句的五种基本句型

语法讲义一、简单句与并列句
简单句的五种基本句型
句子成分详解一览
表
句型种类 主语
谓语部分
谓语动词 表语 宾语 宾补 S+Vi Pat arrived S+Vt+O She plays the piano
S+Vt+C They are(系动词) heroes. S+Vt+Ino+Do I offered him dollars
S+Vt+O+Oc Ann made
me
cry
句子成分
意义
充当词类 例句
主语 The Subject 表示句子说的是什么人,或什么事
名词、代词、数词、不定式、动名词、短语或句子等。 1.We study in No.7 Middle School. 2.Jim is an educated child.
谓语 The predicate 说明主语做什么,是什么或怎么样
由动词或动词词组充当
1.I expect you to take me.
2.Lucy is dancing under the tree.
3.Her parents hate telling lies. 宾语 The object 表示动作、行为的对象
同主语的充当词类
1.Both of the girls like Spanish.
2.Did she call me just now? 表语 The predicative 与系动词连用,一起构成谓语、说明主语
的性质特征
同主语的充当词类
1.Her mother is a chemist.
2.The two states were at war then.
3.What he said sounds reasonable.
定语 The attribute 用来修饰名词或代词 形、代、数、名、副、介词短语或相当于形容词的词或短语 1.The black sweater is mine. 2.What is his father's name ?
3.We have nine lessons every day. 状语
The adverbial
修饰动词、形容词、副词,表示动作发生的时间、地点、目的、方式等
通常由副词、介词短语或相当于副词的词或短语来表示 1.The miners work very hard. 2.She often helps Mike.
3.They held a party in Hollywood.
宾语补足语 The object complement 宾语的补足语,逻辑上与宾语是“主谓”关系 一般由形容词、名词、介词短语等充当
1.They named the baby Lily.
2.She always keeps the house clean every day.
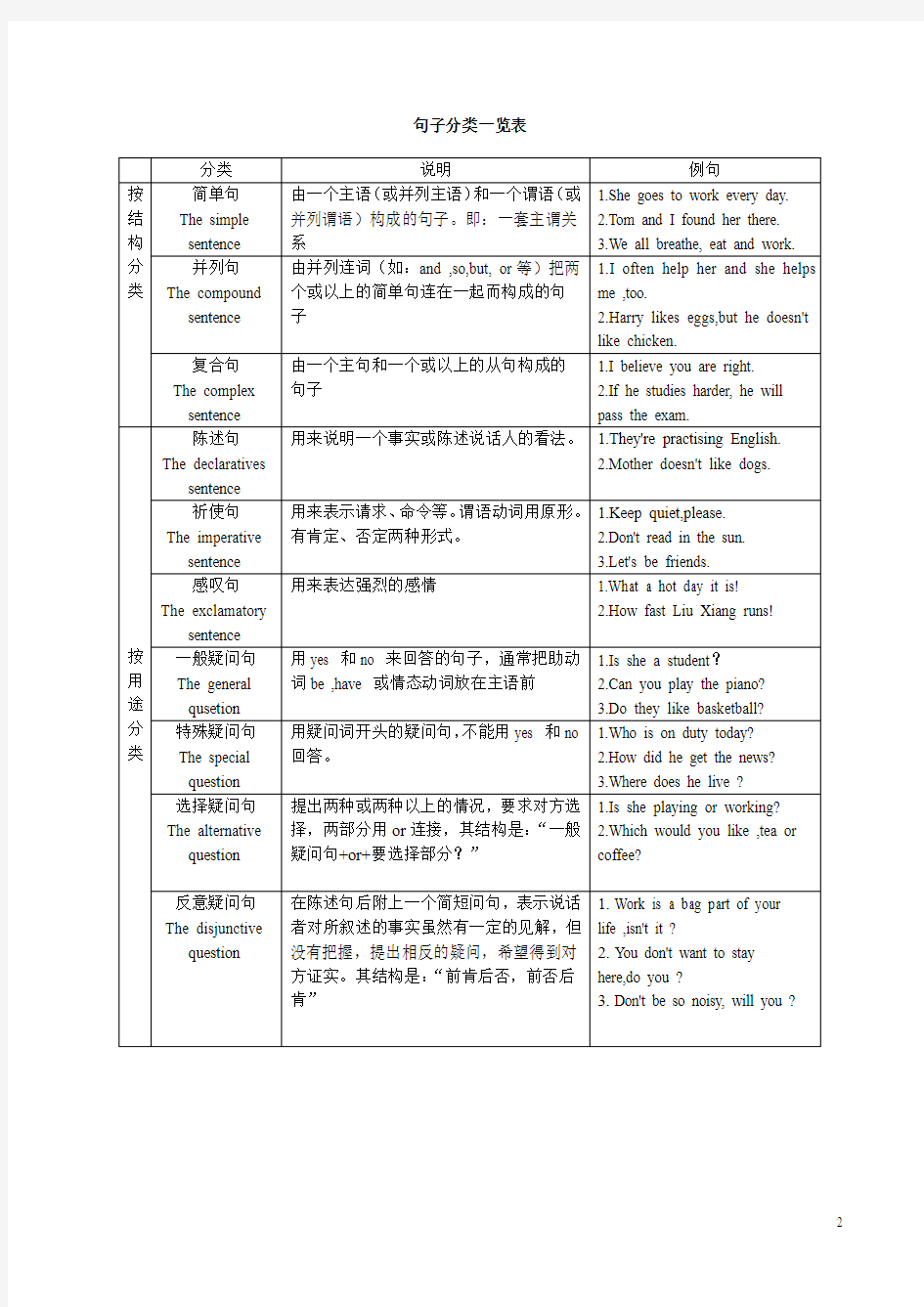
句子分类一览表
分类说明例句
按结构分类
简单句
The simple
sentence
由一个主语(或并列主语)和一个谓语(或
并列谓语)构成的句子。即:一套主谓关
系
1.She goes to work every day.
2.Tom and I found her there.
3.We all breathe, eat and work.
并列句
The compound
sentence
由并列连词(如:and ,so,but, or等)把两
个或以上的简单句连在一起而构成的句
子
1.I often help her and she helps
me ,too.
2.Harry likes eggs,but he doesn't
like chicken.
复合句
The complex
sentence
由一个主句和一个或以上的从句构成的
句子
1.I believe you are right.
2.If he studies harder, he will
pass the exam.
按用途分类
陈述句
The declaratives
sentence
用来说明一个事实或陈述说话人的看法。 1.They're practising English.
2.Mother doesn't like dogs.
祈使句
The imperative
sentence
用来表示请求、命令等。谓语动词用原形。
有肯定、否定两种形式。
1.Keep quiet,please.
2.Don't read in the sun.
3.Let's be friends.
感叹句
The exclamatory
sentence
用来表达强烈的感情 1.What a hot day it is!
2.How fast Liu Xiang runs!
一般疑问句
The general
qusetion
用yes 和no 来回答的句子,通常把助动
词be ,have 或情态动词放在主语前
1.Is she a student?
2.Can you play the piano?
3.Do they like basketball?
特殊疑问句
The special
question
用疑问词开头的疑问句,不能用yes 和no
回答。
1.Who is on duty today?
2.How did he get the news?
3.Where does he live ?
选择疑问句
The alternative
question
提出两种或两种以上的情况,要求对方选
择,两部分用or连接,其结构是:“一般
疑问句+or+要选择部分?”
1.Is she playing or working?
2.Which would you like ,tea or
coffee?
反意疑问句
The disjunctive
question
在陈述句后附上一个简短问句,表示说话
者对所叙述的事实虽然有一定的见解,但
没有把握,提出相反的疑问,希望得到对
方证实。其结构是:“前肯后否,前否后
肯”
1.Work is a bag part of your
life ,isn't it ?
2.You don't want to stay
here,do you ?
