spectrum)包络(envelop)离散性(discrete property)谐波性(harmonic property)收敛性(convergence property)奇谐函数(odd harmonic function)吉伯斯现象(Gibbs phenomenon)周期矩形脉冲信号(periodic rectangular pulse signal)直角的周期锯齿脉冲信号(periodic sawtooth pulse signal)周期三角脉冲信号(periodic triangular pulse signal)三角的周期半波余弦信号(periodic half–cosine signal)周期全波余弦信号(periodic full–cosine signal)傅里叶逆变换(inverse Fourier transform)inverse 相反的频谱密度函数(spectrum density function)单边指数信号(single–sided exponential signal)双边指数信号(two–sided exponential signal)对称矩形脉冲信号(symmetry rectangular pulse signal)线性(linearity)对称性(symmetry)对偶性(duality)位移特性(shifting)时移特性(time–shifting)频移特性(frequency–shifting)调制定理(modulation theorem)调制(modulation)解调(demodulation)变频(frequency conversion)尺度变换特性(scaling)微分与积分特性(differentiation and integration)时域微分特性(differentiation in the time domain)时域积分特性(integration in the time domain)频域微分特性(differentiation in the frequency domain)频域积分特性(integration in the frequency domain)卷积定理(convolution theorem)时域卷积定理(convolution theorem in the time domain)频域卷积定理(convolution theorem in the frequency domain)取样信号(sampling signal)矩形脉冲取样(rectangular pulse sampling)自然取样(nature sampling)冲激取样(impulse sampling)理想取样(ideal sampling)取样定理(sampling theorem)调制信号(modulation signal)载波信号(carrier signal)已调制信号(modulated signal)模拟调制(analog modulation)数字调制(digital modulation)连续波调制(continuous wave modulation)脉冲调制(pulse modulation)幅度调制(amplitude modulation)频率调制(frequency modulation)相位调制(phase modulation)角度调制(angle modulation)频分多路复用(frequency–division multiplex(FDM))时分多路复用(time–division multiplex(TDM))相干(同步)解调(synchronous detection)本地载波(local carrier)载波系统函数(system function)网络函数(network function)频响特性(frequency response)幅频特性(amplitude frequency response)幅频响应相频特性(phase frequency response)无失真传输(distortionless transmission)理想低通滤波器(ideal low–pass filter)截止频率(cutoff frequency)正弦积分(sine integral)上升时间(rise time)窗函数(window function)理想带通滤波器(ideal band–pass filter)太直译了第 4 章拉普拉斯变换代数方程(algebraic equation)双边拉普拉斯变换(two-sided Laplace transform)双边拉普拉斯逆变换(inverse two-sided Laplace transform)单边拉普拉斯变换(single-sided Laplace transform)拉普拉斯逆变换(inverse Laplace transform)收敛域(region of convergence(ROC))延时特性(time delay)s 域平移特性(shifting in the s-domain)s 域微分特性(differentiation in the s-domain)s 域积分特性(integration in the s-domain)初值定理(initial-value theorem)终值定理(expiration-value)复频域卷积定理(convolution theorem in the complex frequency domain)部分分式展开法(partial fraction expansion)留数法(residue method)第 5 章策动点函数(driving function)转移函数(transfer function)极点(pole)零点(zero)零极点图(zero-pole plot)暂态响应(transient response)稳态响应(stable response)稳定系统(stable system)一阶系统(first order system)高通滤波网络(high-pass filter)低通滤波网络(low-pass filter)二阶系统(second order system)最小相位系统(minimum-phase system)高通(high-pass)带通(band-pass)带阻(band-stop)有源(active)无源(passive)模拟(analog)数字(digital)通带(pass-band)阻带(stop-band)佩利-维纳准则(Paley-Winner criterion)最佳逼近(optimum approximation)过渡带(transition-band)通带公差带(tolerance band)巴特沃兹滤波器(Butterworth filter)切比雪夫滤波器(Chebyshew