审计报告英文版(全)

AUDITOR’S REPORT
Yue Hua Shen / Yan Zi (2014) No. 0002
ICPA filing number: 020201401000420
To all shareholders of ****** Co., Ltd:
We have audited the accompanying financial statements of ****** Co., Ltd (“Your Company”), which comprise the balance sheet as of 31 December 2013, the income statement,statement of changes in owner's equity and cash flow statement for the year then ended, and notes to the financial statements.
I. Management’s responsibility for the financial statements
Management of your Company is responsible for the preparation and fair presentation of financial statements. This responsibility includes: (1) in accordance with the Accounting Standards for Business Enterprises and its relevant provisions, preparing the financial statements and reflecting fair presentation; (2) designing, implementing and maintaining the necessary internal control in order to free financial statements from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error.
II. Auditors' responsibility
Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audit. We conducted our audit in accordance with Chinese Certified Public Accountants Auditing Standards. Those standards require that we comply with ethical requirements and plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance whether the financial statements are free from material misstatement.
An audit involves performing procedures to obtain audit evidence about the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. The procedures selected depend on the auditors' judgment, including the assessment of the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to fraud or error. In making those risk assessments, we consider the internal control relevant to the preparation and fair presentation of the financial statements in order to design audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the internal control. An audit also includes evaluating the appropriateness of accounting policies used and the reasonableness of accounting estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements.
We believe that the audit evidence we have obtained is sufficient and appropriate to provide a basis for our audit opinion.
III. Opinion
In our opinion, the financial statements of your Company have been prepared in accordance with the Accounting Standards for Business Enterprise and its relevant provisions in all material respect, and present fairly the financial position of your Company as of 31 December 2013, and the results of its operations and cash flows for the year then ended.
Guangdong Huaxin Accounting Firm (general partner)
Guangdong, China
Chinese Certified Public Accountant:
Chinese Certified Public Accountant:
January 3, 2014
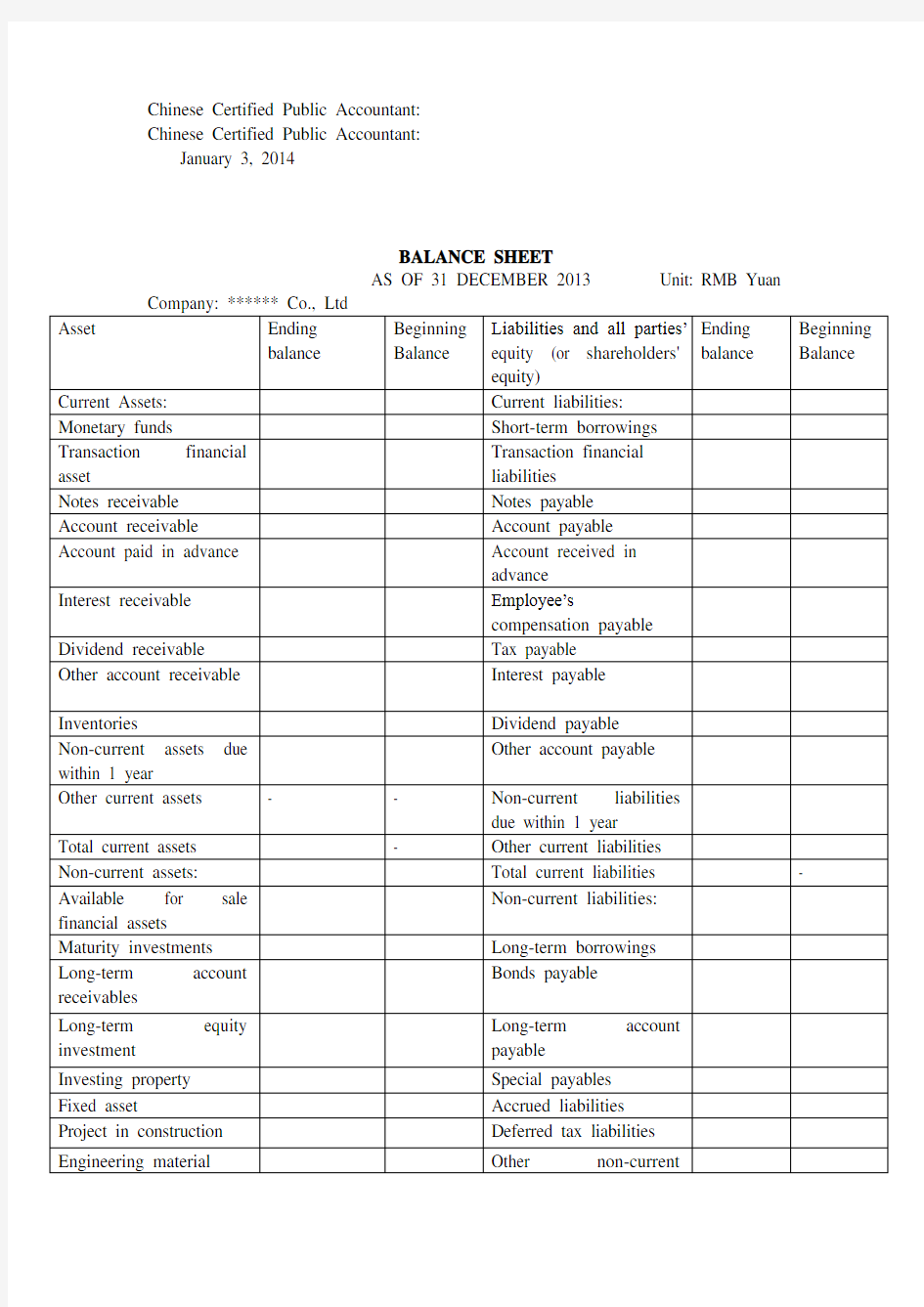
BALANCE SHEET
AS OF 31 DECEMBER 2013 Unit: RMB Yuan
INCOME STATEMENT
FOR THE YEAR ENDED 31 DECEMBER 2013 Unit: RMB Yuan
CASH FLOW STATEMENT
FOR THE YEAR ENDED 31 DECEMBER 2013 Unit: RMB Yuan
STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN OWNERS’ EQUITY FOR THE YEAR ENDED 31 DECEMBER 2013
department:
****** CO., LTD
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2013
(All amounts in RMB Yuan) I. Company Profile
******* Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as the "Company") is a limited liability company (Sino-foreign joint venture) jointly invested and established by **** Co., Ltd. and ******* Limited on 24 June 2013. On December 26, 2013, the shareholders have been changed to ***** CO., LTD and ******* LIMITED.