3.Don't be so noisy, will you ?
感叹句(Exclamatory sentence )与祈使句(Imperative sentence )
感叹句的结构与特点
祈使句结构简表及用法
常见形式
例句
肯定形式
Vi (+副词) 1.Stop! Sit down! Get away! https://www.360docs.net/doc/ec13296351.html,e here,everyone! Vt+宾语 1.stop talking!
2.Give it to your sister!
Be+ adj.
1.Be careful!
2.Be reasonable, Mary. It wasn't my fault.
3.Be sure to turn off the light!
否定形式(Don't/Never +V ) 1.Don't take it away!
2.Never put off till tomorrow what can be done today!
Let 结构
1.Let me try!
2.Let him not waste time!
3.Let's be frank with each other! 有主语结构(以示强调)
(You+V ) 1.You clean the blackboard! 2.John ,you be quiet!
加强语气结构(do/does/did+V.) 1.Do come ,please! 2. Do be brave! 2.Tom did tell me the news!
无动词祈使句
1.Silence!
2.No smoking!
3.No entry!
类别 结构
例句
备注
以What 引导
What +a/an+adj.+ 单数可数名词+主语+谓语!
1.What a silly question he asked!
2.What an interesting story (it is) ! 1.在口语中,后面的主语,谓语可以省略。
2.What 感叹句的中心词是名词,但名词前可以加形容词等来修饰。
3.How “adj+a/an+单数名词”,但不能接“Adj+复数或不可数名词”
What +(adj)+ 复数名词+主语+谓语!
1.What lovely girls they are!
2.What beautiful flowers they are !
3.What fools you are!
What +adj.+ 不可数名词(+主语+谓语)!
1.What fine weather (it is) today!
2.What good advice she gave! How
引导 How +adv./adj.+主语+谓语! 1.How cool it was yesterday! 2.How hard the students study! 其他形式
有时陈述句、一般疑问句、单词或短语也可以用作感叹句
1.She is such a nice girl!
2.Isn't the story interesting!
3.Wonderful!
4.Help !
5.Lovely day,isn't it!
注意
1.感叹句有时可以用How 和What 来转换,但这只能适合于单数可数名词的情况。
2.fun, advice ,information,news,weather 等不可数名词或复数名词前,即使其前有形容词来修饰,也不能加a/an.
注意:祈使句与and 或or 等连用,可以表示条件。如:
Work hard,and you'll succeed.
Don't move ,or I'll fire!
反意疑问句(Tag questions)1.附加问句的肯定与否定
陈述部分附加疑问部分例句hardly, few, little,no, not,
never,nobody,nothing,seldom,nowh ere等否定词或半否定词肯定式
1.Nobody came here while i was out ,did they ?
2.There's little rice at home ,is there ?
3.Dave can hardly cook,can he ?
no one ,no body, one ,nothing,neither等作宾语多用肯定式也可
用否定形式
1.peter has nothing to say ,does(n't) he ?
2.You got nothing from her,did(n't) you?
含有un-, in-,im-,dis-, --less等否定
前、后缀构成的派生词否定形式1.That's unfair ,isn't it ?
2.The boy is hopeless,isn't he?
3.She dislikes pets,doesn't she?
2.一些特殊句式的附加疑问句
陈述部分句式附加问句部分例句
I am... aren't I I'm your friend,aren't I?
I wish... may I I wish to have a look,may I?
Let's (表建议,包括说着) shall we (shan't we) Let's sing an English song, shall we? Let us (表允许,不包括
说话者)
will you(won't you) Let us make it by ourselves,will you?
Let me /him/ them will you Let me do it again,will you ?
Let him join us,will you?
表示邀请、请求的祈使句will/ won't you Come here this evening, will you?
You will speak English,won't you?
否定的祈使句(表示请求)will/ can't you Don't make a noise , will/can you?
感叹句用一般现在时be 的形式What fine weather ,isn't it ?
并列句与邻近的分句一致Mary is a nice girl, but she doesn't like
English,does she?
主从复合句多与主句的主、谓语一致Jim wouldn't go if it rained, would he?
I don't
think/believe/guess...+宾语从句与从句的主,谓语一致,且用肯
定形式
I don't think this story is funny,is it?
I don't believe he knows it, does he?
So..., or..., oh... 前后两部分一致(前否后也否)He is Michael Jordan,or is he?
3.附加部分与陈述部分主语不一致的情况
陈述部分主语附加部分主语例句
this,that ,anything,something,
nothing,everything,不定式,动名词(短语),从句it
1.This /That is your sister,isn't it?
2.Everything seems all right,doesn't it ?
3.Nothing is serious,is it?
4.To learn Japanese isn't easy, is it?
5.What she said was true,wasn't it?
some(none)of... it /they 1.Some of the boys have left,haven't they?
2.None of the food was delicious,was it? these/those they These /Those are not parrots,are they? anybody ,someone,
everyone,either,nobody,each of...no one,one,neither he/they
1.Everyone knows this,don't they/doesn't he?
2.Each of boys had an apple,didn't he /they?
3.Nobody saw him,did they?
4.No one called me just now,did they?
复数代词one one/he One can't always be young,can one/he? the +形容词以及由both ...and ,
either...or, neither...nor, and, not only...but also..., or 等连接的主语复数代词
1.The poor had no right to vote then, did they ?
2.Both Rose and Mary left,didn't they ?
3.Neither you or I am wrong, are we?
4.附加问句部分与陈述部分谓语不一致的情况
陈述部分谓语附加部分谓语例句
have 不作“有”讲do (does/did) 1.They all had a good time,didn't they?
2.We have to say goodbye,don't we? need/dare做实义动词do 1.he needs a lot of money,doesn't he?
2.I've never dared to ask her,have I? must (必须) needn't (不必) We must finish it today, needn't we?
can't (不可能)表示推测根据can't 后的动词
选用相应的形式1.The person can't be an inspector, is he?
2.They can't have finished it now, have they?
must+be 对现在情况进行推测作一般现在时或现在
进行时处理
1.Ann looks pale. She must be ill,isn't she?
2.The boys must be playing football on the playground now,
aren't they?
must+完成时表示对过去情况的推测作一般过去时的附加
疑问句处理
1.The interviewers must have come yesterday,didn't they?
2.He must have been there then, wasn't he?
must+完成时用来推测过去的动作持续到现在按现在完成时的附加
疑问句处理
His cousin must have lived here at least ten years,hasn't he ?
used to+ d动词原形didn't/usedn't + 主语He used to live in the town, usedn't/didn't he?
语法讲义二、状语从句
状语从句在句中起状语的作用,修饰主句的谓语动词、形容词、副词或整个句子。通常由从属连词引导,与主句相接。状语从句放在句首时,常在其后加上逗号,若放在句末时,其前一般不用逗号。
种类连接词例句注意事项
时间状语从句When /by the time /wherever;
once,every/each time;as soon
as=hardly/scarely...when=no
sooner...than;
the moment/minute
=immediately/instantly;
while/as; after;since;until/till
1.Once ha has made up his mind, nothing can
change it.
2.While we are young,we should work hard.
3.I'm going to talk with you as soon as I finish
my work.
4.He didn't go to bed last night until he finished
his work.
5.As she grew older,she began to go deaf.
主“将”从“现”。
when 强调“特定
时间”,while表示
的是时间段,有时
还有对比的含义,
as 用于口语,强
调“同时”。
地点状语where; wherever 1.please stay where you are.
2.I may go wherever I like.
原因状语because; as /for; since/now that
seeing that /as
considering (that)
1.Since no one else is against it, we'll pass the
law.
2.As she is not well today, I'll go myself.
3.Seeing as we're going the same way, I'll give
you a lift.
because引导的从
句一般在主句之
后,且主句不可再
用连词so;
because语气最
强,since较弱,
as次之,for最弱。
比较状语从句than
as....as
not as /so ...as
1.It is warmer in spring than ( it is)in winter.