filter)方框图(block diagram)信号流图(signal flow graph)节点(node)支路(branch)输入节点(source node)输出节点(sink node)混合节点(mix node)通路(path)开通路(open path)闭通路(close path)环路(loop)自环路(self-loop)环路增益(loop gain)不接触环路(disconnect loop)前向通路(forward path)前向通路增益(forward path gain)梅森公式(Mason formula)劳斯准则(Routh criterion)第 6 章数字系统(digital system)数字信号处理(digital signal processing)差分方程(difference equation)单位样值响应(unit sample response)卷积和(convolution sum)Z 变换(Z transform)序列(sequence)样值(sample)单位样值信号(unit sample signal)单位阶跃序列(unit step sequence)矩形序列 (rectangular sequence)单边实指数序列(single sided real exponential sequence)单边正弦序列(single sided exponential sequence)斜边序列(ramp sequence)复指数序列(complex exponential sequence)线性时不变离散系统(linear time-invariant discrete-time system)常系数线性差分方程(linear constant-coefficient difference equation)后向差分方程(backward difference equation)前向差分方程(forward difference equation)海诺塔(Tower of Hanoi)菲波纳西(Fibonacci)冲激函数串(impulse train)第 7 章数字滤波器(digital filter)单边 Z 变换(single-sided Z transform)双边 Z 变换(two-sided (bilateral) Z transform)幂级数(power series)收敛(convergence)有界序列(limitary-amplitude sequence)正项级数(positive series)有限长序列(limitary-duration sequence)右边序列(right-sided sequence)左边序列(left-sided sequence)双边序列(two-sided sequence)Z 逆变换(inverse Z transform)围线积分法(contour integral method)幂级数展开法(power series expansion)z 域微分(differentiation in the z-domain)序列指数加权(multiplication by an exponential sequence)z 域卷积定理(z-domain convolution theorem)帕斯瓦尔定理(Parseval theorem)传输函数(transfer function)序列的傅里叶变换(discrete-time Fourier transform:DTFT)序列的傅里叶逆变换(inverse discrete-time Fourier transform:IDTFT)幅度响应(magnitude response)相位响应(phase response)量化(quantization)编码(coding)模数变换(A/D 变换:analog-to-digital conversion)数模变换(D/A 变换:digital-to- analog conversion)第 8 章端口分析法(port analysis)状态变量(state variable)无记忆系统(memoryless system)有记忆系统(memory system)矢量矩阵(vector-matrix )常量矩阵(constant matrix )输入矢量(input vector)输出矢量(output vector)直接法(direct method)间接法(indirect method)状态转移矩阵(state transition matrix)系统函数矩阵(system function matrix)冲激响应矩阵(impulse response matrix)光学专业词汇大全Accelaration 加速度Myopia-near-sighted近视Sensitivity to Light感光灵敏度boost推进lag behind落后于Hyperopic-far-sighted远视visual sensation视觉ar Pattern条状图形approximate近似adjacent邻近的normal法线Color Difference色差V Signal Processing电视信号处理back and forth前后vibrant震动quantum leap量子越迁derive from起源自inhibit抑制,约束stride大幅前进obstruction障碍物substance物质实质主旨residue杂质criteria标准parameter参数parallax视差凸面镜 convex mirror凹面镜 concave mirror分光镜spectroscope入射角 angle of incidence出射角emergent angle平面镜 plane mirror放大率角度放大率angular magnification 放大率:magnification 折射 refraction反射 reflect干涉 interfere衍射 diffraction干涉条纹interference fringe衍射图像 diffraction fringe衍射条纹偏振polarize polarization透射transmission透射光 transmission light光强度] light intensity电磁波 electromagnetic wave振动杨氏干涉夫琅和费衍射焦距brewster Angle布鲁斯特角quarter Waveplates四分之一波片ripple波纹capacitor电容器vertical垂直的horizontal 水平的airy disk艾里斑exit pupil出[射光]瞳Entrance pupil 入瞳optical path difference光称差radius