Business License of Enterprise Legal Person License No.:
Legal Representative:
Registered Capital: RMB (Paid-in Capital: RMB )
Address:
Business Scope: Financing and leasing business; leasing business; purchase of leased property from home and abroad; residue value treatment and maintenance of leased property; consulting and guarantees of lease transaction (articles involved in the industry license management would be dealt in terms of national relevant stipulations) II. Declaration on following Accounting Standard for Business Enterprises
The financial statements made by the Company are in accordance with the requirements of Accounting Standard for Business Enterprises, which reflects the financial position, financial performance and cash flow of the Company truly and completely.
III. Basic of preparation of financial statements
The Company implements the Accounting Standards for Business Enterprises (…Finance and Accounting [2006] No. 3”) issued by the Ministry of Finance on February 15, 2006 and the successive regulations. The Company prepares its financial statements on a going concern basis, and recognizes and measures its accounting items in compliance with the Accounting Standards for Business Enterprises – Basic Standards and other relevant accounting standards, application guidelines and criteria for interpretation of provisions as well as the significant accounting policies and accounting estimates on the basis of actual transactions and events.
IV. The main accounting policies, accounting estimates and changes
Fiscal year
The Company adopts the calendar year as its fiscal year from January 1 to December 31.
Functional currency
RMB was the functional currency of the Company.
Accounting measurement attribute
The Company adopts the accrual basis for accounting treatments and double-entry bookkeeping of borrowing for financial accounting. The historical cost is generally as the measurement attribute, and when accounting elements determined are in line with the requirements of Accounting Standards for Enterprises and can be reliably measured, the replacement cost, net realizable value and fair value can be used for measurement.
Accounting method of foreign currency transactions
The Company?s foreign currency transactions adopt approximate spot exchange rate of the transaction date to convert into RMB in accordance with systematic and rational method; on the balance sheet date, the foreign currency monetary items use the spot exchange rate of the balance sheet date. All balances of exchange arising from differences between the balance sheet date spot exchange rate and the initial recognition or the former balance sheet date spot exchange rate, except that the exchange gains and losses arising by borrowing foreign currency for the construction or production of assets eligible for capitalization are transacted in accordance with capitalization principles, are included in profit or loss in this period; the foreign currency non-monetary items measured at historical cost will still be converted with the spot exchange rate of the transaction date.
The standard for recognizing cash equivalent
When making the cash flow statement, cash on hand and deposits readily to be paid will be recognized as cash, and short-term (usually no more than three months), highly liquid and readily convertible to known amounts of cash with insignificant risk of changes in value are recognized as cash equivalent.
Financial Instruments
Classification, recognition and measurement of financial assets
- The company at the time of initial recognition of financial assets divides it into the following four categories: financial assets measured at fair value with changes included in the profit or loss of this period, loans and receivables, financial assets available for sale and held-to-maturity investments. Financial assets are measured at fair value when initially recognized. Relevant transaction costs of financial assets measured at fair value with changes included in the profit or loss of this period are recognized in profit or loss of this period, and relevant transaction costs of other categories of financial assets are recognized in the amount initially recognized.
-- Financial assets measured at fair value with changes included in the profit or loss of this period refer to the short-term sales financial assets, including financial assets held for trading or financial assets measured at fair value with changes included in the profit or loss of this period designated upon initial recognition by the management. Financial assets measured at fair value with changes included in the profit or loss of this period are subsequently measured at fair value, and the interest or cash dividends obtained during the holding period will be recognized as investment income, and the gains or losses of the change in fair value at the end of this period are recognized in the profit or loss in this period. When it is disposed, the difference between the fair value and the initial recorded amount is recognized as investment income, while adjusting gains from changes in the fair value.
--Loans and receivables: the non-derivative financial assets without the price in an active market and with fixed and determinable recovery cost are classified as loans and receivables. Loans and receivables adopt the effective interest method and take amortized cost for subsequent measurement, and gains or losses arising from derecognition, impairment or amortization are included in the profit or loss of this period.
-- Financial assets available for sale: including non-derivative financial assets available for sale recognized initially and other non-derivative financial assets except for loans and receivables, held-to-maturity investments and trading financial assets. Financial assets available for sale are subsequently measured at fair value, and interest or cash dividends obtained during the holding period will be recognized as investment income, and gains or losses arising from the changes in fair value at the end of this period are recognized directly in owners' equity until the financial asset is derecognized or impaired and then is recognized as the profit or loss in this period.
-- Held-to-maturity investments: the non-derivative financial assets with clear intention and ability to hold to maturity by the management of the company, a fixed maturity date and fixed or determinable payments are classified as held-to-maturity investments. Held-to-maturity investments adopt the effective interest method and take amortized cost for subsequent measurement, and gains or losses arising from derecognition, impairment or amortization are included in the profit or loss of this period.
Classification, recognition and measurement of financial liabilities
- The company at the time of initial recognition of financial liabilities divides it into the following two categories: financial liabilities measured at fair value with changes included in the profit or loss of this period and other financial liabilities. Financial liabilities are measured at fair value when initially recognized. Relevant transaction costs of financial liabilities measured at fair value with changes included in the profit or loss of this period are recognized in profit or loss of this period, and relevant transaction costs of other financial liabilities are recognized in the amount initially recognized.
-- Financial liabilities measured at fair value with changes included in the profit or loss of this period include the trading financial liabilities and financial liabilities measured at fair value with changes included in the profit or loss of this period designated upon initial recognition. Financial liabilities are subsequently measured at fair value, and the gains or losses of the change in fair value are recognized in the profit or loss in this period.
-- Other financial liabilities: adopting the effective interest method and taking amortized cost for subsequent measurement. The gains or losses arising from derecognition or amortization is included in the profit or loss of this period. Requirements for derecognition of financial liabilities
Financial liabilities shall be entirely or partially derecognized if the present obligations derived from them are entirely or partially discharged. Where the Company enters into an agreement with a creditor so as to substitute the current financial liabilities with new ones, and the contract clauses of which are substantially
different from those of the current ones, it shall recognize the new financial liabilities in place of the current ones. Where substantial revisions are made to some or all of the contract clauses of the current financial liabilities, the Company shall recognize the new financial liabilities after revision of the contract clauses in place of the current ones entirely or partially.
