论文参考文献英文字母意义
英文引用及参考文献格式要求

英文引用及参考文献格式要求一、参考文献的类型参考文献(即引文出处)的类型以单字母方式标识,具体如下:M——专著C——论文集N——报纸文章J——期刊文章D——学位论文R——报告对于不属于上述的文献类型,采用字母“Z”标识。
对于英文参考文献,还应注意以下两点:①作者姓名采用“姓在前名在后”原则,具体格式是:姓,名字的首字母.如:MalcolmRichardCowley应为:Cowley,M.R.,如果有两位作者,第一位作者方式不变,&之后第二位作者名字的首字母放在前面,姓放在后面,如:FrankNorris与IrvingGordon应为:Norris,F.&I.Gordon.作者(主要责任者)为3人或不多于3人应全部写出,之间几","号相隔;3人以上只列出前3人,后加"等"或相应的文字如"et al","等"或"et al"前加","号。
二、参考文献的格式及举例1.期刊类【格式】[序号]作者.篇名[J].刊名,出版年份,卷号(期号):起止页码.【举例】[1]王海粟.浅议会计信息披露模式[J].财政研究,2004,21(1):56-58.[2]夏鲁惠.高等学校毕业论文教学情况调研报告[J].高等理科教育,2004(1):46-52.[3]Heider,E.R.&D.C.Oliver.Thestructureofcolorspaceinnamingandmemo ryoftwolanguages[J].ForeignLanguageTeachingandResearch,1999,(3):62–6 7.三、采用顺序编码制。
顺序编码制是按文章正文部分(包括图、表及其说明)引用的先后顺序连续编码。
在文中参考文献的序号均置于方括号内,并视具体情况把序号作为上角标,或者作为语句的组成部分。
参考文献的类型和标点符号

参考文献的类型和标点符号论文参考文献格式规范一、参考文献的类型参考文献(即引文出处)的类型以单字母方式标识,具体如下:[M]——专著,著作[C]——论文集(一般指会议发表的论文续集,及一些专题论文集,如《***大学研究生学术论文集》。
[N]——报纸文章[J]——期刊文章:发表在期刊上的论文,尽管有时我们看到的是从网上下载的(如知网),但它也是发表在期刊上的,你看到的电子期刊仅是其电子版。
[D]——学位论文:不区分硕士还是博士论文[R]——报告:一般在标题中会有“关于****的报告”字样。
[S]——标准[P]——专利[A]——文章:很少用,主要是不属于以上类型的文章。
[Z]——对于不属于上述的文献类型,可用字母“Z”标识,但这种情况非常少见。
常用的电子文献及载体类型标识:[DB/OL] ——联机网上数据(database online)[DB/MT] ——磁带数据库(database on magnetic tape)[M/CD] ——光盘图书(monograph on CD ROM)[CP/DK] ——磁盘软件(computer program on disk)[J/OL] ——网上期刊(serial online)[EB/OL] ——网上电子公告(electronic bulletin board online)很显然,标识的就是该资源的英文缩写,/前面表示类型,/后面表示资源的载体,如OL表示在线资源。
二、参考文献的格式及举例1.期刊类【格式】[序号]作者.篇名[J].刊名,出版年份,卷号(期号)起止页码.【举例】[1] 周融,任志国,杨尚雷,厉星星.对新形势下毕业设计管理工作的思考与实践[J].电气电子教学学报,2019(6):107-109.[2] 夏鲁惠.高等学校毕业设计(论文)教学情况调研报告[J].高等理科教育,2019(1):46-52.[3] Heider, E.R.& D.C.Oliver. The structure of color space in naming and memory of two languages [J]. Foreign Language Teaching and Research, 1999, (3): 62 – 67.2.专著类【格式】[序号]作者.书名[M].出版地:出版社,出版年份:起止页码.【举例】[4] 刘国钧,王连成.图书馆史研究[M].北京:高等教育出版社,1979:15-18,31.[5] Gill, R. Mastering English Literature [M]. London: Macmillan, 1985: 42-45.3.