2015复试苏大真题
2015年苏州大学英语笔译MTI真题回忆版

2015年苏州大学英语笔译MTI真题回忆版翻译硕士英语词汇与结构,单项选择,30题,30分回忆一些我印象深刻的1.thunderstorm( )all other sounds. 选项有overturn,deafen等2.Sometimes they ( )into an inflammation of mind of him who watches. 选项有emerge,divide 等3.From a plethora of commendations they select. 选项有ocean,excessive……,collection等4.Middle-class,( )house. 选项有solemn,frivolous, boisterous等5.Atrophy的意思6.The father lived vicariously through his son. 选项有A indirectly, B on behalf of a vicar, C kindly, D precariously.7.The sun and moon are simple ,but the forces which have shaped lives (). A.frantic, B gigantic,C.sensational.8.阅读三篇,每篇5个选项,30分第一篇是2010年真题最后一篇阅读的原文,只是5个问题改变。
第二篇是讲科学不只是收集事实数据,还需要想象力。
阅读后面有10分,是给一个段落,归纳主旨。
作文,30分。
以the values of friendship 为题,写约400字英文作文。
英语翻译基础短语互译,各15个,共30分(只能想起一部分)反腐风暴中日甲午战争120周年纪念日城乡协调发展中共第十八届三中全会苏州刺绣(2010年苏州大学翻译基础涉及)阿里巴巴上市食品安全百年孤独社会主义核心价值观基督教、佛教、伊斯兰教(世界三大宗教)PopulismGrassrootismVested interest groupFOB priceNietzsche(German philosopher)Oneness of human and natureHigh-net-worth familiesEcological red lineQuantitatively ease monetary policyNirvana英译中60分starting a new book is a risk like falling in love.中译英,60分关于墨子的文章,2010年中译英考题是其前半部分,2015年是它的后半部分。
苏州大学材料与化学化工学部2015年考研复试面试部分

苏州大学2015复试面试部分一.综合面试1.你本科阶段进行过哪些研究?以及研究的内容和意义?2.玻璃,晶体,陶瓷的区别?陶瓷:陶瓷微观排列小范围有序,整体无序,组成分为晶相、非晶相(玻璃相)、晶界、气相;烧成温度一般较玻璃材料低;绝大多数呈各向异性;机械性能好(耐磨、抗折强度高、但一般陶瓷弹性系数低)、介电性能好、耐化学腐蚀;如传统陶瓷,配方则有石英、长石、粘土构成。
晶体:晶体内部微观排列整齐有序,只有一种相态:晶相,具有各向异性。
玻璃:单一玻璃相构成;烧成温度一般较陶瓷高,烧成后一般需要热处理;抗压(应力)不抗张(应力)、脆性大、耐化学腐蚀;各向同性;如一般玻璃,配方则有石英、长石(氧化物)、澄清剂构成。
3.材料的表征方法有哪些?SEM、FTIR、GPC、DSC、TEM、SAXS、TGA4.XRD、DSC、SEM、TEM的检测原理和应用?5.热力学第一定律?热力学第二定律?1)能量守恒定律:在一个封闭系统的总能量保持不变。
孤立系统的总能量保持不变。
能量既不会凭空产生,也不会凭空消失,它只会从一种形式转化为另一种形式,或者从一个物体转移到其它物体,而能量的总量保持不变。
2)熵增定律:不可能把热从低温物体传到高温物体而不产生其他影响,或不可逆热力过程中熵的微增量总是大于零6.陶和瓷的区别?一、烧成温度不同陶器烧成温度一般都低于瓷器,最低甚至达到800℃以下,最高可达1100℃左右。
瓷器的烧成温度则比较高,大都在1200℃以上,甚至有的达到1400℃左右。
二、坚硬程度不同陶器烧成温度低,坯体并未完全烧结,敲击时声音发问,胎体硬度较差,有的甚至可以用钢刀划出沟痕。
瓷器的烧成温度高,胎体基本烧结,敲击时声音清脆,胎体表面用一般钢刀很难划出沟痕。
三、使用原料不同陶器使用一般黏土即可制坯烧成,瓷器则需要选择特定的材料,以高岭上作坯。
烧成温度在陶器所需要的温度阶段,则可成为陶器,例如古代的白陶就是如此烧成的。
苏州大学考研复试历年上机题目及答案
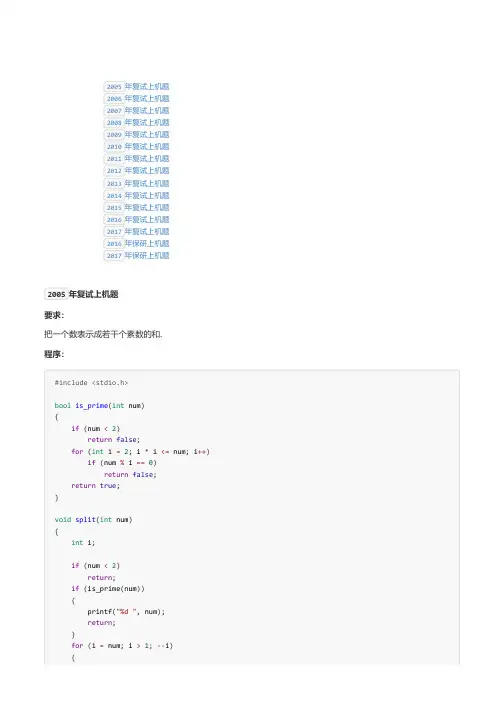
if (is_prime(i) &&num-i>1) {printf("%d ", i);split(num-i);return;}}}int main(void){int i;while (scanf("%d", &i)){split(i);printf("\n");}getchar();}要求:统计篇文章中各英文字母的个数,并排序.程序:#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>typedef struct{char c;int n;} Letter;void swap(Letter*a, Letter*b){Letter temp=*a;*a=*b;*b=temp;}int compare(Letter*a, Letter*b){if (a->n<b->n)return-1;else if (a->n>b->n)return1;elsereturn0;void selection_sort(Letter*ptr, int count){for (int i=0; i<count; i++)for (int j=i+1; j<count; j++)if (compare(&ptr[i], &ptr[j]) >0)swap(&ptr[i], &ptr[j]);}bool is_upper(char c) { return c>='A'&&c<='Z'; } bool is_lower(char c) { return c>='a'&&c<='z'; }int main(void){FILE*fp=fopen("address.txt", "r");Letter letter[26];char c;if(!fp){printf("File opening failed");return EXIT_FAILURE;}for (int i=0; i<26; i++){letter[i].c=i+'a';letter[i].n=0;}while ((c=fgetc(fp)) !=EOF){if (is_upper(c))letter[c-'A'].n++;else if (is_lower(c))letter[c-'a'].n++;}selection_sort(letter, 26);for (int i=0; i<26; i++)printf("%c: %d\n", letter[i].c, letter[i].n);fclose(fp);}2006年复试上机题要求:找出100到1000内的不含9的素数,存到result文件中.程序:#include <stdio.h>bool is_prime(int num){if (num<2)return false;for (int i=2; i*i<=num; i++)if (num%i==0)return false;return true;}bool has9(int num){if (num<0)return false;while (num>0){if (num%10==9)return true;num/=10;}return false;}int main(){FILE*fp=fopen("result.txt", "w");for (int i=100; i<1000; i++)if (is_prime(i) &&!has9(i))fprintf(fp, "%d\n", i);fclose(fp);}2007年复试上机题要求:把10到1000之间满足以下两个条件的数,存到result.txt文件中.是素数.它的反数也是素数,如:123的反数是321.程序:#include <stdio.h>bool is_prime(int num){if (num<2)return false;for (int i=2; i*i<=num; i++)if (num%i==0)return true;}int reverse(int num){int rev=0;while (num>0){rev=rev*10+num%10;num/=10;}return rev;}int main(){FILE*fp=fopen("result.txt", "w");for (int i=100; i<1000; i++)if (is_prime(i) &&is_prime(reverse(i)))fprintf(fp, "%d %d\n", i, reverse(i));fclose(fp);}2008年复试上机题要求:用IE 从FTP 上下载org.dat ,并保存在D盘的根目录中.