Upon entire or partial derecognition of financial liabilities, differences between the carrying amounts of the derecognized financial liabilities and the consideration paid (including non-monetary assets surrendered or new financial liabilities assumed) are charged to profit or loss for the current period.
Where the Company redeems part of its financial liabilities, it shall allocate the carrying amounts of the entire financial liabilities between the relative fair values of the parts that continue to be recognized and the derecognized parts on the redemption date. Differences between the carrying amounts allocated to the derecognized parts and the consideration paid (including non-monetary assets surrendered and the new financial liabilities assumed) are charged to profit or loss for the current period. Recognition and measurement for transfer of financial assets
If the Company has transferred nearly all of the risks and rewards relating to the ownership of the financial assets to the transferee, they shall be derecognized. If it retains nearly all of the risks and rewards relating to the ownership of the financial assets, they shall not be derecognized and will be recognized as a financial liability. If the Company has not transferred nor retained nearly all of the risks and rewards relating to the ownership of the financial assets:(1) to give up the control of the financial assets to be derecognized; (2) not giving up control of the financial asset to be recognized based on the extent of its continuing involvement in the transferred financial assets and liabilities are recognized accordingly.
If the transfer of entire financial assets satisfy the criteria for derecognition, differences between the amounts of the following two items shall be recognized in profit or loss for the current period: (1) the carrying amount of the transferred financial asset; (2) the aggregate consideration received from the transfer plus the cumulative amounts of the changes in the fair values originally recognized in the owners? equity. If the partial transfer of financial assets satisfy the criteria for derecognition, the carrying amounts of the entire financial assets transferred shall be split into the derecognized and recognized parts according to their respective fair values and differences between the amounts of the following two items are charged to profit or loss for the current period: (1) the carrying amounts of the derecognized parts;
(2) The aggregate consideration for the derecognized parts plus the portion of the accumulative amounts of the changes in the fair values of the derecognized parts which are originally recognized in the owners? equity.
Determination of the fair value of financial instruments
- If financial instruments trade in an active market, the quoted price in an active market determines its fair value; if financial instrument trade not in an active market, the valuation techniques determine the fair value. Valuation techniques include recent market transaction price reference to the familiar situation and volunteer transaction, current fair value reference to other substantially similar financial instruments,
discounted cash flow method and option pricing model and so on.
Test and Provisions for impairment loss on financial assets
--Except trading financial assets, the Company makes assessment on the carrying values of financial assets at the balance sheet date. If there is evidence that the fair value of specific financial asset has been impaired, provisions for impairment loss is made accordingly.
-- Measurement of impairment of financial assets measured at amortized cost
If there is objective evidence that the financial asset measured at amortized cost has been impaired, the carrying amount of the financial asset is written down to the present value of estimated future cash flows (excluding future credit losses that have not yet occurred), and the amount of reduction is recognized as impairment loss and is recognized in the profit or loss of this period. The Company carries out the impairment test of significant single financial asset separately, carries out the impairment test on insignificant single financial asset from a single or combination of angles, and carries out the impairment test on single asset without objective evidence of impairment along with the financial assets with similar credit risk characteristics to constitute a combination, but does not carry out the impairment test on the provision for impairment of financial assets based on the single in the portfolio. In the subsequent period, if there is objective evidence that the value of financial asset has been restored and recognized relevant to the objective matters occurring after the impairment, previously recognized impairment loss shall be reversed and charged into the profit or loss of this period. But the book value after the reversal should not exceed the amortized cost at the reversal date of the financial assets supposed no provision for impairment. When the financial assets measured at amortized cost actually occur loss, offset against the related provision for impairment.
--Available for sale financial assets
If there is objective evidence that an impairment of available for sale financial assets occurs, even though the financial asset has not been derecognised, the cumulative loss of decrease of the faire value originally recorded in the owner's equity should be transferred out and charged into the current profit and loss. The cumulative loss is the initial acquisition cost of available for sale financial assets, deducting the fair value of the withdrawing principal and amortization amount and impairment loss as well as net impairment amount originally charged into the profit or loss.
Recognition and provision for bad debts of accounts receivable
If there is objective evidence that receivables are impaired at the end of this period, the carrying value will be written down to its present value of estimated future cash flows, and the amount of reduction is recognized as impairment loss and is recognized in the current profit or loss. Present value of estimated future cash flows is determined through future cash flows (excluding credit losses that have not been incurred) discounted at the original effective interest rate, taking into account the value of related collateral (less estimated disposal costs, etc.). Original effective interest rate is the actual interest rate when the receivables are recognized initially. The estimated future cash flows of short-term receivables have small difference from the present value, and the estimated future cash flows are not discounted in determining the
related impairment loss.
The significant single receivables are separately carried out impairment test at the end of this period, and if there is objective evidence that the impairment has occurred, based on the difference of the present value of future cash flows less than the book value, the impairment loss is recognized and the provision of bad debts is done. The significant single amount refers to top five receivable balances or the sum of payments accounting for more than 10% of receivable balances.
If there is objective evidence that the individual non-significant receivables impairment has occurred, separate impairment test is done, the impairment loss is recognized and the provision for bad debts is done; other individual non-significant receivables and receivables not impaired after separate test are together divided into several combinations for impairment testing with aging as the similar credit risk characteristics, to determine the impairment loss and do provision for bad debts.
In addition to separate provision for impairment of receivables, the company is based on the actual loss rate of receivable portfolio with the same or similar to the previous year and aging as the similar credit risk characteristics, and combines the current
Fixed assets and depreciation accounting method
Recognition criteria of fixed assets: fixed assets refer to tangible assets held for the purpose of producing commodities, providing services, renting or business management with useful lives exceeding one accounting year and high unit value. Classification of fixed assets: buildings and constructions, machinery equipment, transport equipment and office equipment.
Fixed assets pricing and depreciation method: the fixed assets is priced based on actual cost and depreciated in a straight-line method. The estimated useful lives, estimated residual rate and annual depreciation rate of various categories of fixed
end of the reporting period, and if the market continuing to fall or technological obsolescence, damage, long-term idle and other reasons result in fixed assets recoverable amount lower than its book value, in accordance with the difference
provision for impairment of fixed assets, the impairment loss is recognized in fixed assets and can not be reversed in a subsequent accounting period. The recoverable amount is recognized based on the fair value of the assets deducting the net amount after disposal expenses and the present value of cash flows of the estimated future assets. The present value of the future cash flows of the asset is determined in accordance with the resulting estimated future cash flows in the process of continuous use and final disposal to select its appropriate discount rate and the amount of the discount.