报纸类【格式】[序号]作者.篇名[N].报纸名,出版日期(版次).【举例】[6] 李大伦.经济全球化的重要性[N]. 光明日报,1998-12-27(3).[7] French, W. Between Silences: A Voice from China[N]. Atlantic Weekly, 1987-8-15(33).4.论文集【格式】[序号]作者.篇名[C].出版地:出版者,出版年份:起始页码.【举例】[8] 伍蠡甫.西方文论选[C]. 上海:上海译文出版社,1979:12-17.[9] Spivak,G. “Can the Subaltern Speak?”[A]. In C.Nelson & L. Grossberg(eds.). Victory in Limbo: Imigism [C]. Urbana: University of Illinois Press, 1988, pp.271-313.[10] Almarza, G.G. Student foreign language teacher’s knowledge growth[A]. In D.Freeman and J.C.Richards (eds.). Teacher Learning in Language Teaching [C]. New York: Cambridge University Press. 1996. pp.50-78.5.学位论文【格式】[序号]作者.篇名[D].出版地:保存者,出版年份:起始页码.【举例】[11] 张筑生.微分半动力系统的不变集[D].北京:北京大学数学系数学研究所, 1983:1-7.6.研究报告【格式】[序号]作者.篇名[R].出版地:出版者,出版年份:起始页码.【举例】[12] 冯西桥.核反应堆压力管道与压力容器的LBB分析[R].北京:清华大学核能技术设计研究院, 1997:9-10.7.专利【格式】[序号]专利所有者.题名[P].国别:专利号,发布日期.【举例】[13] 姜锡洲.一种温热外敷药制备方案[P].中国专利:881056073, 1989–07–26.8.标准【格式】[序号]标准编号,标准名称[S].【举例】[14] GB/T 16159—1996, 汉语拼音正词法基本规则 [S].9.条例【格式】[序号]颁布单位.条例名称.发布日期【举例】[15] 中华人民共和国科学技术委员会.科学技术期刊管理办法[Z].1991—06—0510.电子文献【格式】[序号]主要责任者.电子文献题名.电子文献出处[电子文献及载体类型标识].或可获得地址,发表或更新日期/引用日期.【举例】[17] 万锦.中国大学学报论文文摘(1983–1993).英文版 [DB/CD]. 北京: 中国大百科全书出版社, 1996.11.各种未定义类型的文献【格式】[序号] 主要责任者.文献题名[Z].出版地:出版者, 出版年.特别说明:凡出现在“参考文献”项中的标点符号都失去了其原有意义,且其中所有标点必须是半角,如果你的输入法中有半角/全解转换,则换到半角状态就可以了,如果你的输入法中没有这一转换功能,直接关闭中文输入法,在英文输入状态下输入即可.其实,很多输入法(如目前比较流行的搜狐输入法)都提供了四种组合:(1)中文标点+全角:这时输入的标点是这样的,。
中英文论文参考文献标准格式

中英文论文参考文献标准格式参考文献(即引文出处)的类型以单字母方式标识,具体如下:?[M]--专着,着作?[C]--论文集(一般指会议发表的论文续集,及一些专题论文集,如《***大学研究生学术论文集》? [N]-- 报纸文章?[J]--期刊文章:发表在期刊上的论文,尽管有时我们看到的是从网上下载的(如知网),但它也是发表在期刊上的,你看到的电子期刊仅是其电子版?[D]--学位论文:不区分硕士还是博士论文?[R]--报告:一般在标题中会有"关于****的报告"字样?[S]-- 标准?[P]--专利?[A]--文章:很少用,主要是不属于以上类型的文章?[Z]--对于不属于上述的文献类型,可用字母"Z"标识,但这种情况非常少见?常用的电子文献及载体类型标识:?[DB/OL] --联机网上数据(database online)?[DB/MT] --磁带数据库(database on magnetic tape)?[M/CD] --光盘图书(monograph on CDROM)?[CP/DK] --磁盘软件(computer program on disk)?[J/OL] --网上期刊(serial online)?