此文件中按文本方式存放了一段其他文章,其中有若干长度小于15的英文单词,单词之间用空格分开,无其他符号.顺序读取这段文章的不同的单词(大小写敏感),同时在读取的过程中排除所有的单词THE以及变形,即这些单词不能出现在读取的结果中.将读取的所有单词的首字母转大写后,输出D 根目录下new.txt,每个单词一行.程序:#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>bool is_the(char word[15]){char the[] ="the";if (strlen(word) !=strlen(the))return false;for (int i=0; i<strlen(word); i++)word[i] |=0x20;return strcmp(word, the) ==0;}int main(){FILE*fporg=fopen("org.dat", "r");FILE*fpnew=fopen("new.txt", "w");char word[15];if(!fporg||!fpnew){printf("File opening failed");return EXIT_FAILURE;}printf("org.dat:\n");while (fscanf(fporg, "%s", word) !=EOF){printf("%s ", word);if (!is_the(word)){word[0] = (word[0] |0x20) -0x20;fprintf(fpnew, "%s\n", word);}}printf("\n");fclose(fporg);fclose(fpnew);fpnew=fopen("new.txt", "r");printf("new.txt:\n");while (fscanf(fporg, "%s", word) !=EOF)printf("%s ", word);printf("\n");fclose(fpnew);return0;}输出:org.dat:The constructor is used to initialize the object The destructor is used to delete the Object the calling seqence of constructor is opposite to the calling sequence of destructornew.txt:Constructor Is Used To Initialize Object Destructor Is Used To Delete Object Calling Seqence Of Constructor Is Opposite To Calling Sequence Of Destructor2009年复试上机题要求:用IE 浏览器从FTP 上下载org.dat ,并保存在D盘的根目录下.此文件中按文本方式存放了一段其他文章,其中有若干长度小于15的十进制或八进制数字,数字之间用,分开,数字内部存在且仅存在空格.顺序读取这些数字将他们转变为十进制数后按从大到小的顺序排序后,输出到D盘根目录下new.txt,每个数字一行.eg:_235_,34__2,_043_1_,1_3,分别是:十进制235,十进制342,八进制431,十进制13,_代表空格.程序:#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>void swap(int*a, int*b){int temp=*a;*a=*b;*b=temp;}int compare(int*a, int*b){if (a<b)return-1;else if (a>b)return1;elsereturn0;}void selection_sort(int*ptr, int count){for (int i=0; i<count; i++)for (int count=i+1; count<count; count++)if (compare(&ptr[i], &ptr[count]) >0)swap(&ptr[i], &ptr[count]);}bool is_num(char c) { return c>='0'&&c<='9'; }bool valid(char c) { return is_num(c) ||c==' '; }int main(){FILE*fporg=fopen("org.dat", "r");FILE*fpnew=fopen("new.txt", "w");int i;int count=0;int arr[128];char c;char num[15];printf("org.dat:\n");{if (is_num(c)){i=0;num[i++] =c;while ((c=fgetc(fporg)) !=EOF&&valid(c))if (is_num(c)) num[i++] =c;num[i] ='\0';printf("%s\n", num);arr[count++] =num[0] =='0'?strtol(num, NULL, 8) :strtol(num, NULL, 10);}}selection_sort(arr, count);for (i=0; i<count; i++)fprintf(fpnew, "%d\n", arr[i]);fclose(fporg);fclose(fpnew);fpnew=fopen("new.txt", "r");printf("new.txt:\n");while (fgets(num, sizeof(num), fpnew))printf("%s", num);fclose(fpnew);}输出:org.dat:235342043113new.txt:235342281132010年复试上机题要求:从FTP 上下载make.exe 和org.dat ,运行make.exe 输入准考证后三位生成data.txt,文件为二进制编码.data.txt内存有2048个整数,其中前n个为非0数,后2048-n个数为0,将其读入数组,计算非零数的个数n.选出n个数中的最大数和最小数.选出n个数中最大素数.将n个数从大到小排序,并平均分成三段(若n非3的整数倍,则不考虑最后的1-2个数),选出中间段的最大数和最小数.程序:#include <math.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <time.h>bool is_prime(int num){if (num<2)return false;for (int i=2; i*i<=num; i++)if (num%i==0)return false;return true;}void swap(int*a, int*b){int temp=*a;*a=*b;*b=temp;}int compare(int*a, int*b){if (a<b)return-1;else if (a>b)return1;elsereturn0;}void selection_sort(int*ptr, int count){for (int i=0; i<count; i++)for (int count=i+1; count<count; count++)if (compare(&ptr[i], &ptr[count]) >0)swap(&ptr[i], &ptr[count]);}int main(void){FILE*fp;int num[2048];int min=RAND_MAX;int max_prime=0;int n, i;fp=fopen("data.txt", "wb");if(!fp){printf("File opening failed");return EXIT_FAILURE;}srand(time(NULL));for (i=0; i<1000; i++)num[i] =rand() %4096;for (; i<2048; i++)num[i] =0;fwrite(num, sizeof(int), 2048, fp);fclose(fp);fp=fopen("data.txt", "rb");if(!fp){printf("File opening failed");return EXIT_FAILURE;}fread(num, sizeof(int), 2048, fp);for (n=0; n<2048; n++)if (num[n] ==0)break;printf("n = %d\n", n);for (i=0; i<n; i++){if (min>num[i]) min=num[i];if (max<num[i]) max=num[i];if (is_prime(num[i]) &&num[i] >max_prime) max_prime=num[i];}printf("min = %d\nmax = %d\nmax_prime = %d\n", min, max, max_prime);selection_sort(num, n);printf("min in mid_seg = %d\nmax in mid_seg = %d\n", num[n/3*2-1], num[n/3]);fclose(fp);}输出:n = 1000min = 1max = 4095max_prime = 4093min in mid_seg = 3630max in mid_seg = 18632011年复试上机题要求:输出1000-9999中满足以下条件的所有数:该数是素数.