Accounting method of construction in progress
The construction in progress is priced on the actual cost, to temporarily transfer to fixed assets when reaching the intended use state in accordance with the project budget and the actual cost of the project, and to adjust the book value of fixed assets according to the actual cost after handling final settlement of accounts. Acquisition, construction or production of assets eligible for capitalization borrowed specifically or the interest on general borrowing costs and auxiliary expenses of specific borrowings occurred can be included in the cost of capital assets and subsequently recognized in the current profit or loss before the acquisition, construction or production of the qualifying asset reaches the intended use state or the sale state.
Impairment of construction in progress: the Company conducts a comprehensive inspection of construction in progress at the end of the reporting period; if the construction in process is stopped for long time and will not be constructed in the next three years and the construction in progress brings great uncertainty to the economic benefits of enterprises due to backward performance or techniques and the construction in progress occurs impairment, the balance of recoverable amount of single construction in progress lower than the book value of construction in progress is for impairment provisions of construction in progress. Impairment loss on the construction in progress shall not be reversed in subsequent accounting periods once recognized.
The pricing and amortizing of intangible assets
Pricing of the intangible assets
---The cost of outsourcing intangible assets shall be priced based on the actual expenditure directly attributable to intangible assets for the expected purpose.
--- Expenditure on internal research and development projects is charged into the current profit or loss, and expense in the development stage can be recognized as intangible costs if meeting the criteria for capitalization.
--- Intangible assets of investment is in accordance with the agreed value of the investment contract or agreement as costs, excluding not fair agreed value of the contract or agreement.
--- Intangible assets of the debtor obtained in the non-cash asset cover debt method can be accepted; if the receivable creditor?s right is changed into intangible assets, then record according to the fair value of intangible assets.
--- For non-monetary transaction intangible assets, the fair value and related taxes payable of non-monetary assets should be the accounting cost.
Amortization of intangible assets: as for the intangible assets with limited service life,
it is amortized by straight-line method when it is available for use within the service period. As for unforeseeable period of intangible assets bringing future economic benefits to the company, it is regarded as intangible assets with uncertain service life, and intangible assets with uncertain service life can not be amortized. The Company?s intangible assets include land use rights, forest land use rights and the production and marketing information management software. The land use rights are amortized averagely in accordance with 50 years of service life, forest land use rights are amortized averagely in accordance with 30 years of service life, and the production and marketing information management software are amortized averagely in accordance with 5 years of service life.
Expenditures arising from development phase on internal research and development projects can be recognized as intangible assets when satisfying all of the following conditions: (1) there is technical feasibility of completing the intangible assets so that they will be available for use or sale; (2) there is intention to complete and use or sell the intangible assets; (3) the method that the intangible assets generate economic benefits, including existence of a market for products produced by the intangible assets or for the intangible assets themselves, shall be proved. Or, if to be used internally, the usefulness of the intangible assets shall be proved; (4) adequate technical, financial, and other resources are available to complete the development of intangible assets, and the Company has the ability to use or sell the intangible assets;
(5) the expenditures arising from development phase of the intangible assets can be measured reliably.
Impairment of intangible assets: the Company conducts a comprehensive inspection on intangible assets at the end of the reporting period. If the intangible assets have been replaced by other new technologies so as to seriously affect its capacity to create economic benefits for the enterprise, the market value of certain intangible assets sharply fall and is not expected to recover in the remaining amortization period, certain intangible asset has exceeded the legal time limit but still has some value in use as well as the intangible asset impairment has occurred, the provision for impairment is done according to the difference between the individual estimated recoverable amount and the book value. Impairment loss on the intangible asset shall not be reversed in subsequent accounting periods once recognized.
Accounting method of capitalization of borrowing costs
Borrowing costs that are directly attributable to the acquisition, construction or production of qualifying assets for capitalization should be charged into the relevant costs of assets and therefore should be capitalized. Borrowing costs incurred after qualifying assets for capitalization reaches the estimated use state are charged to profit or loss in the current period. Other borrowing costs are recognized as expenses based on the accrual and are charged to profit or loss in the current period.
Capitalization of borrowing costs should meet the following conditions: expenditures are being incurred, which comprise disbursements incurred in the form of payments of cash, transfer of non-monetary assets or assumption of interest-bearing debts for the acquisition, construction or production of qualifying assets for capitalization; borrowing costs are being incurred; purchase, construction or manufacturing activities
that are necessary to prepare the assets for their intended use or sale are in progress. Capitalization amount of borrowing interest: the borrowing interest incurred from the acquisition, construction or production of assets eligible for capitalization borrowed specifically or generally should be determined the capitalization amount according to the following method before the acquisition, construction or production of a qualifying asset reaching its intended use or sale state:
---Where funds are borrowed specifically for purchase, construction or manufacturing of assets eligible for capitalization, costs eligible for capitalization are the actual interest costs incurred in current period less the interest income of unused borrowing funds deposited in the bank or any income earned on the temporary investment of such borrowings.
---Where funds allocated for purchase, construction or manufacturing of assets eligible for capitalization are part of a general pool, the eligible capitalization interest amounts are determined by multiplying a capitalization rate of general borrowing by the weighted average of accumulated capital expenditures over those on specific borrowings. The capitalization rate will be determined based on the weighted average rate of the borrowing costs applicable to the general pool.
Suspension for capitalization: Capitalization of borrowing costs should be suspended during periods in which purchase, construction or manufacturing of assets eligible for capitalization is interrupted abnormally with the interruption time exceeding three months continuously. Borrowing costs incurred during the interruption should be charged to profit or loss for the current period, and should continue to be capitalized when purchase, construction or manufacturing of the relevant assets resumes. If the interruption is the necessary procedure to prepare the assets purchased, constructed or manufactured eligible for capitalization for their intended use or sale, the borrowing costs should continue to be capitalized.
Recognition criteria and measurement method of estimated liabilities Recognition criteria of estimated liabilities: when the external security, pending litigation or arbitration, product quality assurance, layoffs, loss of contracts, restructuring obligations, fixed asset retirement obligations and other pertinent business meet the following conditions, it can be recognized as the liability: (1) the obligation is a present obligation of the Company; (2)it is probable that settlement of such an obligation will result in the economic benefit to flow out from the Company;
(3) the amount of the obligation can be measured reliably.