2.I get up as early as my parents do every
morning.
3.He isn't as tall as Bill.
4.Liu Xiang runs much faster than I do.
as和than引导从
句,常省去与主句
中相同部分,留下
相比较的部分;常
用替代动词do等
形式代替与主句
相同的谓语部分。
目的状语so that =in order that
for fear that
that(以便)
in case
1.I got up early so that I could catch the first
bus to Macao.
2.Better take more clothes in case the weather is
cold.
表示目的的so
that=in order that ,
后常接may或
should,could,
would等。
结果状语so.....that
such....that
1.I was so excited that I couldn't go to sleep.
2.She spoke in such a low voice that we
couldn't hear her at all.
注意so和such后
的搭配词
so+adj./adv...
such+(adj.)+n..
条件状语if; unless ; as/so long as
on condition that; suppose that;
in case
1.He'll talk with me if he has time tomorrow.
2.You will fail in the exam unless you work
harder.
3.Stay as long as you like.
4.Send me a message in case you have any
difficulty.
从句中的动词时
态不可用将来时,
只能用现在或过
去时来表示将来
时
方式状语as if =as though
as
1.We heard a noise, as if someone were
breathing.
2.It looks as though it is going to rain this
morning.
3.She will do as she is told.
as if /as though引
导的从句一般用
虚拟语气
让步状语(al)though; even if/though;
no matter what/who/which/how...
1.Native English speakers can understand each
other even if they don't speak the same.
2.They kept on working, though it was raining.
3.No matter how difficult (it may be), we must
go on.
4.Young /Child as he is , he knows a lot.
as 作“尽管”,用
于让步状语从句
时,需用部分倒装
结构,而
although/though
则用正常语序。两
者可和yet连用,
但不可与but连用
语法讲义三、宾语从句
直接引语与间接引语
类型直接引语改变方法间接引语
陈述句 1."I like sports."Jim said.
2.He said to me,"My sister
has been here." 用连词that 引导。从句中的人
称、时态、时间、地点状语及
指示代词等要作相应变化。
1.Jim said that he liked sports.
2.He told me that his sister had been
there.
一般疑问句1.He said to me ,"Are you
out of work?"
2.She said,"Did you see
Bob last night?"
用连词if 或whether引导,主
句中谓语动词是said时,改为
asked, 如无间接宾语,可加
一个(me,him,us等)。语序要
用陈述句语序,句末用句号。
1.he asked whether /if I was out of
work.
2.She asked me if I had seen Bob the
night before.
特殊疑问句1.“Which do you want?”
he asked me.
2."Who has taken my
record?"Tom asked.
用原来问句中的疑问词引导,
注意从句需用陈述语序,句末
用点号。
1.He asked me which wanted.
2.Tom asked who had taken his record.
祈使句 1.She said to us ,"Please
come in."
2.The teacher said,"Don't
make a noise , boys."
将原句中的动词原形变为不
定式,并在前面加上
tell,ask,order等动词,其句型
是tell(ask,order) sb. to do sth.
如果祈使句是否定式,则在不
定式前面加上not.
1.she asked us to come in.
2.The teacher told the boys not to
make a noise.
直接引语变间接引语的一般规律
变项分类直接引语要变项间接引语
主句中的谓语动词时
态
一般现在时-------------------------------------------------------------
一般过去时-------------------------------------------------------------
现在完成时-------------------------------------------------------------
现在进行时------------------------------------------------------------
一般将来时-------------------------------------------------------------
过去完成时-------------------------------------------------------------
一般过去时
过去完成时
过去完成时
过去进行时
过去将来时
过去完成时
情态动词can/may-----------------------------------------------------------------
shall/will-----------------------------------------------------------------
must----------------------------------------------------------------------
could/might
should/would
had to(must)
指示代词this/these-------------------------------------------------------------- that/those 地点状语here------------------------------------------------------------------- there
方向性动词come/bring----------------------------------------------------------- go/take
时间状语now-----------------------------------------------------------------
today-----------------------------------------------------------------
tonight---------------------------------------------------------------
tomorrow----------------------------------------------------------
yesterday-----------------------------------------------------------
last night(week)----------------------------------------------------
next week/month--------------------------------------------------
ago-----------------------------------------------------------------
the day before yesterday----------------------------------------
the day after tomorrow---------------------------------------
then
that day
that night
the next(following) day
the day before
the night (week) before
the next week/month
before
two days before
in two day's time
直接引语变间接引语不变的情况
不变项说明直接引语间接引语
时态所转述的是科
学真理,格言等
已有表示明确
或具体过去的
时间状语
1.He said,"Practice makes
perfect."
2.Nick said,"I was born in May
1978."
1.He said that practice makes perfect.
2.Nick said that he was born in May,1978.
时间地点状语如转述发生在
当地,当时的
事,come,here
today, this
morning ,
tomorrow等不
必变。
She said, "I'll come here this
evening."
She said that she would come here this
evening.
语法讲义四、定语从句
在复合句中,用一个由主谓结构的陈述句修饰某一个名词或代词的句子叫定语从句。被定语从句所修饰的词叫先行词;引导从句的词叫关系词。(放在先行词与定语从句之间起连接作用;充当从句的某个成分;重复先行词的意义,故其数与先行词一致)
关系词先行
词从句成
分
例句备注
关系
who 人主语The boy who helped us is called Nick.
Do you like the kid who is crying?
Whom及that,
which在从句中
作宾语时,在口
语和非正式文体
中常可省,但介
词提前时,that whom 人宾语The girl whom I met looks like Lily.
I know the actor to whom you just talked.
that 人,
物
主语,
宾语
A plane is a machine that can fly.
I am not the fool that you thought me to be.
代词which 物主语,
宾语
This is a book which describes Canada.
The pen (which) you lent me is missing.
不能用,
whom,which不
可省。whose=of
whom指人;
whose=of which
指物
whose 人,
物
定语The room whose window is red is mine.
This is the scientist whose name is known all over the
world.
关系副词
when 时间
状语
Don't forget the time when we met her.
It happened on the day when I was out.
When可用in/on
which 代替where 地点This is the place where (= at/in which ) we lived last
year.
I recently went to the town where(=in which) I was
born.
where可用in、
at which 代替
why 原因The reason why(=for which) he didn't come was that he
missed his train.
why 可用for
which 代替
由介词+关系代词引导的定语从句
关系代词之前如果带介词,可能出于以下三种情况之一:1.由于先行词的要求;2.由于从句某个关键
词的搭配;出于语意表达的需要。
类别语法意义及特征例句
介词位于关系词前关系词which,whom在定语从句
中作介词的宾语时,有时可将介
词前置放在它们前面
1.Mr. Li is the person from whom you should learn.
2.He built a telescope through which he could study the sky.
3.Knowledge is the wings with which we fly to the heavens.
介词位于从句有关动词之后关系词如果是作“动词+介词”固
定词组的宾语,这个介词一般不
拆开,仍放在动词的后面。
1.The baby (whom/who/that) the nurse looks after is healthy.
2.Is this the necklace (which /that) you are looking for?
限制性定语从句与非限制性定语从句用法的区别
类别语法意义及特征例句
限制性定语从句限制性定语从句对先行词起限定作用,是先行词
不可或缺的定语,如去掉,主句的意思就会不完
整,不明确或失去意义。这种从句与主句的关系
十分密切,书写时不用逗号分开。
1.I have found the key that I lost last week.
2.It happened at the time when I left.
3.The person(whom) you talked to has come
again.
非限制性定语从句非限制性定语从句和主句的关系不十分密切,较
松散,从句只对先行词作附加的说明,如去掉,
主句的意思仍然清楚,这种从句和主句之间往往
用逗号分开,相当于一个插入语,翻译时可译成
一个并列句。不能用that引导。
1.Abraham Lincoln, who led the USA through
these years,was shot on April 14,1865 at a theatre
in Washington D.C.