十位数和个位数组成的数是素数,百位数和个位数组成的数是素数.个位数和百位数组成的数是素数,个位数和十位数组成的数是素数. 比如1991,个位和十位组成的数就是19.程序:#include <stdio.h>bool is_prime(int num){if (num<2)return false;for (int i=2; i*i<=num; i++)if (num%i==0)return false;return true;}int main(void){for (int i=1000; i<=9999; i++){int g=i%10;int s= (i/10) %10;int b= (i/100) %10;if (is_prime(i) &&is_prime(i%100) &&is_prime(g*10+b) &&is_prime(g*10+s) &&is_prime(b*10+g))printf("%d ", i);}}输出:1117 1171 1997 2111 2113 2131 2137 2311 2371 2711 2713 2731 2917 3137 3331 3371 3779 3917 4111 4337 4397 4937 5113 5171 5197 5711 5779 6113 6131 6173 6197 6311 6317 6337 6397 6779 6917 6997 7331 7937 8111 8117 8171 8311 8317 8713 8731 8779 9137 9173 9311 9337 9371 93972012年复试上机题要求:从服务器上下载数据文件org.dat文件以二进制方式存放一系列整数,每个整数占4个字节. 从第一个整数规定处于第一象限的坐标点为有效点,请问数据文件中所有点的个数n为多少?有效点的个数k为多少?每个有效点与坐标原点构成一个的矩形,请问k个有效点与坐标原点构成的k个矩形的最小公共区域面积为多少?寻找有效点钟符合下列条件的点:以该点为坐标原点,其它有效点仍然是有效点即处于第一象限(不包括坐标轴上的点). 输出这些点.对所有有效点进行分组,每个有效点有且只有属于一个分组,分组内的点符合下列规则:若对组内所有点的x 坐标进行排序,点p1(x1, y1)在点p2(x2, y2)后面,即x1>x2那么y1>y2,请输出所有的分组.程序:#include <math.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <time.h>typedef struct{int x;int y;} Coordinate;void swap(Coordinate*a, Coordinate*b){Coordinate temp=*a;*a=*b;*b=temp;}int compare(const Coordinate*lhs, const Coordinate*rhs){if (lhs->x<rhs->x)return-1;if (lhs->x>rhs->x)return1;elsereturn0;}void selection_sort(Coordinate*ptr, int begin, int end){for (int i=begin; i<end; i++)for (int j=i+1; j<end; j++)if (compare(&ptr[i], &ptr[j]) >0)swap(&ptr[i], &ptr[j]);}void display(Coordinate*ptr, int count){for (int i=0; i<count; i++)printf("\n");}int main(void){FILE*fp;Coordinate*xy;int*num;int n, count;fp=fopen("org.dat", "wb");num= (int*) malloc(sizeof(int) *128);srand(time(NULL));for (int i=0; i<128; i++)num[i] =rand() %128-64;fwrite(num, sizeof(int), 128, fp);free(num);fclose(fp);fp=fopen("org.dat", "rb");fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_END);count=ftell(fp) /sizeof(int);n=count/2;num= (int*) malloc(sizeof(int) *count);xy= (Coordinate*) malloc(sizeof(Coordinate) *n);rewind(fp);fread(num, sizeof(int), count, fp);fclose(fp);int k=0;int minx=RAND_MAX;int miny=RAND_MAX;for (int i=0; i<count; i+=2){if (num[i] >0&&num[i+1] >0){xy[k].x=num[i];xy[k].y=num[i+1];if (minx>xy[k].x)minx=xy[k].x;if (miny>xy[k].y)miny=xy[k].y;k++;}}selection_sort(xy, 0, k);printf("valid points:\n");display(xy, k);printf("n = %d k = %d\n", n, k);printf("min area = %d\n", minx*miny);int sorted=0;{selection_sort(xy, sorted, k);printf("points grouped by (%2d, %2d): ", xy[sorted].x, xy[sorted].y);miny=xy[sorted++].y;for (int i=sorted; i<k; i++){if (xy[i].y>=miny){miny=xy[i].y;printf("(%d, %d) ", xy[i].x, xy[i].y);swap(&xy[i], &xy[sorted++]);}}printf("\n");}}输出:valid points:( 3, 8) (10, 62) (11, 40) (20, 6) (26, 7) (26, 20) (29, 31) (33, 10) (34, 37) (37, 33) (50,55) (52, 59) (53, 49) (53, 8) (57, 16) (58, 20)n = 64 k = 16min area = 18points grouped by ( 3, 8): (10, 62)points grouped by (11, 40): (50, 55) (52, 59)points grouped by (20, 6): (26, 20) (29, 31) (34, 37) (53, 49)points grouped by (26, 7): (33, 10) (37, 33)points grouped by (53, 8): (57, 16) (58, 20)2013年复试上机题要求:IntroductionThe project will read flight data from an input file and flight path requests from another input file and output the required information.Your TaskYour program should determine if a particular destination airport can be reached from a particular originating airport within a particular number of hops. A hop (leg of a flight) is a flight from oneairport to another on the path between an originating and destination airports. For example, the flight plan from PVG to PEK might be PVG -> CAN -> PEK. So PVG -> CAN would be a hop and CAN -> PEK would be a hop.Input Data FilesPath Input File(PathInput.txt)This input file will consist of a