Measurement method of estimated liabilities: The Company?s estimated liabilities shall be initially measured at the best estimates of the necessary expenditures for the fulfillment of the present obligations. To determine the best estimates, the Company shall take into full account the risks, uncertainties, time value of money, and other factors relating to the contingencies. If the time value of money is significant, the best estimates shall be determined after discounting the relevant future cash outflows. If there is a continuous range for the necessary expenses, and probabilities of occurrence of all the outcomes within this range are equal, the best estimate shall be determined at the average amount within the range. The best estimates shall be determined as follows in other circumstances: (1) if the contingency involves a single item, the best
estimate shall be determined at the most likely outcome; (2) if the contingency involves two or more items, the best estimate should be determined according to all the possible outcomes with their relevant probabilities; (3) when all or part of the expenses necessary for the settlement of estimated liabilities of the Company are expected to be compensated by a third parties, the compensations should be separately recognized as assets only when it is virtually certain that the compensations will be received. The carrying amount of the estimated liabilities should be checked at each balance sheet date, and if any changes occur, the book value should be adjusted to reflect the current best estimate.
Salary payable to staff
The staff?salary means that the enterprise gives various remunerations and other relevant expenses to employees for obtaining services provided by the employees in the accounting period, including staff?s salary, bonus, allowance and subsidy, staff?s welfare, hospitalization insurance, endowment insurance, unemployment insurance, occupational injury insurance and childbirth insurance and other social insurances as well as housing public reserve and so on. In the event that the Company terminates the employment relationship with employees unilaterally before the end of the employment contracts, or offers to compensate the employees in order to encourage them to accept voluntary redundancy (if the Company has formally formulated plans for termination of the employment relationship or offer for voluntary redundancy, and the plans will be implemented shortly afterwards and can not be recalled by the Company unilaterally), compensations for redundancy shall be recognized as estimated liabilities and charged to profit or loss for the current period.
Revenue recognition principle
The revenue from selling goods shall be recognized when meeting all following conditions: the significant risks and rewards of ownership of the goods have been transferred to the buyer by the Company; the Company retains neither continuous management right that usually keeps relation with the ownership nor effective control over the sold goods; the amount of revenue can be measured in a reliable way; it is probable that the economic benefits associated with the transaction will flow to the enterprise; the relevant costs can be measured reliably.
The revenue from providing labor services shall be recognized with the percentage of completion method when meeting all following conditions: the amount of revenue can be measured in a reliable way; it is probable that the economic benefits associated with the transaction will flow to the enterprise; the schedule of completion under the transaction can be measured in a reliable way; the relevant costs in the transactions can be measured reliably. When the outcome of labor service can not be estimated reliably and the labor service costs incurred are expected to be fully recoverable, the revenue is recognized based on the labor cost incurred; when the labor service costs incurred are expected to be partially recoverable, the revenue is recognized based on the labor cost recovered; the labor service costs incurred are not expected to be recoverable, the revenue is not recognized.
The revenue from others making use of the Company?s assets is recognized when meeting the following conditions: the economic benefits associated with the
transaction will flow to the Company; the amount of revenue can be measured reliably. Royalty revenue receivable from providing others to use the Company's assets is recognized as the operating revenue based on the charging time and method stipulated in the contract and the agreement.
Government grants
Government grants can be recognized when meeting all the following conditions: meeting the conditions attached to government grants; receiving government grants.
If government grants are the monetary assets, measure in accordance with the amount received or receivable; if the government grants are non-monetary assets, measure at fair value or nominal amount if the fair value can not be reliably achieved. Government grants related to assets should be recognized as deferred income, and equally distributed in the life of the related asset and charged in profit or loss of the current period. The government grants measured at the nominal amount is directly charged into the profit or loss of the current period. Government grants related to income used for compensation of related expenses or losses in subsequent periods should be recognized as deferred income and charged in profit or loss of the current period; government grants related to income used for compensation of related expenses or losses already incurred are directly charged in the profit or loss of the current period.
Deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities
The Company carries out the accounting treatment of income tax using the balance sheet liability method. In addition to the related tax effects to transactions or matters recognized directly in shareholders' equity, the current income tax expense and deferred income tax expense (or income) is recognized in the current profit or loss. Deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities are recognized based on temporary differences deductible and taxable temporary differences and measured in accordance with the expected recovery of assets or the tax rate applicable during the period of settlement of liabilities. Temporary difference is the difference between the book value of an asset or liability and its tax base, including the annual deductible losses carried forward and tax decrease. Recognition of deferred tax assets is likely to take taxable income used to deduct temporary difference as the limit. When the deferred tax asset has been recognized, and it is unlikely to obtain sufficient taxable income to offset against the deferred tax assets in the future, the carrying value of deferred tax assets should be written down. When it is probable to obtain sufficient taxable income, the amount of such reduction should be reversed.
When the temporary difference is arisen from the initial recognition of the assets or liabilities incurring in the transaction which is not business combination and does not affect the accounting profits or the taxable amount (or the deductible loss), the corresponding deferred income tax shall not recognized. Temporary difference resulting from the initial recognition of goodwill does not generate deferred tax. Profit allocation method
According to the Articles of Association, the Company's profits are allocated in the following order:
---Making up for losses in previous years;
--- Extraction of three funds;
--- The remaining profits are distributed according to the board resolution.
V. Major taxations
Value Added tax (V AT)
V AT is calculated and paid with tax rate of 3% of small-scale taxpayers of the business income.
Income tax
According to the “People's Republic of China Enterprise Income Tax Law” issued in 2007, the corporate income tax rate is 25%.
VI.Notes to the main items of financial statements
1. Monetary fund
The balance of monetary funds of the Company on December 31, 2013 is RMB
related financial institutions.
2. Other receivables
Other net receivables of the Company on December 31, 2013 are RMB
370,000,000.00, representing 100% of the balance of other receivables.
--- No arrearage from the shareholders holding over 5% (including 5%) of the equity of the Company existed in the ending balance of other accounts receivable.
3. Long-term equity investments
existed in the ending balance of other accounts payable and related accounts payable is shown in the Note VII.