of curvature曲率半径spherical mirror球面镜reflected beam反射束YI= or your information供参考phase difference相差interferometer干涉仪ye lens物镜/目镜spherical球的field information场信息standard Lens标准透镜refracting Surface折射面principal plane主平面vertex顶点,最高点fuzzy失真,模糊light source 光源wavelength波长angle角度spectrum光谱diffraction grating衍射光栅sphere半球的DE= ens data editor Surface radius of curvature表面曲率半径surface thickness表面厚度semi-diameter半径focal length焦距field of view视场stop 光阑refractive折射reflective反射金属切削 metal cutting机床 machine tool tool 机床金属工艺学 technology of metals刀具 cutter摩擦 friction传动 drive/transmission轴 shaft弹性 elasticity频率特性 frequency characteristic误差 error响应 response定位 allocation动力学 dynamic运动学 kinematic静力学 static分析力学 analyse mechanics 力学拉伸 pulling压缩 hitting compress剪切 shear扭转 twist弯曲应力 bending stress强度 intensity几何形状 geometricalUltrasonic超声波精度 precision交流电路 AC circuit机械加工余量 machining allowance变形力 deforming force变形 deformation应力 stress硬度 rigidity热处理 heat treatment电路 circuit半导体元件 semiconductor element反馈 feedback发生器 generator直流电源 DC electrical source门电路 gate circuit逻辑代数 logic algebra磨削 grinding螺钉 screw铣削 mill铣刀 milling cutter功率 power装配 assembling流体动力学 fluid dynamics流体力学 fluid mechanics加工 machining稳定性 stability介质 medium强度 intensity载荷 load应力 stress可靠性 reliability精加工 finish machining粗加工 rough machining腐蚀 rust氧化 oxidation磨损 wear耐用度 durability随机信号 random signal离散信号 discrete signal超声传感器 ultrasonic sensor摄像头 CCD cameraLead rail 导轨合成纤维 synthetic fibre电化学腐蚀 electrochemical corrosion 车架 automotive chassis悬架 suspension转向器 redirector变速器 speed changer车间 workshop工程技术人员 engineer数学模型 mathematical model标准件 standard component零件图 part drawing装配图 assembly drawing刚度 rigidity内力 internal force位移 displacement截面 section疲劳极限 fatigue limit断裂 fracture 破裂塑性变形 plastic distortionelastic deformation 弹性变形脆性材料 brittleness material刚度准则 rigidity criterion齿轮 gearGrain 磨粒转折频率 corner frequency =break frequencyConvolution 卷积Convolution integral 卷积积分Convolution property 卷积性质Convolution sum 卷积和Correlation function 相关函数Critically damped systems 临界阻尼系统Crosss-correlation functions 互相关函数Cutoff frequencies 截至频率transistor n 晶体管diode n 二极管semiconductor n 半导体resistor n 电阻器capacitor n 电容器alternating adj 交互的amplifier n 扩音器,放大器integrated circuit 集成电路linear time invariant systems 线性时不变系统voltage n 电压,伏特数Condenser=capacitor n 电容器dielectric n 绝缘体;电解质electromagnetic adj 电磁的adj 非传导性的deflection n偏斜;偏转;偏差linear device 线性器件the insulation resistance 绝缘电阻anode n 阳极,正极cathode n 阴极breakdown n 故障;崩溃terminal n 终点站;终端,接线端emitter n 发射器collect v 收集,集聚,集中insulator n 绝缘体,绝热器oscilloscope n 示波镜;示波器gain n 增益,放大倍数forward biased 正向偏置reverse biased 反向偏置P-N junction PN结MOS(metal-oxide semiconductor)金属氧化物半导体enhancement and exhausted 增强型和耗尽型integrated circuits 集成电路analog n 模拟digital adj 数字的,数位的horizontal adj, 水平的,地平线的vertical adj 垂直的,顶点的amplitude n 振幅,广阔,丰富multimeter n 万用表frequency n 频率,周率the cathode-ray tube 阴极射线管dual-trace oscilloscope 双踪示波器signal generating device 信号发生器peak-to-peak output voltage 