number of single origination/destination airport pairs (direct flights).The first line of the file will contain an integer representing the total number of pairs in the rest of the file.6[PVG, CAN][CAN, PEK][PVG, CTU][CTU, DLC][DLC, HAK][HAK, LXA]Path Request File(PathRequest.txt)This input file will contain a sequence of pairs of origination/destination airports and a max number of hops. The first line of the file will contain an integer representing the number of pairs in the file.2[PVG, DLC, 2][PVG, LXA, 2]Output File(Output.txt )For each pair in the Path Request File, your program should output the pair followed by YES or NO indicating that it is possible to get from the origination to destination airports within the max number of hops or it is not possible, respectively.[PVG, DLC, YES][PVG, LXA, NO]Assumptions you can make:You may make the following simplifying assumptions in your project:C/C++ is allowed to be used.All airport codes will be 3 letters and will be in all capsOrigination/destination pairs are unidirectional. To indicate that both directions of flight arepossible, two entries would appear in the file. For example, [PVG, PEK] and [PEK, PVG] wouldhave to be present in the file to indicate that one could fly from Shanghai to Beijing and fromBeijing to Shanghai.程序:#include <math.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <time.h>typedef struct Edge{int index;char city[4];struct Edge*next;typedef struct{char city[4];Edge*first;} Vertex;typedef struct{int size;int capacity;Vertex*vertices;} Graph;int find(Vertex*vertices, int count, char src[4]){int i;for (i=0; i<count; i++)if (strcmp(src, vertices[i].city) ==0)break;return i;}void add_edge(Graph*g, char src[4], char dst[4]){int i, j;Edge*e;i=find(g->vertices, g->size, src);if (i==g->size){strcpy(g->vertices[g->size].city, src);g->vertices[g->size].first=NULL;g->size++;}j=find(g->vertices, g->size, dst);if (j==g->size){strcpy(g->vertices[g->size].city, dst);g->vertices[g->size].first=NULL;g->size++;}for (e=g->vertices[i].first; e!=NULL; e=e->next) if (strcmp(e->city, dst) ==0)break;if (e==NULL){e= (Edge*) malloc(sizeof(Edge));strcpy(e->city, dst);e->index=j;e->next=g->vertices[i].first;g->vertices[i].first=e;}bool is_possible(Graph*g, bool*visited, char src[], char dst[], int step){int current;Edge*e;current=find(g->vertices, g->size, src);if (step==0||visited[current])return false;else{visited[current] =true;for (e=g->vertices[current].first; e!=NULL; e=e->next){if (strcmp(e->city, dst) ==0&&step==1)return true;else if (is_possible(g, visited, e->city, dst, step-1))return true;}visited[current] =false;}return false;}void destruct(Graph*g){for (int i=0; i<g->size; i++){while (g->vertices[i].first!=NULL){Edge*e=g->vertices[i].first->next;free(g->vertices[i].first);g->vertices[i].first=e;}}free(g->vertices);}void display(Graph*g){printf("adjacency list:\n");for (int i=0; i<g->size; i++){printf("%s: ", g->vertices[i].city);for (Edge*edge=g->vertices[i].first; edge!=NULL; edge=edge->next) printf("%s ", edge->city);printf("\n");}printf("\n");}int main(void)FILE*fpi=fopen("PathInput.txt", "r");FILE*fpr=fopen("PathRequest.txt", "r");FILE*fpo=fopen("Output.txt", "w");char line[16];char src[4];char dst[4];bool*visited;int step;int num;Graph g;if (!fpi||!fpr||!fpo){printf("failed to open files.\n");exit(-1);}memset(line, 0, sizeof(line));if (fgets(line, sizeof(line), fpi) !=NULL){g.size=0;g.capacity=atoi(line) *2;g.vertices= (Vertex*) malloc(g.capacity*sizeof(Vertex));memset(g.vertices, 0, g.capacity);}while (fgets(line, sizeof(line), fpi) !=NULL){memcpy(src, line+1, 3);src[3] ='\0';memcpy(dst, line+6, 3);dst[3] ='\0';add_edge(&g, src, dst);}display(&g);printf("flight info:\n");visited= (bool*) malloc(g.size);if (fgets(line, sizeof(line), fpr) !=NULL)num=atoi(line);while (fgets(line, sizeof(line), fpr) !