审计报告英文版(全)
AUDITOR’S REPORT Yue Hua Shen / Yan Zi (2014) No. 0002 ICPA filing number: 0420 To all shareholders of ****** Co., Ltd: We have audited the accompanying financial statements of ****** Co., Ltd (“Your Company”), which comprise the balance sheet as of 31 D ecember 2013, the income statement,statement of changes in owner's equity and cash flow statement for the year then ended, and notes to the financial statements. I. Management’s responsibility for the financial statements Management of your Company is responsible for the preparation and fair presentation of financial statements. T his responsibility includes: (1) in accordance with the Accounting Standards f or Business Enterprises and its relevant provisions, preparing the financial statements and reflecting fair presentation; (2) designing, implementing and maintaining the necessary internal control in order to free financial statements from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error. II. Auditors' responsibility Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audit. We conducted our audit in accordance with Chinese Certified Public Accountants Auditing Standards. Those standards require that we comply with ethical requirements and plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable a ssurance whether the financial statements are free from material misstatement. An audit involves performing procedures to obtain audit evidence about the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. The procedures selected depend on the auditors' judgment, including the assessment of the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, w hether due to fraud or error. In making those risk assessments, we consider the internal control relevant to the preparation and fair presentation of the financial statements in order to design audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the internal control. An audit also includes evaluating the appropriateness o f accounting policies used and the reasonableness of accounting estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that the audit evidence we have obtained is sufficient and appropriate to provide a basis for our audit opinion. III. Opinion In our opinion, the financial statements of your Company have been prepared in accordance with the Accounting Standards for Business Enterprise and its relevant provisions in all material respect, and present fairly the financial position of your Company as of 31 December 2013, and the results of its operations and cash flows for the year then ended. Guangdong Huaxin Accounting Firm (general partner) Guangdong, China
中英文审计报告-五种审计意见
审计报告-标准无保留意见 Auditors’ Report 安明(2007)审字第XXXXX 号 An Ming (2007) Audit No. XXXXXXXX ABC股份有限公司全体股东: To the shareholders of ABC Co., Ltd. (the “Company”): 我们审计了后附的ABC股份有限公司(以下简称“贵公司”)及其子公司和合营企业(以下统称“贵集团”)财务报表,包括2006年12月31日的合并及母公司资产负债表、2006年度的合并及母公司利润及利润分配表、股东权益增减变动表和现金流量表以及财务报表附注。 We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheet of ABC (the “Company”) a nd its subsidiaries (collectively referred to as the “Group”) as of 31st December 2006 and the related consolidated income statement, consolidated statement of changes in equity an d consolidated cash flow statement for the year then ended, and a summary of significant accounting policies and other explanatory notes. 一、管理层对财务报表的责任 按照企业会计准则和《企业会计制度》的规定编制财务报表是贵公司管理层的责任。这种责任包括:(1) 设计、实施和维护与财务报表编制相关的内部控制,以使财务报表不存在由于舞弊或错误而导致的重大错报;(2) 选择和运用恰当的会计政策;(3) 作出合理的会计估计。 1. Management’s Responsibility for the Financial Statements The management is responsible for the preparation and fair presentation of these financial statements in accordance with the Accounting Standards for Business Enterprises and Chin a Accounting System for Business Enterprises. This responsibility includes: (i) designing, i mplementing and maintaining internal control relevant to the preparation and fair presentati on of financial statements that are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error; (ii) selecting and applying appropriate accounting policies; and (iii) making accou nting estimates that are reasonable in the circumstances. 二、注册会计师的责任 我们的责任是在实施审计工作的基础上对财务报表发表审计意见。我们按照中国注册会计师审计准则的规定执行了审计工作。中国注册会计师审计准则要求我们遵守职业道德规范,计划和实施审计工作以对财务报表是否不存在重大错报获取合理保证。 2. Auditor’s Responsibility Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audi t. We conducted our audit in accordance with the Standards on Auditing for Certified Pub lic Accountants. Those standards require that we comply with ethical requirements and pla
中英文对照的标准版审计报告
标准审计报告的参考格式Example of Standard Auditor’s Report 审计报告 Auditor’s Report ABC股份有限公司全体股东: To the shareholders of ABC Company Limited, 我们审计了后附的ABC股份有限公司(以下简称ABC公司)财务报表,包括20×1年12月31日的资产负债表,20×1年度的利润表、股东权益变动表和现金流量表以及财务报表附注。 We have audited the accompanying financial statments of ABC Company Limited (hereinafter “ABC Company”),which comprise the balance sheet as at December 31,20XX, and the income statement, statement of changes in equity and cash flow statement for the year then ended, and a summary of significant accounting policies and other explanatory note s. 一、管理层对财务报表的责任 Management’s Responsibility for the Financial Statements 按照企业会计准则和《××会计制度》的规定编制财务报表是ABC公司管理层的责任。这种责任包括:(1)设计、实施和维护与财务报表编制相关的内部控制,以使财务报表不存在由于舞弊或错误而导致的重大错报;(2)选择和运用恰当的会计政策;(3)作出合理的会计估计。 Management is responsible for the preparation and fair presentation of these financial statements in accordance with the Accounting Standards for Busine ss Enterprise s and China Accounting System for Busine ss Enterprise s. This re sponsibility includes: (a) designing, implementing and maintaining internal control relevant to the preparation and fair presentation of financial statements that are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error; (b) selecting and applying appropriate accounting policies; and (c) making accounting estimates that are reasonable in the circumstance s. 二、注册会计师的责任 Auditor’s Re sponsibility 我们的责任是在实施审计工作的基础上对财务报表发表审计意见。我们按照中国注册会计师审计准则的规定执行了审计工作。中国注册会计师审计准则要求我们遵守职业道德规范,计划和实施审计工作以对财务报表是否不存在重大错报获取合理保证。 Our re sponsibility is to express an opinion on the se financial statements ba sed on our audit. We conducted our audit in accordance with China Standards on Auditing. Those standards require that we comply with ethical requirements and plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance to whether the financial statements are free from material misstatement. 审计工作涉及实施审计程序,以获取有关财务报表金额和披露的审计证据。选择的审计程序取决于注册会计师的判断,包括对由于舞弊或错误导致的财务报表重大错报风险的评估。在进行风险评估时,我们考虑与财务报表编制相关的内部控制,以设计恰当的审计程序,但目的并非对内部控制的有效性发表意见。审计工作还包括评价管理层选用会计政策的恰当性和作出会计估计的合理性,以及评价财务报表的总体列报。 An audit involve s performing audit procedure s to obtain audit evidence about the