2.Yesterday I met Li Ping, who seemed to be very
busy.
3.He lives in Boston, which is about five hours'
ride from here.
that 与Which,whom /who用法区别情况用法说明
Which 与that Whom 与that 可互用情况1.限制性定语从句中,先行词是物时,which,that两者可以互换
2.限制性定语从句中,先行词是人时,who/whom,that两者可以互换
只能用which,who/whom 的情况1.在非制性定语从句中,指物只能用which引导定语从句,which可以引导修饰整个主句的定语从句(代替前面主句),用who/whom指人。如:
She was awarded a gold medal,which the whole family considered a great honour.
只用that的情况1.all,everything,anything,nothing (something除外),little,much等不定代词作先行词时;
2.当先行词被序数词或形容词最高级以及first,last,only,very等修饰时;
3.当先行词既有人又有物时;
4.先行词被all,any,every,wach,few,little,no,some等修饰时;
5.先行词是who,which时;
6.在there, be 句型中;
7.介词提前;
8.在非限制性定语从句中
as 在定语从句中的用法
as 的用法 1.as可用作关系代词或关系副词,在所引导的限制性定语从句中,既可作主语、宾语,又可作状语。As多和such,the same连用,它代替的先行词既可以是人,又可以是物或整个句子。
2.在the same ...as 结构中,有时也有the same ...that,但两者句意不同。As表示“相似性”;
that表示“同一性”。
as 与who,which 的区别1.当先行词被so,as,such,the same所修饰时,关系代词用as;
2.As引导非限制性定语从句,可以指代后面整个主句,有“正如,好像”之意,其位置可以在主句前或主句后。而which引导的非限制性定语从句只能在主句后,并无as所表之意。
3.Such作先行词的修饰语,关系代词只能用as.
习惯用法as anybody can see
as has been said before
as often happens
as mentioned above
as has been pointed out
as we all know/ as is known to us as is often the case
as as may be imagined
as is hoped
as is usual with sb
高中英语语法练习-动词的虚拟语气
一、基础练习
1. ---I’ve bought a box of chocolates for our daughter.
---Oh, how good a dad! But she doesn’t like sweet things, _____that?
A. Don’t you know
B. Haven’t you known
C. Didn’t you know
D. Hadn’t you known
2. ---Have you decided already?---Yes, I ____at once.
A. have decided
B. decided
C. will decide
D. had decided
3. Glad to see you back. How long _____in Russia?
A. did you stay
B. have you stayed
C. were you staying
D. have you been staying
4. He works in a factory now, but he _____ on a farm for 20 years.
A. worked
B. has worked
C. had worked
D. had been working
5. Where on earth have you been? We _____ you back much earlier.
A. were expecting
B. are expecting
C. had expected
D. expect
6. ---I beg your pardon!---Oh, you _____ to me carefully. (just now)
A. didn’t
B. haven’t listened
C. don’t listen
D. weren’t listening
7. ---Mr. White didn’t come last night, did he?---No. We ______ .
A. had waited
B. have been waiting
C. were waiting D, had been waiting
8. ---Could you take a message for Mr. Green?
---Certainly. I _____ him about something at any case, so it _____ may other.
A. may see; isn’t
B. see; won’t be
C. will see; isn’t
D. will be seeing; won’t be
9. ---Who is the old man talking with your teacher? ---I don’t know. I _____ him before.
A. was never seeing
B. had never seen
C. never saw
D. wouldn’t see
10. I can guess you were in a hurry. You ______ your sweater inside out.
A. had worn
B. wore
C. are wearing
D. were wearing
11. Going out for tea with friends _____ increasingly popular during the past twenty years.
A. becomes
B. became
C. has become
D. had become
12. As far as we know, Tom spends at least as much time watching TV as he ______ .
A. does writing
B. writes
C. writing
D. does to write
13. ---I hope you enjoyed the film last night.
---How on earth do you know I went to a film? I ______ you.
A. won’t tell
B. didn’t
C. haven’t told
D. don’t tell
14. Turn off the tap please. The water _______ .
A. was wasted
B. wastes
C. is wasting
D. is wasted
15. ---I thought I asked you to fix the radio. ---Oh, I’m sorry. I ______ it right away.
A. am to do
B. will do
C. was about to do
D. am going to do.
16. ---The farmer president was caught at last. ---Really? Where _____ himself?
A. had hidden
B. has he hidden
C. was he hidden
D. has he been hiding
二、提高练习
1.Were it not for the snowy weather, we __________all right.
A. would be
B. would have been
C. were
D. may be
2. ________more careful, his ship would not have sunk.
A. If the captain were
B. Had the captain been
C. Should the captain be
D. If the captain would have been
3. If he _________ me tomorrow, I would let him know.
A. should call
B. should not have been able
C. were not able
D. are not able
4. If you asked your father, you ______________ permission.
A. may get
B. might get
C. should have called
D. maybe get
5. _____________today, he would get there by Friday.
A. Would he leave
B. Was he leaving
C. Were he to leave
D. If he leaves
6. ______I you, I would go with him to the party.
A. Was
B. Had been
C. Will be
D. Were
7. Had Paul received six more votes in the last election, he ____________our chairman now.
A. must have been
B. would have been
C. were
D. would be
8. ____________ the English examination I would have gone to the concert last Sunday
A. In spite of
B. But for
C. Because of
D. As for
9. Look at the terrible situation I am in! If only I _____________your advice
A. follow
B. would follow
C. had followed
D. have followed
10. If the horse won today, it _____________ thirty races in five years.
A. would have won
B. won
C. must have won
D. did have won
11. There is a real possibility that these animals could be frightened, _______a sudden loud noise.
A. being there
B. should there be
C. there was
D. there having been
12. If you hadn’t taken such a long time to get dressed, we’d______________ there by now.
A. be
B. circles
C. is circling
D. be circling
13. I wish I ___________ with her.
A. would be
B. am
C. was
D. were
14. The picture exhibition bored me to death. I wish I_______________ to it.
A. had not gone
B. have not gone
C. did not go
D. can not have gone
15. George would certainly have attended the meeting, ____________________ .
A. if he didn’t get a flat tire
B. if the flat tire hadn’t happened
C. had he not had a flat tire
D. had the tire not flattened itself
16. The teacher suggested that her students _____________ experiences with ESP.
A. write a composition on their
B. to write composition about the
C. wrote some compositions of his or her
D. had written any compositions for his
17. He speaks Chinese as fluently as if he ______________a Chinese.
A. were
B. had been
C. is
D. has been
18. Looking round the town, he felt as though he ______________ away for ages.
A. has been
B. was
C. is
D. had been
19. Most insurance agents would rather you ___________ anything about collecting claims until they investigate the situation.
A. do
B. don’t
C. didn’t
D. didn’t do
20. It is important that the TOEFL office ________ your registration.
A. will confirm
B. confirm
C. confirms
D. must confirm
21. Without electronic computers, much of today’s advanced technology __________.
A. will not have been achieved
B. have not been achieved
C. would not have been achieved
D. had not been achieved
22. He speaks Chinese as fluently as if he ____________a Chinese.
A. were
B. had been
C. is
D. has been
23. It is time that the government ______________measures to protect the rare birds and animals.
A. takes
B. took
C. has taken
D. taking
24. Some people are too particular about school records, insisting that every applicant ________ all diplomas from elementary school to university.