=NULL){memcpy(src, line+1, 3);src[3] ='\0';memcpy(dst, line+6, 3);dst[3] ='\0';step=line[11] -'0';memset(visited, false, g.size);if (is_possible(&g, visited, src, dst, step)){printf("[%s, %s, %d, YES]\n", src, dst, step);fprintf(fpo, "[%s, %s, YES]\n", src, dst);}elseprintf("[%s, %s, %d, NO]\n", src, dst, step);fprintf(fpo, "[%s, %s, NO]\n", src, dst);}}destruct(&g);free(visited);fclose(fpi);fclose(fpr);fclose(fpo);}输出:adjacency list:PVG: CTU CANCAN: PEKPEK:CTU: DLCDLC: HAKHAK: LXALXA:flight info:[PVG, DLC, 2, YES][PVG, LXA, 2, NO]2014年复试上机题要求:从网页上下载input.dat 文件,里面是用二进制编写的,里面放了一堆int 型的数,每个数占4个字节,每次读取两个,这两个数构成一个坐标.规定处于第一象限的数是有效点(即x>0, y>0的坐标),问这么多点中有效点有多少个?现在用户从键盘输入一个坐标和一个数字k,设计算法输出k个离该坐标距离最近的点的坐标和每个坐标到该点的距离,写入到output.txt文件中.程序:#include <math.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <time.h>typedef struct{int x;int y;} Coordinate;Coordinate point;double distance(const Coordinate*a, const Coordinate*b) {int val= (a->x-b->x) * (a->x-b->x) +(a->y-b->y) * (a->y-b->y);return sqrt((double) val);}void swap(Coordinate*a, Coordinate*b){Coordinate temp=*a;*a=*b;*b=temp;}int compare(const Coordinate*a, const Coordinate*b){double dista=distance(a, &point);double distb=distance(b, &point);if (dista<distb)return-1;if (dista>distb)return1;elsereturn0;}void selection_sort(Coordinate*ptr, int begin, int end) {for (int i=begin; i<end; i++)for (int j=i+1; j<end; j++)if (compare(&ptr[i], &ptr[j]) >0)swap(&ptr[i], &ptr[j]);}void display(Coordinate*ptr, int count){for (int i=0; i<count; i++)printf("(%2d, %2d) ", ptr[i].x, ptr[i].y);printf("\n");}int main(void){FILE*fp;Coordinate*xy;int*num;int count, coord_count;num= (int*) malloc(sizeof(int) *128);srand(time(NULL));for (int i=0; i<128; i++)num[i] =rand() %128-64;fwrite(num, sizeof(int), 128, fp);free(num);fclose(fp);fp=fopen("org.dat", "rb");fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_END);count=ftell(fp) /sizeof(int);coord_count=count/2;num= (int*) malloc(sizeof(int) *count);xy= (Coordinate*) malloc(sizeof(Coordinate) *coord_count);rewind(fp);fread(num, sizeof(int), count, fp);fclose(fp);int valid=0;fp=fopen("output.txt", "w");for (int i=0; i<count; i+=2){if (num[i] >0&&num[i+1] >0){xy[valid].x=num[i];xy[valid].y=num[i+1];valid++;}}printf("valid points:\n");display(xy, valid);printf("total: %d\n", valid);int k;printf("coordinate: ");scanf("%d %d", &point.x, &point.y);printf("k = ");scanf("%d", &k);selection_sort(xy, 0, valid);printf("the nearest %d points to (%d, %d) are:\n", k, point.x, point.y);for (int i=0; i<k; i++){printf("(%2d, %2d) %7.2f\n", xy[i].x, xy[i].y, distance(&xy[i], &point));fprintf(fp, "(%2d, %2d) %7.2f\n", xy[i].x, xy[i].y, distance(&xy[i], &point));}fclose(fp);}输出:valid points:(49, 38) (59, 45) (53, 19) (34, 55) (23, 62) ( 2, 11) (14, 14) (55, 52) (62, 37) (46, 29) (19,57) (12, 18) ( 4, 7)total: 13coordinate: 0 0k = 5the nearest 5 points to (0, 0) are:( 4, 7) 8.06( 2, 11) 11.18(14, 14) 19.80(12, 18) 21.63(46, 29) 54.382015年复试上机题要求:从网页上下载input.dat 文件,里面是用二进制编写的,里面放了一堆int 型的数,每个数占4个字节,每次读取两个,这两个数构成一个坐标.规定处于第一象限的数是有效点(即x>0, y>0的坐标),问这么多点中有效点有多少个?从键盘上输入k 和n ,从第一问中的有效点中找出距离小于n ,距离小于n 的点的个数要大于k,将它们以文本格式输出到文件中.程序:#include <math.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <time.h>typedef struct{int x;int y;} Coordinate;Coordinate point;double distance(const Coordinate*a, const Coordinate*b){int val= (a->x-b->x) * (a->x-b->x) +(a->y-b->y) * (a->y-b->y);return sqrt((double) val);}void swap(Coordinate*a, Coordinate*b){Coordinate temp=*a;*a=*b;*b=temp;}int compare(const Coordinate*a, const Coordinate*b){double dista=distance(a, &point);double distb=distance(b, &point);if (dista<distb)return-1;if (dista>distb)return1;elsereturn0;}void selection_sort(Coordinate*ptr, int begin, int end){for (int i=begin; i<end; i++)for (int j=i+1; j<end; j++)if (compare(&ptr[i], &ptr[j]) >0)swap(&ptr[i], &ptr[j]);}void display(Coordinate*ptr, int count){for (int i=0; i<count; i++)printf("(%2d, %2d) ", ptr[i].x, ptr[i].y);printf("\n");}int main(void){FILE*fp;Coordinate*xy;int*num;int count, coord_count;fp=fopen("org.dat", "wb");num= (int*) malloc(sizeof(int) *128);srand(time(NULL));for (int i=0; i<128; i++)num[i] =rand() %128-64;fwrite(num, sizeof(int), 