审计报告中英文范本
审计报告 AUDITOR’S REPORT 晋**审字(2007)第000**号 Jin ** (2007) Audit No.00** **铸造有限公司 To **foundry Co., Ltd: 我们审计了后附的**铸造有限公司(以下简称贵公司)财务报表,包括2006年12月31 日的资产负债表,2006年度的利润表以及财务报表附注 We have audited the accompanying balance sheet of ** foundry Co., Ltd (the “Company”) as of Dec.31,2006, and the related consolidated income statement for the 2006 then ended, and a summary of significant accounting policies and other explanatory notes 一、管理层对财务报表的责任 1.Management’s Responsibility for the Financial Statements 按照企业会计准则和《企业会计制度》的规定编制财务报表是贵公司管理层的责任。这种责任包括:(1)设计、实施和维护与财务报表编制相关的内部控制,以使财务报表不存在由于舞弊或错误而导致的重大错报:(2)选择和运用恰当的会计政策:(3)作出合理的会计估计 The management is responsible for the preparation and fair presentation of these financial statements in accordance with the Accounting Standards for Business Enterprises and China Accounting System for Business Enterprises. This responsibility includes: (i) designing, implementing and maintaining internal control relevant to the preparation and fair presentation of financial statements that are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error; (ii) selecting and applying appropriate accounting policies; and (iii) making accounting estimates that are reasonable in the circumstances 二、注册会计师的责任 2. Auditor’s Responsibility 我们的责任是在实施审计工作的基础上对财务报表发表审计意见。我们按照中国注册会计师审计准则的规定执行了审计工作。中国注册会计师审计准则要求我们遵守职业道德规范,计划和实施审计工作以对财务报表是否不存在重大错报获取合理保证 Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audit. We conducted our audit in accordance with the Standards on Auditing for Certified Public Accountants.Those standards require that we comply with ethical requirements and plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance whether the financial statements are free from material misstatement 审计工作涉及实施审计程序,以获取有关财务报表金额和和披露的审计证据。选择的审计程序取决于注册会计师的判断,包括对由于舞弊或错报导致的财务报表重大错报风险的评估。在进行风险评估时,我们考虑与财务报表编制相关的内部控制,以设计恰当的审计程序,但目的并非对内部控制的有效性发表意见。审计工作还包括评价管理层选用会计政策的恰当性和作出会计估计的合理性,以及评
审计报告中的会计及审计英语 (2)
年度审计报告中的会计及审计英语 English for Accounting & Auditing in Annual Repor 主要内容 Contents 年度审计报告框架 Framework of Annual Report 年度审计报告中所应用的相关专业会计及审计英语 Accounting and Audit English in Annual Report 年度审计报告框架 Framework of Annual Report 审计意见Audit opinion 管理层责任Management’s Responsibility for the Financial Statements 注册会计师责任Auditors’ Responsibility 审计意见Auditor’s Opinion 管理层财务报表Management Financial statements 资产负债表Balance Sheet 利润表Income Statements 现金流量表Cash flow statement 财务报表附注Notes to the financial statements 年度审计报告范例-管理层责任(1) Example - Management’s Responsibility(1) 按照中华人民共和国财政部颁布的企业会计准则的规定编制财务报表是贵公司管理层的责任。 The Company’s management is responsible for the pre paration of these financial statements in accordance with China Accounting Standards for Business Enterprises issued by the Ministry of Finance of the People’s Republic of China. 年度审计报告范例-管理层责任(2) Example - Management’s Responsibility (2) 这种责任包括:(1)设计、实施和维护与财务报表编制相关的内部控制,以使财务报表不存在由于舞弊或错误而导致的重大错报;(2)选择和运用恰当的会计政策;(3)作出合理的会计估计。 This responsibility includes: designing, implementing and maintaining internal control relevant to the preparation of financial statements that are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error; selecting and applying appropriate accounting policies; and making accounting estimates that are reasonable in the circumstances.
中英文审计报告五种审计意见
中英文审计报告五种审计意见
审计报告-标准无保留意见Auditors’ Report 安明( )审字第 XXXXX 号 An Ming ( ) Audit No. XXXXXXXX ABC股份有限公司全体股东: To the shareholders of ABC Co., Ltd. (the “Company”): 我们审计了后附的ABC股份有限公司(以下简称“贵公司”)及其子公司和合营企业(以下统称“贵集团”)财务报表,包括 12月31日的合并及母公司资产负债表、的合并及母公司利润及利润分配表、股东权益增减变动表和现金流量表以及财务报表附注。 We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheet of ABC (the “Company”) and its subsidiaries (collectively referred to as the “Group”) as of 31st December and th e related consolidated income statement, consolidated statement of changes in equity a nd consolidated cash flow statement for the year then ended, and a summary of significa nt accounting policies and other explanatory notes. 一、管理层对财务报表的责任 按照企业会计准则和《企业会计制度》的规定编制财务报表是贵公司管理层的责任。这种责任包括:(1) 设计、实施和维护与财务报表编制相关的内部控制,以使财务报表不存在由于舞弊或错误而导致的重大错报;(2) 选择和运用恰当的会计政策;(3) 作出合理的会计估计。 1. Management’s Responsibility for the Financial Statements
审计报告中英文对照
最新审计报告中英文对照 山西**联合会计师事务所 ShanXi**Unite Accountant Office 审计报告 AUDITOR’S REPORT 晋**审字(2007)第000**号 Jin ** (2007) Audit No.00** **铸造有限公司: To **foundry Co., Ltd: 我们审计了后附的**铸造有限公司(以下简称贵公司)财务报表,包括2006年12月 31 日的资产负债表,2006年度的利润表以及财务报表附注。 We have audited the accompanying balance sheet of ** foundry Co., Ltd (the “Company”) as of Dec.31,2006, and the related consolidated income statement for the 2006 then ended, and a summary of significant accounting policies and other explanatory notes. 一、管理层对财务报表的责任 1.Management’s Responsibility for the Financial Statements 按照企业会计准则和《企业会计制度》的规定编制财务报表是贵公司管理层的责任。这种责任包括:(1)设计、实施和维护与财务报表编制相关的内部控制,以使财务报表不存在由于舞弊或错误而导致的重大错报:(2)选择和运用恰当的会计政策:(3)作出合 理的会计估计。 The management is responsible for the preparation and fair presentation of these financial statements in accordance with the Accounting Standards for Business Enterprises and China Accounting System for Business Enterprises. This responsibility includes: (i) designing, implementing and maintaining internal control relevant to the preparation and fair presentation of financial statements that are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error; (ii) selecting and applying appropriate accounting policies; and (iii) making accounting estimates that are reasonable in the circumstances. 二、注册会计师的责任 2. Auditor’s Responsibility 我们的责任是在实施审计工作的基础上对财务报表发表审计意见。我们按照中国注册会计师审计准则的规定执行了审计工作。中国注册会计师审计准则要求我们遵守职业道德规范,计划和实施审计工作以对财务报表是否不存在重大错报获取合理保证。 Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audit. We conducted our audit in accordance with the Standards on Auditing for Certified Public Accountants. Those standards require that we comply with ethical