输出电压峰峰值sine wave 正弦波triangle wave 三角波square wave 方波amplifier 放大器,扩音器oscillator n 振荡器feedback n 反馈,回应phase n 相,阶段,状态filter n 滤波器,过滤器rectifier n整流器;纠正者band-stop filter 带阻滤波器band-pass filter 带通滤波器decimal adj 十进制的,小数的hexadecimal adj/n十六进制的binary adj 二进制的;二元的octal adj 八进制的domain n 域;领域code n代码,密码,编码v编码the Fourier transform 傅里叶变换Fast Fourier Transform 快速傅里叶变换microcontroller n 微处理器;微控制器assembly language instrucions n 汇编语言指令chip n 芯片,碎片modular adj 模块化的;模数的sensor n 传感器plug vt堵,塞,插上n塞子,插头,插销coaxial adj 同轴的,共轴的fiber n 光纤relay contact 继电接触器Artificial Intelligence 人工智能Perceptive Systems 感知系统neural network 神经网络fuzzy logic 模糊逻辑intelligent agent 智能代理electromagnetic adj 电磁的coaxial adj 同轴的,共轴的microwave n 微波charge v充电,使充电insulator n 绝缘体,绝缘物nonconductive adj非导体的,绝缘的simulation n 仿真;模拟prototype n 原型array n 排队,编队vector n 向量,矢量inverse adj倒转的,反转的n反面;相反v倒转high-performance 高精确性,高性能two-dimensional 二维的;缺乏深度的three-dimensional 三维的;立体的;真实的object-oriented programming面向对象的程序设计spectral adj 光谱的distortion n 失真,扭曲,变形wavelength n 波长refractive adj 折射的ivision Multiplexing单工传输simplex transmission半双工传输half-duplex transmission全双工传输full-duplex transmission电路交换 circuit switching数字传输技术Digital transmission technology灰度图像Grey scale images灰度级Grey scale level幅度谱Magnitude spectrum相位谱Phase spectrum频谱frequency spectrum相干解调coherent demodulation coherent相干的数字图像压缩digital image compression图像编码image encoding量化quantization人机交互man machine interface交互式会话Conversational interaction路由算法Routing Algorithm目标识别Object recognition话音变换Voice transform中继线trunk line传输时延transmission delay远程监控remote monitoring光链路optical linkhalf-duplex transmission 半双工传输accompaniment 伴随物,附属物reservation 保留,预定quotation 报价单,行情报告,引语memorandum 备忘录redundancy 备用be viewed as 被看作…be regards as 被认为是as such 本身;照此;以这种资格textual 本文的,正文的variation 变化,变量conversion 变化,转化。
开关电源的相关术语知识

开关电源的相关术语知识开关电源是一种将交流电转换为稳定直流电的电子设备,被广泛应用于各个领域,包括电子设备、通信设备、工业控制等。
了解开关电源的相关术语知识对于理解其工作原理和性能具有重要意义。
下面将介绍一些常用的开关电源术语。
1. 输入电压范围(Input Voltage Range):指开关电源能够正常工作的输入电压范围。
一般来说,开关电源的输入电压范围比较宽,可以适应不同的电源电压。
2. 输出电压(Output Voltage):指开关电源转换后的输出直流电电压。
开关电源的输出电压通常可以通过电压调节器进行调节,以满足不同设备的需求。
3. 输出电流(Output Current):指开关电源输出的电流大小。
输出电流的大小取决于设备的功率需求,一般以安培(A)为单位。
4. 输出功率(Output Power):指开关电源输出的电功率大小。
输出功率等于输出电压乘以输出电流,以瓦特(W)为单位。
5. 效率(Efficiency):指开关电源将输入电能转换为输出电能的效率。
开关电源的效率越高,能量转换的损耗就越小,通常以百分比表示。
6. 电流纹波(Ripple Current):指开关电源输出直流电的纹波大小。
电流纹波的大小影响到设备的稳定性,一般以安培(A)为单位。
7. 电压稳定性(Voltage Stability):指开关电源输出电压的稳定性能。
电压稳定性好的开关电源可以确保设备稳定运行,避免因电压波动而引起的故障。
8. 过载保护(Overload Protection):指开关电源在输出电流超过额定值时自动切断输出电路的保护功能。
过载保护可以避免因电流过大而损坏设备。
9. 过压保护(Overvoltage Protection):指开关电源在输出电压超过额定值时自动切断输出电路的保护功能。
过压保护可以避免因电压过高而损坏设备。
10. 短路保护(Short Circuit Protection):指开关电源在输出电路短路时自动切断电路的保护功能。
MSC302E-C0C0配电隔离器说明书
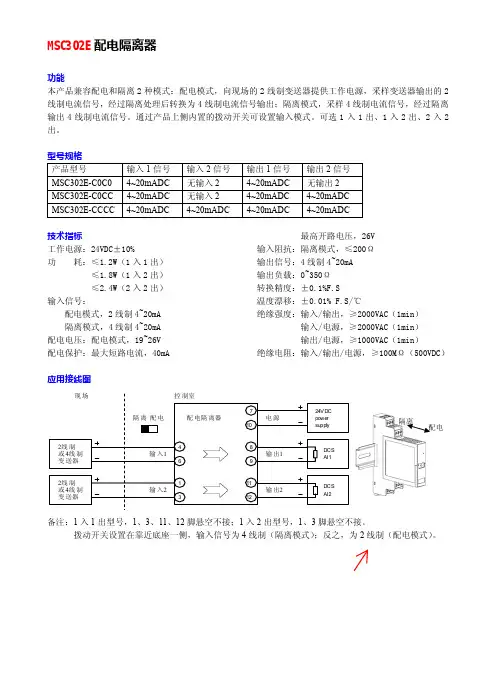
输入参数(Input): AC0~250V
辅助电源: DC12V±10% Power Supply: DC12V±10%
输出参数(Output): DC4~20mA
注:订货时,请用户根据实际需要按上表仔细核对类型、
输入范围、输出范围和辅助电源。 Please check the Type, Input range, Output range and Power supply at your order.