A. has
B. will have
C. should have
D. must have
25. He was very busy yesterday, otherwise he _____ to the meeting.
A. would come
B. came
C. would have come
D. had come
26. If I had seen the movie, I ______________ you all about it now.
A. would tell
B. will tell
C. have told
D. would have told
27. I had hoped that John _______ a year in Africa, but he stayed there only for three months.
A. spends
B. spent
C. would spend
D. will spend
28. It’s high time they____________ this road.
A. mend
B. mended
C. must have mended
D. will mend
29. It’s about time people______ notice of what women did during the war.
A. take
B. took
C. have taken
D. will take
30. He’s working hard for fear that he_____________ .
A. should fall behind
B. fell behind
C. may fall behind
D. would fall behind
31. In the past men generally preferred that their wives_______________ in the home.
A. worked
B. would work
C. work
D. were working
32. For a child to give up his less mature idea for a more mature one, it requires that the child _____ psychologically ready for the new idea.
A. is
B. were
C. be
D. would be
33. Your advice that_____________ till next week is reasonable.
A. she waits
B. she wait
C. wait she
D. she waited
34. It was essential that we lease before the end of the month.
A. sing
B. singed
C. had signed
D. were signing
35. I advised that the sick child ________ a hospital as soon as possible.
A. should send to
B. should be sent
C. be went to
D. must be sent to
36. The workers in the factory demanded that their pay ________ be 20 percent.
A. be raised
B. would be raised
C. raised
D. raise
37. The guard at the gate insisted that everybody ________ the rules.
A. obeys
B. obey
C. will obey
D. would obey
38. My suggestion is that she ________ more exercise, which will do a lot of
good to her.
A. takes
B. must take
C. take
D. took
39. If only I ________ driving before.
A. learn
B. learned
C. had learned
D. would learn
40. ________ she ________ yesterday, she would meet the famous singer today.
A. If, didn’t leave
B. Had not, left
C. Hadn’t, left
D. Didn’t, leave
答案
一、1---5 CBAAC 6---10 DDDCC CABCBA
二、1 ~ 20: ABABC DDBCA BADAC AADDB
21 ~ 40: CDBCC ACBBA CCBAC ABCCC
英语简单句的五种基本句型
简单句的五种基本句型讲解及习题 一、句子成份 英语句子成分有主语,谓语,宾语,宾语补足语,表语,定语,状语等。 顺序一般是主语,谓语,宾语,宾语补足语,而表语,定语,状语的位置要根据情况而定。 1、主语:表示句子主要说明的人或事物,一般位于句首。但在there be结构、疑问句(当主语不疑问词时)和倒装句中,主语位于谓语、助动词或情态动词后面。主语可由名词、代词、数词、不定式、动名词、名词化的形容词和主语从句等表示。例如: Country music has become more and more popular.(名词) We often speak English in class.(代词) One-third of the students in this class are girls.(数词) To swim in the river is a great pleasure.(不定式) Smoking does harm to the health.(动名词) The rich should help the poor.(名词化的形容词) When we are going to have an English test has not been decided.(主语从句) It is necessary to master a foreign language.(it作形式主语,真正的主语为后面的不定式) 2、谓语:谓语说明主语的动作,状态或特征。可以有不同的时态,语态和语气。 1)简单谓语: We study for the people. 2)复合谓语: I can speak a little English. We are reading books. He has gone to Beijing.. 3、表语: 它位于系动词(比如be)之后,说明主语身份,特征,属性或状态。 My sister is a nurse. Is it yours?(代词) The weather has turned cold.(形容词) The speech is exciting.(分词) Three times seven is twenty one?(数词) His job is to teach English.(不定式) His hobby(爱好)is playing football.(动名词) The ruler must be in your box.(介词短语) Time is up. The class is over.(副词) The truth is that he has never been abroad.(表语从句) 4、宾语: 宾语表示动作行为的对象,跟在及物动词之后,We like English. How many dictionaries do you have? I have five.(数词) They helped the old with their housework yesterday.(名词化形容词) It began to rain.(不定式短语) I enjoy listening to popular music.(动名词短语) I think(that)he is fit for his office.(宾语从句) 有些及物动词可以带两个宾语,往往一个指人,一个指物,指人的叫间接宾语,指物的叫直接宾语。 He gave me some ink. 有些及物动词的宾语后面还需要有一个补足语,意思才完整,宾语和它的补足语构成复合宾语。如:We make him our monito r(班长). 5、宾补: 就是宾语补足语,就是补充说明宾语的 I see you crossing the street His father named him David.(名词) They painted(涂漆) their boat white.(形容词) Let the fresh(新鲜的) air in.(副词) You mustn’t force him to lend his money to you.(不定式短语) We saw her entering the room.(现在分词) We found everything in the lab in good order.(介词短语) 6、定语: 在句中修饰名词或代词的成分叫定语。 He is a new student. 但副词,动词不定式,介词短语等作定语时,则放在被修饰的词之后。 The bike in the room/over there/ is mine. Guilin is a beautiful city.(形容词) China is a developing(发展中) country; America is a developed(发达) country.(分词)
英语的五种基本句型到复杂句型
简单句和复合句 一、主系表复杂难句 Vitamins are organic compounds. Vitamins are organic compounds necessary for the normal growth of life. Vitamins are organic compounds necessary for the normal growth of life of animals, including man. Vitamins are organic compounds necessary in small amounts in the diet for the normal growth of life of animals, including man. 维他命是人和动物在日常的饮食生活中所需的一种微量的有机化合物。 主谓 This trend began during the Second World War. This trend began during the Second World War, when several governments came to this conclusion. This trend began during the Second World War, when several governments came to this conclusion that the specific demands cannot generally foreseen in detail. This trend began during the Second World War, when several governments came to this conclusion that the specific demands that a government wants to make of its scientific establishment cannot generally foreseen in detail. 这种趋势发生在二战时,当时许多政府总结出:政府对科学建立的具体要求并不能被普遍的详细预见 主谓宾 The emphasis helped to obscure the great importance. The emphasis given by both scholars and statesmen helped to obscure the great importance. The emphasis given by both scholars and statesmen to the presumed disappearance of the American frontier helped to obscure the great importance. The emphasis given by both scholars and statesmen to the presumed disappearance of the American frontier helped to obscure the great importance of changes in the conditions and consequences of international trade. 学者和政治家同时强调:假设美国边境的消失并不能对国际贸易的状况和影响产生重大的改变。 The emphasis given by both scholars and statesmen to the presumed disappearance of the American frontier helped to obscure the great importance of changes in the conditions and consequences of international trade that occurred during the second half of the nineteenth century. 学者和政治家同时强调:假设美国边境的消失并不能对在十九世纪下半年期间的国际贸易的状况和影响产生重大的改变。