中英文审计报告五种审计意见
审计报告-标准无保留意见A u d i t o r s’R e p o r t 安明(2007)审字第XXXXX 号 An Ming (2007) Audit No. XXXXXXXX ABC股份有限公司全体股东: To the shareholders of ABC Co., Ltd. (the “Company”): 我们审计了后附的ABC股份有限公司(以下简称“贵公司”)及其子公司和合营企业(以下统称“贵集团”)财务报表,包括2006 We have (colle ctively statement, cons olidated and a sum mary of (1) 设计、实 (2) 选择和运1. The in accordanc e with Enterprises. This the preparatio n and to fraud or e rror; (ii) that are reas onable in 我们的责任是在实施审计工作的基础上对财务报表发表审计意见。我们按照中国注册会计师审计准则的规定执行了审计工作。中国注册会计师审计准则要求我们遵守职业道德规范,计划和实施审计工作以对财务报表是否不存在重大错报获取合理保证。 2. Auditor’s Responsibility Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audit. We conducted our au dit in accordance with the Standards on Auditing for Certified Public Accountants. Those standards require that w e comply with ethical requirements and plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance whether the fin ancial statements are free from material misstatement.
审计分析报告翻译
审计报告翻译
————————————————————————————————作者:————————————————————————————————日期: 2
3 最新审计报告中英文对照(转载) 审计报告中英对照 2008-12-27 13:38:21 阅读2557 评 论5 字号:大中小 订阅 山西**联合会计师事务所 shanxi**unite accountant office 审 计 报 告 audit or’s report 晋**审字(2007)第000**号 jin ** (2007) audit no.00** **铸造有限公司: to **foundry co., ltd: 我们审计了后附的**铸造有限公司(以下简称贵公司)财务报表,包括2006年12月 31 日的资产负债表,2006年度的利润表以及财务报表附注。 2006 then ended, and a summary of significant accounting policies and other explanatory notes. 一、管理层对财务报表的责任 1. management’s responsibility for the financial statements 按照企业会计准则和《企业会计制度》的规定编制财务报表是贵公司管理层的责任。这种 责任包括:(1)设计、实施和维护与财务报表编制相关的内部控制,以使财务报表不存在由于 舞弊或错误而导致的重大错报:(2)选择和运用恰当的会计政策:(3)作出合 理的会计估计。 the management is responsible for the preparation and fair presentation of these financial statements in accordance with the accounting standards for business enterprises and china accounting system for business enterprises. this responsibility includes: (i) designing, implementing and maintaining internal control relevant to the preparation and fair presentation of financial statements that are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error; (ii) selecting and applying appropriate accounting policies; and (iii) making accounting estimates that are reasonable in the circumstances. 二、注册会计师的责任 2. auditor’s responsibility 我们的责任是在实施审计工作的基础上对财务报表发表审计意见。我们按照中国注册会计 师审计准则的规定执行了审计工作。中国注册会计师审计准则要求我们遵守职业道德规 范,计划和实施审计工作以对财务报表是否不存在重大错报获取合理保证。 requirements and plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance whether the financial statements are free from material misstatement 审计工作涉及实施审计程序,以获取有关财务报表金额和和披露的审计证据。选择的审计 程序取决于注册会计师的判断,包括对由于舞弊或错报导致的财务报表重大错报风险的评估。 在进行风险评估时,我们考虑与财务报表编制相关的内部控制,以设计恰当的审计程序,但目 的并非对内部控制的有效性发表意见。审计工作还包括评价管理层选用会计政策的恰当 性和作出会计估计的合理性,以及评价财务报表的总体列报。 an audit involves performing procedures to obtain audit evidence about the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. the procedures selected depend on the auditor’s judgment, including the assessment of the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to fraud or error. in making those ris assessments, the auditor considers internal control relevant to the
标准审计报告英文版(1501号准则)
Auditors' Report to the Shareholders of ABC (SUZHOU) CO., LTD We have audited the accompanying financial statements of ABC (SUZHOU) CO., LTD, which comprise the balance sheet as at December 31, 2006, and the income statement, cash flow statement for the y ear then ended, and a summary of significant accounting policies and other explanatory notes. Management’s Responsibility for the Financial Statements Management is responsible for the preparation of these financial statements in accordance with the Accounting Standards for Business Enterprises and Accounting Systems for Business Enterprises. This responsibility includes: (1) designing, implementing and maintaining internal control relevant to the preparation of financial statements that are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error; (2) selecting and applying appropriate accounting policies; (3) making accounting estimates that are reasonable in the circumstances. Auditor’s Responsibility Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audit. We conducted our audit in accordance with the Independent Auditing Standards of China. These standards require that we comply with ethical requirements and plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit involves performing procedures to obtain audit evidence about the amount and disclosures in the financial statements. The procedures selected depend on the auditor’s judgme nt, including the assessment of the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to fraud or error. In making those risk assessments, the auditor considers internal control relevant to the entity’s preparation of the financial s tatements in order to design audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the entity’s internal control. An audit also includes evaluating the appropriateness of accounting policies used and reasonableness of accounting estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that the audit evidence we have obtained is sufficient and appropriate to provide a basis for our audit opinion. Opinion In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of ABC (SUZHOU) CO., LTD as of December 31, 2006, and of its financial performance and its cash flows for the year then ended in accordance with the Accounting Standards for Business Enterprises and Accounting Systems for Business Enterprises . AAA Certified Public Accountant BBB Certified Public Accountant