输出 DC Output
O1: 0~5V, O2: 1~5V, O3: 0~20mA, O4: 4~20mA, O5: RS485.
范例1 (Example 1): YDD-I-A2-P2-O4
说明:
YDD系列单交流电流变送器
Details: YDD Series Single Phase AC Current Transducer
型号规格 产品型号 MSC302E-C0C0 MSC302E-C0CC MSC302E-CCCC
输入 1 信号 4~20mADC 4~20mADC 4~20mADC
输入 2 信号 无输入 2 无输入 2
4~20mADC
输出 1 信号 4~20mADC 4~20mADC 4~20mADC
输出 2 信号 无输出 2 4~20mADC 4~20mADC
输入参数(Input): AC0~300V
辅助电源: AC220V±15% Power Supply: AC220V±15%
输出参数(Output): DC4~20mA
注:订货时,请用户根据实际需要按上表仔细核对类型、输入范
围、输出范围和辅助电源。 Please check the Type, Input range, Output range and Power supply at your order.
非线性系统第四讲输入输出稳定性

y (t )
u
T
(t )u (t )dt
Finite gain L2 stability
Topic 4 Input-Output stability
4.3 L2 gain
According to Parseval’s Relation
Fourier transform of the output signal:
x R , u R , f (0) 0, h(0) 0.
n m
Topic 4 Input-Output stability
Remark: in order to obtain V(x), we need solve the following Hamilton-Jacobi inequality
Topic 4 Input-Output stability
LaSalle's invariance principle
Asymptotically stable
Topic 4 Input-Output stability
Example: f(x)
The condition is not hold globally, we need other lemmas to show the small signal finite gain stability!
is small-signal finite-gain L2 stable.
Topic 4 Input-Output stability
Proof: “x = 0 is an asymptotically stable equilibrium”
Topic 4 Input-Output stability
输入-状态稳定性 input-to-state stability 非线性控制 英文材料

i.e
(6) (7) (8) (9)
Theorem 2 : (Global ISS Theorem) If the preceeding conditions are satisfied with D = Rn and Du = Rm, and if α1 , α2 , α3 ∈ K∞, then the system (1) is globally input-to-state stable.
x ≤d L∞ ). L∞
< ru will
Once inside this region, it is trapped inside Ωd, because of the condition on ˙. V
L∞ )},
∀t ≥ 0, 0 ≤ T ≤ t.
(3)
Definition 2 : A continuously differentiable function V : D → R is said to be an ISS Local Lyapunov function on D for the system (1) if there exist class K functions α1 , α2 , α3 , and X such that: ∀x ∈ D, t > 0 (4) α1( x ) ≤ V (x(t)) ≤ α2 ( x ) ∂V (x) f (x, u) ≤ −α3( x ) u ∈ Du : x ≥ X ( u ). (5) ∂x V is said to be an ISS Global Lyapunov function if D = Rn , Du = Rm, and α1 , α2, α3 ∈ K∞. Remarks: this means that V is an ISS Lyapunov function if (a) It is positive definite in D. (b) It is negative definite along the trajectories of (1) whenever the trajectories are outside of the ball defined by x∗ = X ( u ).