128, fp);free(num);fclose(fp);fp=fopen("org.dat", "rb");fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_END);count=ftell(fp) /sizeof(int);coord_count=count/2;num= (int*) malloc(sizeof(int) *count);xy= (Coordinate*) malloc(sizeof(Coordinate) *coord_count);输出:rewind(fp);fread(num, sizeof(int), count, fp); fclose(fp);int valid=0;fp=fopen("output.txt", "w");for (int i=0; i<count; i+=2){if (num[i] >0&&num[i+1] >0){xy[valid].x=num[i];xy[valid].y=num[i+1];valid++;}}printf("valid points:\n");display(xy, valid);printf("total: %d\n", valid);int k, n, pivot;printf("k = ");scanf("%d", &k);printf("n = ");scanf("%d", &n);pivot=0;while (pivot<valid){point.x=xy[pivot].x;point.y=xy[pivot].y;pivot++;selection_sort(xy, pivot, valid);printf("the points with a distance of less than %d to (%2d, %2d) are:\n", n, point.x, point.y);if (distance(&xy[pivot+k], &point) < (double)n){while (pivot<valid&&distance(&xy[pivot], &point) < (double)n){printf("(%2d, %2d) %7.2f\n", xy[pivot].x, xy[pivot].y, distance(&xy[pivot],&point));fprintf(fp, "(%2d, %2d) %7.2f\n", xy[pivot].x, xy[pivot].y, distance(&xy[pivot], &point));pivot++;}}}fclose(fp);}valid points:2016年复试上机题要求:文本文件input.txt 由若干英文单词和分隔符(空格,回车,换行)构成. 根据如下说明编写程序统计不同单词出现的次数(频度). 将统计结果按出现频度从高到低排序,并将出现频度大于5的单词及其频度输出到文件output.txt 中. 文件格式如图所示多个连续的分隔符被视为一个分隔符.大小写敏感. 每个单词的长度不超过20个字符.单词的数量未知. 如使用定义静态大数组的方式来统计,将被扣除5分.(11, 2) (26, 6) (24, 19) ( 8, 50) ( 2, 18) (60, 32) ( 4, 7) (50, 21) (21, 6) (34, 37) (30,40) ( 5, 16) (31, 59) (60, 34) (18, 32)total: 15k = 3n = 30the points with a distance of less than 30 to (11, 2) are:( 4, 7) 8.60(21, 6) 10.77( 5, 16) 15.23(26, 6) 15.52( 2, 18) 18.36(24, 19) 21.40the points with a distance of less than 30 to (18, 32) are:(30, 40) 14.42(34, 37) 16.76( 8, 50) 20.59(31, 59) 29.97the points with a distance of less than 30 to (50, 21) are:the points with a distance of less than 30 to (60, 32) are:the points with a distance of less than 30 to (60, 34) are:程序:#include <math.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>typedef struct Word{int freq;char str[20];} Word;int compare(const Word*lhs, const Word*rhs){if (lhs->freq>rhs->freq) return-1;else if (lhs->freq<rhs->freq) return1;else return0;}void swap(Word*e1, Word*e2){Word tmp=*e1;*e1=*e2;*e2=tmp;}void insertion_sort(Word*ptr, int count){for (int i=1; i<count; i++){int j=i;Word ref=ptr[i];while (j>0&&compare(&ptr[j-1], &ref) >0) {ptr[j] =ptr[j-1];j--;}ptr[j] =ref;}}int find(Word*words, int count, char*str){int i;for (i=0; i<count; i++)if (strcmp(words[i].str, str) ==0)break;return i;}int main(void){FILE*fpr=fopen("input.txt", "r");FILE*fpw=fopen("output.txt", "w");Word*words;char buf[20];int count=0;while (fscanf(fpr, "%s", buf) !=EOF)count++;words= (Word*) malloc(sizeof(Word)*count);rewind(fpr);count=0;while (fscanf(fpr, "%s", buf) !=EOF){int i=find(words, count, buf);if (i==count){strcpy(words[count].str, buf);words[count].freq=0;count++;}words[i].freq++;}insertion_sort(words, count);for (int i=0; i<count&&words[i].freq>5; i++) {fprintf(fpw, "%s %d\n", words[i].str, words[i].freq);printf("%s %d\n", words[i].str, words[i].freq);}free(words);fclose(fpr);fclose(fpw);}输出:that 13The 11It 9to 8we 8here 8a 7and 62017年复试上机题要求:已知:二进制数据文件data.bin中存放了若干个整数,请编写程序完成如下功能:编写程序读取所有数据.以每相邻两个整数为一对按顺序构成二维平面上的坐标点. 例如:有数据12,34,53,25,61,28,78等,则构成六个坐标点如下:(12, 34)、(34, 53),(53, 25), (25, 61), (61, 28), (28,78);以每个坐标点为圆心,以该点与其后面第一个点的欧氏距离为半径r. 计算每个圆包含的坐标点数. 计算最后一个点时以其和第一个点的欧氏距离为半径.例如:坐标点(12, 34)的圆半径$r=\sqrt{(12-34)^2+(34-53)^2}$是坐标点(12, 34)与(34, 53)的欧式距离.坐标点(28, 78)的圆半径$r=\sqrt{(28-12)^2+(78-34)^2}$是坐标点(28, 78)与(12, 34)的欧式距离.计算所有圆的点密度值,然后输出点密度值最大的5个坐标点以及相应圆中包含的点数和点密度值. 输出格式要求:坐标点包含点数点密度(x坐标,y坐标)(占5列,右对齐)(占7列,右对齐,保留2位小数)上述文字部分不需要显示.其中:圆的点密度为圆包含的点数除以圆面积,如果点在圆上,则也算圆包含该点,在计算点密度时,圆心也算一个点. 计算圆面积时$\pi=3.14$. 例如:坐标点(2, 1),则该坐标点也属该坐标点的圆内的一个点.程序:#include <math.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <time.h>#define PI 3.14typedef struct{int x;int y;} Coordinate;typedef struct{double r;Coordinate point;int points_num;double density;} Circle;static int compare(const Circle*a, const Circle*b){if (a->density>b->density) return-1;else if (a->density<b->density) return1;else return0;。