简单句的五种基本句型教案
教学讲义
三、主语+系动词+表语(S+V+P) [例句]1. This is an English-Chinese dictionary. 这是本英汉辞典。 2. The cake smells good. 蛋糕味道很好。 3. Everything looks different. 一切看来都不同了。 4. He is growing tall and strong. 他长得又高又壮。 5. The trouble is that they are short of money. 麻烦的是他们缺少钱。 6. Our well has gone dry. 我们的井干枯了。 7. His face turned red. 他的脸红了。 [分析]这些句子有一个共同的特点:谓语动词都不能表达一个完整的意思,必须加上一个表明主语身份或状态的表语构成复合谓语,才能表达完整的意思。这类动词叫做连系动词。系动词分两类:be, look, keep, seem等属一类,表示情况;get, grow, become, turn等属另一类,表示变化。be 本身没有什么意义,只起连系主语和表语的作用。其它系动词仍保持其部分词义。 四、主语+及物动词+间接宾语+直接宾语(S+V+IO+DO) [例句]1. He brought you a dictionary. 他给你带来了一本字典。 2. She cooked her husband a delicious meal. 她给丈夫做了一顿美餐。 3. I showed him my pictures.我给他看我的照片。 4. I gave my car a wash.我洗了我的汽车。 5. I told him that the bus was late. 我告诉他汽车晚点了。 6. He showed me how to run the machine.他教我开机器。 [分析]这些句子有一个共同的特点:谓语动词必须跟有两个宾语才能表达完整的意思,故这类动词被称作双宾语动词。这两个宾语一个是动作的直接承受者,另一个是动作的间接承受者。一般来说指人的宾语叫间接宾语,指物的宾语叫直接宾语。通常
五种简单句的基本句型练习题
英语中的五种基本句型练习题 一)判断这些句子的类型并理解be 动词的用法(连系动词/助动词)1.The boy is asleep (_____ 式_ ) 2.The boy is sleeping. (__ 式_ )3.The boy is playing the guitar. (_____ 式) 4.He is playing happily. ( ________________________________ 式) 5.His music is very beautiful. (____ 式) 6.It is beautiful music. ( ______________________________ 式) 二)判断这些句子的类型 1. Sheis a very good girl .( ________________________ ___式_ ) (__语)(__词)(___语) 2. Thegirl is very good.(____ __式) (__语)(__词)(___语) 3. They I laughed.( ____ 式 __)_ (__语)(__词) 4. The kites I fly in the sky.(_ 式) (__语)(__词) 5. I I bought a new bike.(___ 式) (__语)(__词)(__语) 6. He I plays volleyball.( ___ 式) (__语)(__词)(__语) 7. She I told me a story.( ________________________ 式)(__语)(__词)(__语)(__语)
简单句的五种基本句型
简单句的五种基本句型 只包含一个主谓结构的句子叫简单句。简单句有五种基本句型结构: ★主语+谓语(S+V) 谓语是不及物动词,其后可加副词、介词短语等。例如: They sat together quietly. 他们静静地坐在一起。 The meeting begins at nine. 会议9点开始。 ★主语+谓语+宾语(S+V+O) 谓语是及物动词,宾语通常是名词、代词、动词不定式、V-ing形式等。例如: He doesn’t like the movie. 他不喜欢这部电影。 Do you know them, Li Ming? 李明,你认识他们吗? ★主语+系动词+表语(S+V+P) 常见的系动词有be, look, sound, smell, taste, feel, become, turn, get等,表语通常是形容词、名词、代词等。例如: Your new watch looks very nice. 你的新手表看起来很漂亮。 That sounds a good idea. 听起来是个好主意。 ★主语+谓语+间接宾语+直接宾语(S+V+InO+DO) 某些动词后的间接宾语可改为to引导的短语,如:give, lend, pass, show, send等;某些动词后的间接宾语可改为for引导的短语,如:buy, choose, cook, make, sing等。例如:Can you pass me the book? = Can you pass the book to me? 你能把书递给我吗? She sang us an English song. = She sang an English song for us. 她为我们唱了一首英语歌。★主语+谓语+宾语+宾语补足语(S+V+O+OC) 这类谓语动词主要有find, keep, feel, wish, think, name, call, ask, advise, teach, want, notice 等。宾语补足语用来补充说明宾语的动作或状态,通常是形容词、名词、动词不定式、介词短语等。例如: He found his new job very interesting. 他发现他的新工作很有趣。 Mr. Li asked us to write a report. 李老师让我们写一份报告。 即时操练 ( ) 2. Can you lend me your dictionary? ( ) 3. Mum is cooking in the kitchen. ( ) 4. Danny made all of us laugh.
(完整word版)简单句的五种基本句型
简单句的五种基本句型 一、句子分为简单句、并列句和复合句。 ①简单句的基本形式是由一个主语加一个谓语构成,其它各种句子形式都是由此句型发展而来。 ②并列句是由两个或两个以上的简单句用并列连词连在一起构成的句子。并列连词有:and, but, or, so等。 ③复合句是由主句+从句构成。由从属连词连接,如because, if, when, while, until, after, before, as soon as等。分为名词性从句,形容词性从句(即定语从句),副词性从句(即状语从句)三大类。其中最著名的是宾语从句,定语从句和状语从句。 二、简单句的五个基本句式: ①主谓②主谓宾③主谓双宾④主谓宾补⑤主系表 主语: 句子说明的人或事物。 谓语:说明主语的动作、状态和特征。 表语:系动词之后的成分,表示主语的性质、状态和特征。 宾语:1. 动作的承受者——动宾。2. 介词后的名词、代词和动名词——介宾。 补语:宾补,对宾语的补充。主补,对主语的补充。 判断下列句子是那种结构: 1. He is swimming. 2. It made him angry. 3. The little boy is asking the teacher questions. 4. She is young. 5. My mom bought me a beautiful gift. 6. He kept his eyes closed. 7. He told us an exciting story. 8. We must keep our classroom tidy and clean. 9. I heard the baby crying in the sitting room. 10.Can you push the window open? 11. He seemed tired. 1.主谓 2.主谓宾补 3.主谓双宾 4.主系表 5.主谓双宾 6.主谓宾补 7.主谓双宾 8.主谓宾补 9.主谓宾补10.主谓宾补11.主系表
简单句的五种基本句型
简单句的五种基本句型 句子最重要的部分是主语和谓语,主语是句子的中心, 谓语是主语的动作或者主语所处的状态。简单句的骨架 就是一个主谓结构,共有五种句型,这五种句型是写作 学习的核心内容,因为所谓的复杂的句子,即并列句、主从复合句,全部是简单句组合或相套而来。五种 简单句句型如下: 一、主语+谓语(不及物动词) 该句型常用来表示主语的动作或状态。其特点为:句子的谓语动词都能表达完整的意思,这类动词叫做不及物动词,后面可以跟副词、介词短语、状语从句等修饰。 The birdis flying high in the sky. 主语谓语 鸟儿在天空中翱翔。 We'll gather at the Students' Club at 8 p.m.this Friday,after the evening classes. 本周五晚自习之后我们将于8:00 在学生俱乐部集合。 二、主语+谓语(及物动词)+宾语 该句型特点为:谓语动词均为实义动词,都是主语发出的动作,但不能表达完整的意思,必须跟有一个宾语(宾语可以由名词、代词、动名词、不定式等来充当),即动作的承受者,才能使意思完整。 We all possessthe same chance. 主语谓语宾语 我们拥有同样的机会。 We must learn to handle conflicts calmly and wisely. 我们必须学会平和地、理智地处理冲突。(不定式短语to handle conflicts作宾语) [名师指津]该句式的谓语动词要用及物动词。如果是不及物动词,后面一定要跟介词构成及物词组。 Some of the students are always longing for holidays. 有些学生总是渴望着放假。 三、主语+系动词+表语 这就是常说的主系表结构。此句式侧重说明主语是什么或怎么样,谓语动词需用系动词(主要是be动词),表语多为形容词,也可以是名词、介词短语、不定式及分词等。 In other words,wearethe master of our own future. 主语系动词表语 换句话说,我们是自己未来的掌控者。Conflicts with others are common in everyday life. 在日常生活中,与其他人发生冲突是正常的。 [名师指津]除了be动词外,还有一些动词也可以用作系动词: (1)表感官的动词:feel,smell,taste,sound,look,appear等。 (2)表转变、变化的动词:become,get,grow,turn,go等。 (3)表延续的动词:remain,keep,stay,等。 The problem remains to be settled. 这个问题有待解决。 四、主语+谓语(及物动词)+间接宾语+直接宾语 该句型中的谓语动词必须跟两个宾语才能表达完整的意思。一个是表示人的间接宾语;一个是表示物的直接宾语。间接宾语一般在前面,直接宾语在后面。 He gave me some beautiful photos. 主语谓语间接宾语直接宾语 他给了我一些漂亮的照片。 [名师指津]双宾语结构只能跟在某些及物动词后面,主要有以下三类动词: (1)give,tell,teach,write,bring,lend,hand,show,offer,send,pay,pass,return等。这一类动词后的间接宾语可以用介词to引导的短语来表示。 Please hand him a book! =Please hand a book to him! 请递给他一本书。 (2)buy,do,get,fetch,save,make,sing,choose等。这一类动词后的间接宾语可以用介词for引导的短语来表示。 Her father bought her a bike. =Her father bought a bike for her. 她的父亲给她买了一辆自行车。 (3)ask,answer,take,cost等。这一类动词无法改变结构形式。 The car cost me 2,000 yuan for the repair. 这次修车我花了两千元。 五、主语+谓语(及物动词)+宾语+宾语补足语 该句型中的动词虽然是及物动词,但是只跟一个宾语还不能表达完整的意思,必须加上一个补充成分来说明宾语,才能使意思完整。宾语补足语是用来补充说明宾语的情况的,直接跟在宾语之后。 We elected him monitor of our class. 主语谓语宾语宾补 我们选举他为班长。 As a high school student,I consider English a very important subject. 作为一名中学生,我认为英语是一门非常重要的科目。