自动控制原理英文词汇索引
Signal input single output SISO 单输入单输出Dynamic system 动态系统Multivariable control 多变量控制Multi input and multi output 多输入多输出Root locus method 根轨迹方法Time domain 时域Disturbance 干扰Frequency domain 频域Stochastic system 随机系统Phase 相位Uncertainty 不确定性Distributed parameter system 分布参数系统Discrete system 离散系统Robust control 鲁棒控制System identification 系统辨识Adaptive control 自适应控制Simulation 仿真Nonlinear 非线性Symbolic computation 符号计算Toolbox 工具箱Numerical computation 数值计算Diagonal canonical form 对角线规范形Jordan canonical form 约当规范形Controlled system 受控系统、被控系统Ordinary differential equation 常微分方程Derivative 导数Time-invariant system 定常系统、时不变系统Matrix 矩阵Continuous-time system 连续系统、连续时间系统Time-varying system 时变系统、非定常系统Output equation 输出方程Mathematic model 数学模型Linear system 线性系统Vector 向量State 状态State equation 状态方程State trace 状态轨迹State space model 状态空间模型Transfer function 传递函数Inverted pendulum 倒立摆Diagonal matrix 对角线矩阵Fourier transformation 傅里叶变换Inertial element 惯性环节Block diagonal matrix 块对角矩阵Linearization 线性化Phase variable 相变量Strictly proper rational function 严格真有理函数Companior matrix 友矩阵Jordan matrix 约当矩阵Adjoint matrix 伴随矩阵Non-singurler matrix 非奇异矩阵、可逆矩阵Generality eigenvector 广义特征向量Canonical form 规范形、标准形、典范形Geometric multiple number 几何重数Algebraic multiple number 代数重数Characteristic polynomial 特征多项式Characteristic equation 特征方程Eigenvecto 特征向量rLinear transformation 线性变换Rank 秩Parallel connection 并行联接Transfer function matrix 传递函数矩阵Series connection 串联联接Feedback connection 反馈联接Laplace transformation 拉普拉斯变换Rational matrix function 有理矩阵函数Composition system 组合系统Analog to Digital converter A/D 转换、数模转换Digital to Analog converter D/A 转换、数模转换z transformation z变换sampled system 采样系统difference equation 差分方程discrete-time system 离散系统、离散时间系统delay 延迟initial time 初始时间initial state 初始状态polynomial 多项式non-homogenerous state equation 非齐次状态方程step signal 阶跃信号matrix exponent function 矩阵指数函数convolution 卷积zero-input response 零输入响应zero-state response 零状态响应impulse response 脉冲响应impulse signal 脉冲信号homogenerous 齐次性homogenerous state equation 齐次状态方程output response 输出响应state transistion matrix 状态转移矩阵Cayley-Hamilton Theorem 凯莱-哈密顿定理Momic polynomial 首一多项式Minimal polynomial 最小多项式Recursive algorithm 递推算法Gram matrix 格拉姆矩阵Functional linear independence 函数线性无关Functional linear denpendence 函数线性相关Modality criterion 模态判据Controllability 能控性、可控性Controllability Matrix 能控性矩阵Output controllability 输出能控性Rank criterion 秩判据State controllability 状态能控性Observability 能观测性、可观测性Observability matrix 能观性矩阵Observability criterion 能观性判据Reachability 能达性、可达性Duality 对偶性Structural decomposition 结构分解Zero 零点Zero-pole cancel 零极点相消Subspace 子空间Subsystem 子系统Luenberger controllability canonical form 龙伯格能控规范形Observability canonical form 能观规范形controllability canonical form 能控规范形controllability index 能控性指数Wonham controllability canonical form 旺纳姆能控规范形System realization 系统实现Minimal realization 最小实现Definite sign 定号性Norm 范数Non-positive definite matrix 非正定矩阵Euclidean norm 2-norm 欧几里德范数、2范数Equilibrium state 平衡点Input-output stability 输入输出稳定性Stability 稳定性Consistent stability 一致稳定Bounded-input bounded-output stability BIBO stability 有界输入有界输出稳定性State stability 状态稳定性Algebraic equation 代数方程Symmetry matrix 对称矩阵Quadratic function 二次型函数Non-negative definite matrix 非负定矩阵Negative definite matrix 负定矩阵Asymptotic stability 渐进稳定Sylvester Theorem 赛尔维斯特定理Stability criterion 稳定判据Jacobi matrix 雅可比矩阵Positive-definite matrix 正定矩阵Output feedback 输出反馈State feedback 状态反馈Pole assignment 极点配置System synthesis 系统综合Stable control 镇定控制Compensator decouple 补偿器解耦Decouple 解耦Observer 观测器Reduction-dimension observer 降维观测器Full-dimension observer 全维观测器State estimation 状态观测器State observating error 状态观测器误差State observatory 状态观测器。
离散时间信号处理(英文版)chap9-第1讲
01
02
03
Discrete-time systems are mathematical models that describe the behavior of systems in which the input and output signals are functions of discrete time variables.