2015年苏州大学翻译硕士(MTI)汉语写作与百科知识真题试卷.doc

2015年苏州大学翻译硕士(MTI)汉语写作与百科知识真题试卷(总分:54.00,做题时间:90分钟)一、单项选择题(总题数:25,分数:50.00)1.背景:1964年( )发表《林纾的翻译》一文,提出:“文学翻译的最高标准是‘化’”。
“化境”是指艺术上臻于精妙超凡之境,以言翻译,大概就是得心应手、至善至美。
(分数:2.00)A.钱钟书B.谭嗣同C.严复D.郭沫若2.背景:印度人( )不但一生从事创作,写了50余部诗集、12部中长篇小说、100余篇短篇小说,而且还创作了2 000余首优美的歌曲,其中一首被定为今日印度的国歌。
(分数:2.00)A.泰戈尔B.果戈理C.甘地D.阿兰达蒂3.背景:中篇小说《伊豆的舞女》是日本作家( )的作品,借此他成为当年日本文坛的风云人物。
(分数:2.00)A.大江健三郎B.川端康成C.小林多喜二D.井上靖4.背景:《不列颠百科全书》介绍说:“他是20世纪前半个世纪中的最杰出的东方学家,也是将东方文种译为英文的最杰出的翻译家。
……他是一位诗人和诗歌的创新者。
”此人就是( )。
(分数:2.00)A.亚瑟.韦利B.爱德华兹C.劳费尔D.庞德5.背景:( )是20世纪英国最伟大的哲学家、思想家、数学家和逻辑学家,他提出了“中立一元论”的学说,并撰写了大量的哲学著作。
(分数:2.00)A.罗素B.杜威C.笛卡尔D.休谟6.背景:在下面的四部作品中,哪一部不是杰克.伦敦的著作?( )(分数:2.00)A.《马丁.伊登》B.《白牙》C.《野性的呼唤》D.《嘉莉妹妹》7.背景:梁启超翻译的很多小说用的都是( ),与林纾和严复的古奥的译文形成了鲜明的对比,具有很强的文学感染力。
(分数:2.00)A.白话文B.文言文C.方言D.北京话8.背景:莫扎特生前未完成的作品是( )。
(分数:2.00)A.《卡农》B.《婚礼进行曲》C.《安魂曲》D.《欢乐颂》9.背景:1936~1939年西班牙内战期间,在共和国后方活动的叛徒、间谍和破坏分子等反革命分子被统称为( )。
2015-2018苏大FUNSOM考研复试题

2015苏大FUNSOM考研复试题(化学专业)(抱歉只给了正确答案,请大家已知识点的新式掌握,不要只记正确答案,红色标记的是本人考试时拿不准的题目,下来均已查好正确答案,选择题一共有30个,当时只记了17个下来)一、选择题。
1、泡沫灭火器的成分(A)A、Al2(SO)4 NaHCO3B、 Na2CO3 NaHCO32、电气设备失火,应该怎么做(A)A、首先切断电源,再用CO2灭火器3、不常用的干燥剂有哪些(B)B、氢氧化钠、氢氧化钾、无水碳酸钠、氧化钙4、眼睛里不小心溅入酸液,应该怎么做(B)B、先用大量水洗,再用稀NaHCO3冲洗5、洗脱能力最弱的是(C) C、石油醚6、不溶于水的是(D)A、甲醇B、丙酮C、吡啶D、二氯甲砜7、一份氯化钠和三份干冰混合,所能达到的温度是(B)A、-15℃B、-21℃8、减压蒸馏的操作是(B )A、先关泵,再停止加热,最后通入冷凝水B、先关热源,再通入冷凝水,最后关泵9、如果吸收过多的盐酸气体该怎么办?(A)A、吸乙醇B、吸丙酮10、铬酸洗液是用什么酸配置?(B) B、浓硫酸11、不能精确量取的仪器有(A) A、胶头滴管、漏斗、分液漏斗12、AR是(B) B、分析纯分级标准:按杂质含量的多少分等级。
13、在保存硫酸亚铁离子溶液时,哪个做法不对(C)B、加入稀硫酸使溶液保持酸性C、加入盐酸使溶液保持酸性14、下列说法不正确的是(C)A、金属钠保存在煤油中B、白磷保存在水中C、石油保存在带橡皮塞的玻璃瓶中15、下列物质有毒的是(B ) B、NaCN16、下列PH计不需要润洗的是(A)A、侵泡在KCl溶液中的PH计B、测定过浓酸或浓碱的PH计17、毛细血管壁太厚,会造成熔点(A)A、偏高B、偏低C、无影响二、问答题1、简述石墨和金刚石的结构特征?2、沸石为什么能防暴沸?若加热液体时忘加沸石,应该怎么做?若中途停止加热,再次加热时,是否需要重加沸石,为什么?3、在萃取过程中,若有机溶剂与水的密度相差不大且比水小,会出现什么情况?应该怎么做?若有机溶剂在水中的溶解度比较大,会出现什么情况?应该怎么做?。
苏州大学复试题及答案

苏州大学复试题及答案一、单项选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 苏州大学位于哪个省份?A. 浙江省B. 江苏省C. 广东省D. 上海市答案:B2. 苏州大学成立于哪一年?A. 1900年B. 1910年C. 1921年D. 1931年答案:C3. 苏州大学的校训是什么?A. 厚德、博学、求是、创新B. 求是、创新、厚德、博学C. 厚德、博学、笃行、创新D. 笃行、厚德、博学、求是答案:A4. 苏州大学的主要校区位于哪个城市?A. 南京B. 苏州C. 无锡D. 扬州答案:B5. 苏州大学是否属于“211工程”高校?A. 是B. 否答案:A6. 苏州大学是否属于“985工程”高校?A. 是B. 否答案:B7. 苏州大学是否设有研究生院?A. 是B. 否答案:A8. 苏州大学的图书馆藏书量大约是多少?A. 100万册B. 200万册C. 300万册D. 400万册答案:C9. 苏州大学有多少个学院?A. 20个B. 30个C. 40个D. 50个答案:C10. 苏州大学的校徽颜色是什么?A. 蓝色B. 红色C. 绿色D. 黄色答案:A二、多项选择题(每题3分,共15分)1. 苏州大学的优势学科包括哪些?()A. 工程学B. 材料科学C. 化学D. 计算机科学答案:A B C2. 苏州大学提供的学位类型包括哪些?()A. 学士B. 硕士C. 博士D. 博士后答案:A B C3. 苏州大学的校园文化活动包括哪些?()A. 学术讲座B. 文艺演出C. 体育比赛D. 社团活动答案:A B C D4. 苏州大学在哪些领域有国际合作项目?()A. 教育B. 科研C. 经济D. 文化答案:A B5. 苏州大学的校园设施包括哪些?()A. 图书馆B. 实验室C. 体育馆D. 学生宿舍答案:A B C D三、简答题(每题5分,共20分)1. 请简述苏州大学的历史沿革。
2. 苏州大学在国内外的学术影响力如何?3. 苏州大学的教育特色是什么?4. 苏州大学为学生提供了哪些就业指导服务?四、论述题(每题10分,共20分)1. 论述苏州大学在推动地方经济发展中的作用。
苏大2015年学科教学(语文)真题回忆版
333教育综合
一、名词解释5*6
1、班级授课制
2、课程
3、学制
4、中世纪大学
5、葵卯学制
6、教学模式
二、简答题10*4
1、简述英国《1944教育法》的内容
2、教育对人的发展的作用
3、简述教育工程的性质
4、简述罗杰斯的人本主义教育思想
三、论述20*4
1、洋务学堂的特点,洋务教育兴起的背景及在近代教育中的作用
2、卢梭的自然主义教育思想
3、从教育的社会流动性来论述我国现阶段的教育不公平
4、如何培养学生的创造性思维能力
864语文教学论
一、论述30*3
1、论述阅读教学的目标
2、写作教学的一般原则
3、举例说明新课程下语文老师角色与行为的转变
二、设计题60
教学对象5分,教学目标20分,教学方法5分,教学重点难点10分,板书设计20分。
文章《李广的悲剧》。
2015苏州大学中国语言文学真题
我自学过水彩画和水墨画后,便特别喜欢画阴天和微雨天的景色,我不喜欢英国古老风格的水彩画。我已往的水彩画可说是水墨画的变种,从意境和情趣方面看,模仿西洋的手法少,受益于中国画的成分多。西洋画中也有表现风雨的题材,但西洋画中是将风雨作为一种事故或大自然的变态来描写的,很少将阴雨作为一种欣赏对象的审美趣味来表现。西方风景画之独立始于印象派,印象派发源于阳光。画家们投靠阳光,说光就是画面的主人,因之一味分析色彩与阳光的物理关系,甚至说“黑”与“白”都不是色彩,而中西画家大都陶醉于阳光所刺激的强烈的色彩感,追求亮、艳、丽、华、鲜??多半是从“晴”派生出来的。 曾有画油画的人说:江南不宜画油画。大概就是因为江南阴雨多,或者他那油画技法只宜对付洋式的对象。数十年来,我感到在生活中每次表现不同对象时,永远需寻找相适应的技法,现成的西方的和我国传统的技法都不很合用。浓而滞的油画里有时要吸收水分,娇艳的色彩往往须渗进墨韵??人们喜欢晴天,有时也喜欢阴天,如果阴与晴中体现了两种审美趣味,则鱼和熊掌是可以兼得的。又画油画又画水墨,我的这两个画种都不纯了,只是用了两种不同的工具而已。头发都灰白了,还拿不定主意该定居到油画布上呢,还是从此落户在水墨之乡了!
3 文学经典的转变是否代表文学价值的判断标准具有相对性(前面引用了一句话但是不记得了?_?? )
4 卢梭《忏悔录》“我的内心完全暴露出来了,和你亲自看到的完全一样,请你把那无数的众生叫到我跟前来!让他们听听我的忏悔,让他们为我的种种堕落而叹息,让他们为我的种种恶行而羞愧。然后,让他们每一个人在您的宝座前面,同样真诚地披露自己的心灵,看看有谁敢于对您说:“我比这个人好!” 《忏悔录》的思想内容是什么?与19世纪批判现实主义文学有什么联系?