简单句共有五种基本句型
简单句 一、1. 五种基本句型 1. S+ V 即:主语+不及物动词 My head aches. Everybody laughed. 不及物动词加一个介词后构成的动词短语可以加宾语。如:agree with lie in, work at, belong to, come across, to etc. 2、S+ V+ P 即:主语+连系动词+表语 English is very easy. He looks tired. 常见的系动词(link v. )有be, look, seem, appear, sound, feel, taste, smell grow, get, fall ill / asleep, stand / sit still , become, turn etc. 3、S+ V+ O 即:主语+及物动词+宾语 She likes the flowers. Dad bought a car. 4、S+ V + INO + DO即:主语+及物动词+间接宾语+直接宾语常见的须带双宾语的动词有give, ask, bring, offer, send, pay, lend, show, tell, buy, get, rob, warn etc. He told her the news. = He told the news to me. My father bought me a bike. = My father bought a bike for me. 5、S+ V+ O + OC 即:主语+及物动词+宾语+宾语补语常带宾语补足语的词有形容词、副词、介词短语、名词、不定式、现在分词、过去分词。常见的动词有find, make, leave, get ,see, etc. He told me to stay home. The smell made him sick. 说明:上述各例都简化到了最低限度,在此基础上,我们可以加上一些修饰成分使句子变得更复杂,表达更丰富的内容。如: In fact, English is very easy to teach. She likes the flowers very much. He told her the news on the home. 二、疑问句 1. 一般疑问句:Do you like reading novels? 2. 特殊疑问句: Mom is coming. What present do you expect she has got for your birthday. 3. 选择疑问句: Will you stay home or go sightseeing on National Day?
简单句的五种基本句型典型例句
简单句的五种基本句型典型例句 五种基本句型结构 一、句型1:Subject (主语) +Verb (谓语) (谓语为不及物动词) The red sun rises in the east.红彤彤的太阳从东方升起来。 Lucy and Mary get up early every morning.露西和玛丽每天早上很早就起床。 His parents have worked in the company for ten years. 他的父母在这家公司工作十年了。 What he said does not matter.他说的话不重要。 They had to travel by boat.他们不得不乘船旅行。 二、句型2:Subject (主语) +Link. V(系动词) +Predicate(表语) Our English teacher is thirty years old.我们的英语老师30岁了。 The cake tastes delicious.这个蛋糕吃起来很可口。 The potatoes went bad in the field.土豆在地里就坏了。 They seemed very happy together.他们在一起好像很幸福。 It gets colder and colder.天气越来越冷了。 The leaves have turned yellow. 树叶已经变黄了。 三、句型3:Subject(主语) +Verb (谓语)(谓语为及物动词)+Object (宾语) He put the dictionary in the backpack. 他把词典放进了背包里。 I saw her just now and she was doing her homework in the classroom.我刚 才看到她了,她正在教室做作业。 They haven’t decided when and where to hold the party. 他们还没有决定什么时候、在哪儿举办这次聚会。
五种基本句型
句子的成分 一:句子的成分 组成句子的各个部分叫做句子的成分。句子成分包括:主语、谓语、表语、宾语(直接宾语、间接宾语)、宾语补足语、定语和状语。主语和谓语是句子主体部分(在英文中一般的句子必须有主语和谓语)。表语、宾语和宾语补足语是谓语里的组成部分。其他成分如定语和状语是句子的次要部分。 下面我们分别讲述一下句子的各个成分: 1): 主语 主语是谓语讲述的对象,表示所说的“是什么”或“是谁”。一般由名词、代词、不定式或相当于名词的词或短语来充当。它在句首。 We study in No.1 Middle School.(讲述“谁”~) The classroom is very clean. (讲述“什么”很干净) Three were absent.(数词作主语) To teach them English is my job. (不定式作主语) 注意 不定式作主语时,常用形式主语it句型,因此左例可变为It is my job to teach them English. (真正的主语是to teach them English.) 2):谓语 说明主语“做什么”,“是什么”或“怎么样”。 谓语(谓语部分里主要的词)必须用动词。谓语和主语在人称和数两方面必须一致。它在主语后面。 His Parents are doctors. (系动词作谓语) She looks well.(系动词作谓语) We study hard.(实义动词作谓语) He can speak English. (情态动词和实义动词作谓语) 3):表语 表语说明主语“是什么”或者“怎么样”,由名词、形容词、副词、介词、不定式及相当于名词或形容词的词或短语来担任。它的位置在系动词后面。 You look younger than before.(形容词作表语) I am a teacher.(名词作表语) Everybody is here.(副词作表语) They are at home now.(介词短语作表语) My job is to teach them English.(不定式作表语) 4):宾语
初中英语简单句的五种基本句型
初中英语简单句的五种基本句型 简单句的五种基本句型。 简单句的五种基本句型,对于提高同学们的听、说、读、写、译能力有至关重要的作用。下面我们就一起再来回顾一下简单句的五种基本句型吧~简单句的五种基本句型包括: a. 主语+连系动词+表语 (S+ Link-V+P) 此句型中的谓语动词为连系动词,作表语成分的有形容词、名词、代词、分词、不定式介词短语等。常见的系动词有be, feel, taste, smell, sound,seem, look(看起来),get(变),become(变),turn(变)等。 )The story sounds interesting. 那个故事听起来很有趣。 1 2) Her dream has come true. 她的梦想实现了。 3)My books are on the desk. 我的书在书桌上。 4)The food seems to be nice. 这食物似乎不错 本句型的特点是"连系动词+表语"二者缺一不可。例如"The teacher angry"和"We in the classroom." She sixteen.都不成其为一个句子。汉语中形容词、介词短语、数词都可以用作谓语,但是英语中它们不能单独作谓语,它们前面必须加上一个系动词才能构成谓语。 b.主语+不及物动词 (S+V) 在此句型中,谓语动词是不及物动词,其后没有宾语。因为此句型中的动词表达的意思已经很明确,所以不需要跟宾语。有时为了表示动作发生的频率、程度、原因、结果、目的、场所、时间等,可以带状语修饰动词。如: 1)My head aches. 我头疼。 2)The students are listening( 学生们正在听。 3) We study hard. 我们努力学习。 4) The red sun rises in the east. 一轮红日从东方升起。
五种基本句型及练习
基本句型一: 主+系+表 此句型的句子有一个共同的特点:句子谓语动词都不能表达一个完整的意思,必须加上一个表明主语身份或状态的表语构成复合谓语,才能表达完整的意思.这类动词叫做连系动词.系动词分两类:be, look, keep, seem等属一类;get, grow, become, turn等属另一类,表示变化.be 本身没有什么意义,只起连系主语和表语的作用.其它系动词仍保持其部分词义. 1. This │is │an English-Chinese dictionary. 这是本英汉辞典. 2. The dinner │smells │good. 午餐的气味很好. 3. His face │turned │red. 他的脸红了 4. Everything │looks │different. 一切看来都不同了. 5. He │is growing │tall and strong. 他长得又高又壮. 基本句型二: 主+谓(不及物动词) 此句型的句子有一个共同特点,即句子的谓语动词都能表达完整的意思.这类动词叫做不及物动词,后面可以跟副词,介词短语,状语从句等. 1. The sun │was shining. 太阳在照耀着. 2. The moon │rose. 月亮升起了. 3. What he said │does not matter. 他所讲的没有什么关系. 4. They │talked for half an hour. 他们谈了半个小时. 5. The pen │writes smoothly. 这支笔书写流利. 基本句型三: 主+谓(及物)+宾语 此句型句子的共同特点是:谓语动词都具有实义,都是主语产生的动作,但不能表达完整的意思,必须跟有一个宾语,即动作的承受者,才能使意思完整.这类动词叫做及物动词. 1. Who │knows │the answer?谁知道答案? 2. He │enjoys │reading. 他喜欢看书. 3. He │admits │that he was mistaken. 他承认犯了错误. 基本句型四: 主+谓(及物)+双宾(间宾+直宾) 此句型的句子有一个共同特点:谓语动词必须跟有两个宾语才能表达完整的意思.这两个宾语一个是动作的直接承受者,另一个是动作的间接承受者.通常这一间接承受者用一个介词来连接,当动作的间接承受者在动作的直接承受者之前时,这一介词往往被省略. 1. She │ordered │herself │a new dress. 她给自己定了一套新衣裳. 2. I │showed │him │my pictures. 我给他看我的照片. 3. He │bought │you │a dictionary.他给你买了一本字典. 4. I │told │him │that the bus was late. 我告诉他汽车晚点了. 5. He │showed │me │how to run the machine. 他教我开机器. 基本句型五: 主+谓(及物)+复合宾语(宾+宾补) 此句型的句子的共同特点是:动词虽然是及物动词,但是只跟一个宾语还不能表达完整的意思,必须加上一个补充成分来补足宾语,才能使意思完整. 1. They │painted │the door │green. 他们把门漆成绿色. 2. They │found │the house │deserted. 他们发现那房子无人居住. 3. What │makes │him │think so?他怎么会这样想?. 4. We │saw │him │out. 我们送他出去. 5. He │asked │me │to come back soon. 他要我早点回来. 6. I │saw │them │getting on the bus at that time. 我看见他们当时在上了那辆公共汽车.