Periodic signals repeat at regular intervals, while aperiodic signals have no repeating pattern.
Classification of discrete-time signals
延时符
03
Operation of discrete-time signals
延时符
Contents
目录
Basic concepts of discrete-time systems Stability analysis of discrete-time systems
延时符
01signal processing is a branch of signal processing that deals with signals that vary over discrete time instants rather than continuously. It finds applications in various fields such as digital communication, audio processing, image processing, and more.
Background Introduction
信号与系统郑君里复习要点
信号与系统郑君里复习要点一、引言信号与系统是电子信息科学与技术专业的核心学科之一,是掌握该领域知识的重要基础。
本文将对信号与系统中郑君里复习要点进行整理与总结,帮助广大学生更好地掌握这一学科。
二、信号的类型1. 连续时间信号(Continuous-time Signal):在连续时间上定义的信号,可用数学函数表示。
2. 离散时间信号(Discrete-time Signal):在离散时间上定义的信号,可用数列表示。
3. 连续幅度信号(Analog Signal):在幅度上连续变化的信号,可用模拟电路处理和传输。
4. 离散幅度信号(Digital Signal):在幅度上离散变化的信号,可用数字电路处理和传输。
三、系统的性质1. 因果性(Causality):系统的输出只依赖于当前和过去的输入。
2. 稳定性(Stability):当输入有界时,系统的输出也有界;当输入趋于无穷时,输出也趋于有界。
3. 线性性(Linearity):系统满足叠加原则,即输入的线性组合对应于输出的线性组合。
4. 时不变性(Time Invariance):系统的输入延时,输出也相应延时。
5. 可逆性(Invertibility):系统存在逆系统,即能恢复原输入信号。
四、连续时间信号与系统1. 连续时间傅里叶变换(Continuous-time Fourier Transform):用于将信号从时域转换到频域,获取信号的频率成分。
2. 系统的传输函数(Transfer Function):描述了输入信号和输出信号之间的关系,通过传输函数可计算系统的频率响应。
3. 连续时间卷积(Convolution):两个信号经过卷积运算得到新的信号。
卷积运算用于描述系统的输入和输出之间的关系。
五、离散时间信号与系统1. 离散时间傅里叶变换(Discrete-time Fourier Transform):类似于连续时间傅里叶变换,用于将离散时间信号从时域转换到频域。
Cuk变换器输入输出线性化直接电流控制
Cuk变换器输入输出线性化直接电流控制帅定新【摘要】Two nonlinear control methods are proposed to control Cuk converter:Lyapunov’s direct method and the in⁃put/output linearization method. On the basis of Lyapunov’s direct method,a direct current control method is pro⁃posed,which can control the output voltage directly through the regulation of inductor current and realize the lineariza⁃tion of part of the original system,i.e.,input/output linearization. Moreover,it is pointed out that the control structure of the input/output linearization control system is simpler than that of the Lyapunov’s direct method,and its control cost is also lower. The validity of the control scheme is verifiedby numerical simulation and experiments. The controlled sys⁃tem has excellent steady-state and dynamic characteristics.%对于Cuk变换器,提出了两种非线性控制方案包括李雅普诺夫直接法和输入输出线性化控制法。
- 1、下载文档前请自行甄别文档内容的完整性,平台不提供额外的编辑、内容补充、找答案等附加服务。
- 2、"仅部分预览"的文档,不可在线预览部分如存在完整性等问题,可反馈申请退款(可完整预览的文档不适用该条件!)。
- 3、如文档侵犯您的权益,请联系客服反馈,我们会尽快为您处理(人工客服工作时间:9:00-18:30)。
h ( u ) = a + b tanh cu = a + b
ecu − e− cu ecu + e− cu
for some nonnegative constants a , b and c . Using the fact
h' ( u ) =
4bc
(e
cu
+ e− cu
)
2
≤ bc , ∀u ∈ℜ
u
L∞
= sup u ( t ) < ∞
t ≥0
and the space is denoted by L∞ m . For the space of piecewise continuous, square-integrable functions, the norm is defined by
u
function h ( u ) = u 2 cannot be bounded by a straight line of the form h ( u ) ≤ γ u + β , for all u ∈ ℜ . ∆
Example 1.1: The signal u ( t ) = t does not belongs to the space L∞ , but its truncation
⎧ t, 0 ≤ t ≤ τ uτ ( t ) = ⎨ ⎩0, t > τ
belongs to L∞ for every finite τ . Hence, u ( t ) = t belongs to the extended space L∞e . ∆
1 Input-Output Stability
Input-output stability analysis allows us to analyze the stability of a given system without knowing the internal state x of the system. Before going forward, we have to introduce some input-output mathematical models.