湿,渲染了山林、村落,改变了大自然的色调。山区的红土和绿竹,本来并不很协调,雨后,红土成了棕红色,草绿色的竹林也偏暗绿了,它们都渗进了深暗色的成分,统一于含灰的中间调里,或者说它们都含蕴着墨色了。衣服湿了,颜色变深,湿衣服穿在身上不舒服,但湿了的大自然景色却格外地有韵味。中国画家爱画风雨归舟,爱画“斜风细雨不须归”的诗境。因为雨,有些景物朦胧了,有些形象突出了,似乎那位宇宙大画家在挥写不同的画面,表达着不同的意境。
苏州大学细胞生物学2015真题答案
苏州大学2015年攻读硕士学位研究生入学考试试题答案解析细胞生物学一、名词解释1.反面高尔基体处于高尔基体反面的管网状结构,主要功能是负责对蛋白质进行分选,并定向将蛋白质转运到细胞内或细胞外的最终位置。
2.膜泡运输指真核细胞通过胞吞作用和胞吐作用完成大分子与颗粒性物质的跨膜运输,在转运过程中,物质包裹在脂双层膜围绕的囊泡中故称为膜泡运输,因涉及到膜的融合与断裂,耗能,因此属于主动运输。
膜泡运输包括COP II有被小泡运输、COP I有被小泡运输、网格蛋白有被小泡运输。
3.离子通道即通道蛋白,细胞膜上的脂质双分子层中存在着一类能形成孔道,供某些分子进出细胞的特殊蛋白质(跨膜蛋白)。
通道蛋白只进行物质的被动转运。
通道蛋白所介导的被动运输不需与溶质分子结合,允许大小和带电荷适宜的离子通过。
绝大多数的通道蛋白形成有离子选择性的、门控的跨膜通道。
因为这些通道蛋白几乎都与离子的转运有关,所以又称为离子通道。
与载体蛋白相比,有三个显著特征:具有极高的转运速率,离子通道没有饱和值,离子通道并非连续性开放而是门控的。
4.P53p53是一种抑癌基因,该基因编码一种分子量为53kDa的蛋白质,命名为P53。
p53蛋白由393个氨基酸组成,具有特异的转录激活作用。
在所有恶性肿瘤中,50%以上会出现该基因的突变。
由这种基因编码的蛋白质是一种转录因子,其控制细胞周期的启动。
许多有关细胞健康的信号向p53蛋白发送,关于是否开始细胞分裂就由这个蛋白决定。
如果这个细胞受损,又不能得到修复,则p53蛋白将参与启动过程,使这个细胞发生细胞凋亡。
p53缺陷的细胞没有这种控制,甚至在不利条件下继续分裂。
像所有其它肿瘤抑制因子一样,p53基因在正常情况下对细胞分裂起着减慢或监视的作用。
细胞中抑制癌变的基因“p53”会判断DNA变异的程度,如果变异较小,这种基因就促使细胞自我修复,若DNA变异较大,“p53”就诱导细胞凋亡。
5.动粒是由着丝粒结合蛋白在有丝分裂期间特别装配起来的、附着于主缢痕外侧的圆盘状结构,内侧与着丝粒结合,外侧与动粒微管结合。
苏州大学材料与化学化工学部2015-2018年 考研复试真题
2015年材料与工程复试笔试1.材料的四大要素是什么?它们之间的关系如何?1.材料的四要素为:合成与加工、组成与结构、性质、使用性能a)组成和结构是材料在原子分子的度量,b)合成与加工是指建立原子、分子和分子聚集体的新排列,在原子尺度到宏观尺度的所有尺度上对结构进行控制以及高效而有竞争力地制造材料和零件的演变过程。
c)性质是材料功能特性和效用的定量度量和描述。
d)使用性能通常是指材料在最终的使用过程中的行为和表现。
2.材料学就是研究四要素之间的关系的一门学科。
对材料科学与工程的发展来说,上述四个要素是基本的,整体的,缺一不可的。
材料的四要素反映了材料科学与工程研究的共性问题,其中合成和加工、使用性能是两个普遍的关键要素。
在四个要素上,各种材料相互借鉴、相互补充、相互渗透。
1)材料的合成与加工决定了组成与结构,2)组成与结构决定了材料的性质,3)材料的性质是组成与结构的外在反映,又提供了材料的使用性能。
4)只有通过合成与加工改变了材料的结构与成分,才能改变和控制材料的使用性能,5)材料的使用性能与使用环境有关要有效地使用材料,必须了解合成与加工、组成与结构、性质、使用性能及使用环境的影响。
在四要素关系中,最基本的是组成与结构和使用性能的关系,材料学的主要任务就是研究材料的组成与结构、使用性能及二者间的关系。
2.材料的加工与合成的定义和内容、关系以及发展前景。
定义和内容:1.合成还是新技术开发和3.加工(成型加工),除了上述为生产材料而进行的原子、分子控制外,还包括较大尺度的概念,有时也包括制造等工程问题。
关系:1.材料的合成与加工工艺决定了材料的组成与结构,从而决定了材料的性质;2.合成决定材料的组成,赋予材料的基本性质;加工改变材料的结构,进一步改进和实用化材料,最终赋予材料使用性能3.合成时需要考虑材料的加工性能,而加工又对合成工艺的改进提出要求4.合成与加工是控制产品质量、成本的关键发展前景:现今,合成与加工的区别日渐模糊,这是由于材料在合成时往往预先考虑到后续加工,如高分子材料的注射成型将单体快速混合,充模,瞬间同步完成聚合反应与成型。
- 1、下载文档前请自行甄别文档内容的完整性,平台不提供额外的编辑、内容补充、找答案等附加服务。
- 2、"仅部分预览"的文档,不可在线预览部分如存在完整性等问题,可反馈申请退款(可完整预览的文档不适用该条件!)。
- 3、如文档侵犯您的权益,请联系客服反馈,我们会尽快为您处理(人工客服工作时间:9:00-18:30)。
苏州大学复试试题2015
每题30分,选做5题
1、介绍下面纤维的化学组成,聚集态结构和形态结构特点。
比较和分析它们的性能特征以及目前在服装、家纺领域的应用。
如何鉴别这些纤维?具体说明鉴别的方法。
蚕丝腈纶粘胶羊
毛棉锦纶
2、试述加捻的定义、作用以及评价指标。
加捻对纱线的结构和性能有哪些影响?列举3个以上采用长丝加捻纱为原料的面料名称及其特点。
3、从纤维原料、纱线结构和织物结构及加工等方面,阐述与织物的抗起毛起球性、热湿舒适性密切相关的因素?在纺织品的设计及加工中,可以通过哪些手段改善织物的抗起毛起球性和热湿舒适性。
4、水及酸、碱、蛋白质分解酶的水溶液分别对蚕丝丝素有什么影响?
5、简述家蚕丝丝素与丝胶在结构和性质方面有哪些不同?
6、什么是生物应用材料?列举2例蚕丝丝素作为生物医用材料的例子,分别说明列举例中蚕丝丝素起了什么作用?
7、请详细叙述影响上浆率的各种因素。
8、筒子卷绕过程为什么会产生重叠现象?定轴传动和摩擦传动的防叠原理有何差异?
9、一平纹织物织造过程发现“筘痕”现象严重,请详细分析如何调整织机的织造参数,消除该病疵。
10、论述三原组织的构成方法,并比较其织物在可密性方面的差异。
11、举例叙述机织物组织上机图的基本穿综方法(三种以上),并说明各自适用的条件。
12、试绘制表组织为五枚纬缎,里组织为五枚经缎,排列比为1:1的重组织图。
13、简述转杯纺纱机各组成机构的主要作用。
14、熔喷非织造加工中会出现“料滴”现象,又称“shot”现象。
解释何谓“shot”现象?说明出现这种现象的主要原因,并分析如何避免发生这种现象。