五种基本句型和简单句详细讲解
五种基本句型和简单句详细讲解 英语的句子按使用目的可分为陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句。 1)陈述句(Declarative Sentences):说明一个事实或陈述一种看法。有肯定句和否定句之分。 2)疑问句(Interrogative Sentences):提出问题。有以下四种: a. 一般疑问句(General Questions): Can you finish the work in time? 你能按时完成工作吗? b. 特殊疑问句(W Questions; H Questions): Where do you live?你住那儿? How do you know that? 你怎么知道那件事? c. 选择疑问句(Alternative Questions): Do you want tea or coffee? 你是要茶还是要咖啡? d. 反意疑问句(Tag-Questions): He doesn't know her, does he? 他不认识她,对不对? 3)祈使句(Imperative Sentences):提出请求,建议或发出命令,例如: Sit down, please.请坐。Don't be nervous!别紧张! 4)感叹句(Exclamatory Sentences):表示说话人惊奇、喜悦、愤怒等情绪,例如: What good news it is!多好的消息啊! A. 简单句的五种基本句型。 简单句的五种基本句型,对于提高同学们的听、说、读、写、译能力有至关重要的作用。下面我们就一起再来回顾一下简单句的五种基本句型吧!简单句的五种基本句型包括: a. 主语+连系动词+表语(S+ Link-V+P) 此句型中的谓语动词为连系动词,作表语成分的有形容词、名词、代词、分词、不定式介词短语等。常见的系动词有be, feel, taste, smell, sound, seem, look(看起来),get(变),become(变),turn(变)等。 1)The story sounds interesting. 那个故事听起来很有趣。 2) Her dream has come true. 她的梦想实现了。 3)My books are on the desk. 我的书在书桌上。
英语中五种基本句型详解
英语中五种基本句型详解 句子是由主语、谓语动词、表语、宾语、宾语补足语等组成的。英语句子有长有短,有简有繁,似乎千变万化,难以捉摸,但其实只有五种基本句型。所有英语句子都可以看成是这五种基本句型的扩大、组合、省略或倒装。因此掌握这五大句型,是掌握其他各种英语句子结构的基础。 英语句子依其组合方式可分为以下五种基本句型,句子成分的表示法为: S: Subject(主语), V: Verb(动词), O: Object(宾语), IO : Indirect Object (间接宾语), DO: Direct Object (直接宾语) , P: Predicative(表语), OC:Object Complement(宾语补足语)。 五种基本句型见下表 种类句型例句
第1种S+V (主语+不及物动词) We work. (不及物) 第2种 S+V+O (主语+及物动词+宾语) He plays (及物) the piano. 第3种 S+V+P (主语+系动词+表语) We are (系动词) students. 第4种 S+V+IO+DO (主语+及物动词+间接宾语+直接宾语) She gave (及物) me a pen. 第5种 S+V+O+OC (主语+及物动词+宾语+宾语补足语)He made (及物) the boy laugh. 说明:(S=主,V=谓,O=宾,P=表,IO=间宾,DO=直宾,OC=宾补) 一、第1种句型:S+V(主语+不及物动词) 1、Birds fly. 鸟飞。 主语+谓语 (不及物动词) 2、He runs in the park. 他在公园里跑。
简单句的五种基本句型
简单句的五种基本句型 简单句是英语中的基本句子,了解和掌握这五种基本句型对学好英语极为重要。这五种基本句型是: 1.主语+不及物动词(主谓结构) 本结构是由主语加不及物动词构成,常用来表示主语的动作。此句型中不及物动词的常用法: (1)一般表达型。此类不及物动词常与表示时间、距离、重量、价值等的副词修饰语连用。 如:They worked day and night. 他们夜以继日地工作。 (2)主动形式表示被动含义型。此类动词常见的有:read, sell, wash, write, clean 等。 如:The theatre tickets sold well. 戏票很畅销。 This kind of cloth washes well.这种布料很容易洗。 2.主语+系动词+表语(主系表结构) 本结构是由"主语+系动词+表语"组成,主要用以说明主语的特征、类属、状态、身份等。此句型中常见的系动词:be, become, come, get, smell, taste, feel, sound, remain, stay, appear, go, turn, fall, keep等。 (1)主语+系动词+形容词(作表语) 如:That argument sounds reasonable. 那个论据听起来有道理。 It feels good to be home. 在家的感觉真好。 (2)主语+系动词+名词(作表语) 如:Later he became a scientist. 他后来成为一个科学家。 He is a student. 他是个学生。 (3)主语+系动词+副词、介词短语或反身代词(作表语) 如:He is near. 他在附近。 This is of importance. 这很重要。 You’re not looking yourself today. 今天你看上去气色不太好。 3. 主语+及物动词+宾语(主谓宾结构) 此结构是由"主语+谓语+宾语"构成。其中的谓语动词须是及物动词(短语),宾语须是名词或相当于名词的成分。 (1)主语+及物动词+名词或代词(作宾语) 如:He raised his arms above his head. 他把手臂举过头顶。 Will you spend your holidays abroad this year? 你今年去国外度假吗? (2)主语+及物动词+动名词(作宾语)。此类及物动词(短语)有:advise, consider, avoid, mind, miss, suggest, finish, practise, imagine, enjoy, delay, escape, feel like, put off, insist on, give up, can’t help, stick to等。 如:I suggested taking a walk. 我建议去散步。 You should not give up studying. 你不该放弃学习。 (3)主语+及物动词+不定式(作宾语)。此类及物动词有:afford, agree, ask, expect, hope, want, wish, manage, pretend, decide, determine, learn, offer, plan, refuse等。 如:I hope to go to college. 我希望上大学。 The firm could not afford to pay such large salaries. 公司无法支付如此巨额的工资。