1.1 L Stability
We consider a system whose input-output relation is represented by
y = Hu
where H is some mapping or operator that specifies y in terms of u . The input u belongs to a space of signals that map the time interval [ 0, ∞ ) into the Euclidian space v ;
( Hu )τ
for all u ∈ Le m and τ ∈ [ 0, ∞ ) .
L
≤ γ uτ
L
+β
Note that β is called bias term and the smallest possible γ is called the gain of H .
Example 1.2: A memoryless, possibly time-varying, function h : [ 0, ∞ ) × ℜ → ℜ can be
h ( t , u ) ≤ a u , ∀t ≥ 0 , ∀u ∈ ℜ for some positive constant a . For each p ∈ [1, ∞ ] , the operator H is finite-gain L p stable with zero bias and γ = a . Finally let
monotone increasing. α : [ 0, a ) → [ 0, ∞ ) is a class K ∞ if α is class K , a = ∞ and
α ( r ) → ∞ as r → ∞ .
Definition 1.3: A mapping H : Le m → Le q is L stable if there exists a class K function
h (u ) = u 2
Since
sup h ( u ( t ) )
t ≥0
⎞ ≤⎛ ⎜ sup u ( t ) ⎟ ⎝ t ≥0 ⎠
2
H and L∞ stable with zero bias and α ( r ) = r 2 . It is not finite-gain L∞ stable because the
Definition 1.1: A system is causal if the value of the output is only determined by past inputs, that is
Or equivalently, that for all times τ , for any input signals u, v, if Error! Objects cannot be created from editing field codes., then Error! Objects cannot be created
viewed as an operator H that assigns to every input signal u ( t ) the output signal
Let
y ( t ) = h ( t , u ( t ) ) . We use this simple operator to illustrate the definition of L stability.
L2
=
∫
∞
0
uT ( t ) u ( t ) dt < ∞
and the space is denoted by L2 m . More generally, the space L p m for 1 ≤ p < ∞ is defined
as
the set of all piecewise continuous functions u : [ 0, ∞ ) → ℜm such that
e.g. u : [ 0, ∞ ) → ℜm . Examples are the space of piecewise continuous, bounded functions; that is, sup u ( t ) < ∞ , and the state space of piecewise continuous, square-integrable
Le m = u uτ ∈ Lm , ∀τ ∈ [ 0, ∞ )
{
}
and uτ is a truncation of u defined by
⎧u ( t ) , 0 ≤ t ≤ τ uτ ( t ) = ⎨ t >τ ⎩ 0,
The extended space Le m is a linear space that contains the unextended space Lm as a subset. It allows us to deal with unbounded ever-growing signals.
we have h ( u ) ≤ a + bc u , ∀u ∈ℜ
Hence, H is finite-gain L∞ stable with γ = bc and β = a . Furthermore, if a = 0 , then for each p ∈ [1, ∞ ) ,
∫ h (u (t ))
tis,
∫
0
u T ( t ) u ( t ) dt < ∞ . To measure the size of a signal, we introduce the
norm function u , which satisfies the following three properties: 1) The norm of a signal is zero if and only if the signal is identical zero and is strictly positive otherwise 2) Scaling a signal results in a corresponding scaling of the norm; that is, au = a u for any positive constant a and every signal u 3) The norm satisfies the triangle inequality u1 + u2 ≤ u1 + u2 for any signals u1 and u2 . For the space of piecewise continuous, bounded functions, the norm is defined as
from editing field codes.
( Hu )τ = ( Huτ )τ
& = f ( x, u ) , y = h ( x, u ) are causal Remark 1.1: All systems of the form x
Definition 1.2: α : [ 0, a ) → [ 0, ∞ ) , continuous is a class K function if α ( 0 ) = 0 and is
u =
Lp
(∫
∞
0
u ( t ) dt
p
)
1
p
<∞