[EB/OL] --网上电子公告(electronic bulletin board online)?很显然,标识的就是该资源的英文缩写,/前面表示类型,/后面表示资源的载体,如OL表示在线资源?二、参考文献的格式及举例?1.期刊类?【格式】[序号]作者.篇名[J].刊名,出版年份,卷号(期号)起止页码.?【举例】?[1] 周融,任志国,杨尚雷,厉星星.对新形势下毕业设计管理工作的思考与实践[J].电气电子教学学报,2003(6):107-109.?[2] 夏鲁惠.高等学校毕业设计(论文)教学情况调研报告[J].高等理科教育,2004(1):46-52.??2.专着类?【格式】[序号]作者.书名[M].出版地:出版社,出版年份:起止页码.?【举例】?[4] 刘国钧,王连成.图书馆史研究[M].北京:高等教育出版社,1979:15-18,31.?[5] Gill, R. Mastering English Literature [M]. London: Macmillan, 1985: 42-45.?3.报纸类?【格式】[序号]作者.篇名[N].报纸名,出版日期(版次).?【举例】?[6] 李大伦.经济全球化的重要性[N]. 光明日报,1998-12-27(3).?[7] French, W. Between Silences: A Voice from China[N]. Atlantic Weekly, 1987-8-15(33).? 4.论文集?【格式】[序号]作者.篇名[C].出版地:出版者,出版年份:起始页码.?【举例】?[8] 伍蠡甫.西方文论选[C]. 上海:上海译文出版社,1979:12-17.?[9] Spivak,G. "Can the Subaltern Speak"[A]. In C.Nelson & L. Grossberg(eds.). Victory in Limbo: Imigism [C]. Urbana: University of Illinois Press, 1988, pp.271-313.??5.学位论文?【格式】[序号]作者.篇名[D].出版地:保存者,出版年份:起始页码.?【举例】?[11] 张筑生.微分半动力系统的不变集[D].北京:北京大学数学系数学研究所, 1983:1-7.? 6.研究报告?【格式】[序号]作者. 篇名[R].出版地:出版者,出版年份:起始页码.?【举例】?[12] 冯西桥.核反应堆压力管道与压力容器的LBB分析[R].北京:清华大学核能技术设计研究院, 1997:9-10.?7.专利?【格式】[序号]专利所有者.题名[P].国别:专利号,发布日期.?【举例】??8.标准?【格式】[序号]标准编号,标准名称[S].?【举例】?[14] GB/T 16159-1996, 汉语拼音正词法基本规则[S].?9.条例?【格式】[序号]颁布单位.条例名称.发布日期?【举例】?[15] 中华人民共和国科学技术委员会.科学技术期刊管理办法[Z].1991-06-05?10.电子文献?【格式】[序号]主要责任者.电子文献题名.电子文献出处[电子文献及载体类型标识].或可获得地址,发表或更新日期/引用日期.【举例】??[17] 万锦.中国大学学报论文文摘(1983 1993).英文版[DB/CD]. 北京: 中国大百科全书出版社, 1996.?11.各种未定义类型的文献?【格式】[序号] 主要责任者.文献题名[Z].出版地:出版者, 出版年.?特别说明:凡出现在"参考文献"项中的标点符号都失去了其原有意义,且其中所有标点必须是半角,如果你的输入法中有半角/全解转换,则换到半角状态就可以了,如果你的输入法中没有这一转换功能,直接关闭中文输入法,在英文输入状态下输入即可.?其实,很多输入法(如目前比较流行的搜狐输入法)都提供了四种组合:?(1)中文标点+ 全角:这时输入的标点是这样的,:【1】-(而这时,我没有找到哪个键可以输入/ 符号)也就是说,这些符号是一定不能出现在"参考文献"中的;?(2)中文标点+半角:这时输入的标点是这样的,:【1】-(这时,我还是没有找到哪个键可以输入/ 符号)也就是说,这些符号也不能出现在"参考文献"中的;?上面列出的符号,中间没有任何的空格,你能看出它们有什么区别吗?我看只是-的宽度有一点点不同,其它都一样?(3)英文标点+全角:这时输入的标点是这样的,.:[1]-/?(4)英文标点+半角:这时输入的标点是这样的,.:[1]-/?从这两项可以明显的看出,半角和全角其实最大的差别是所占的宽度不一样,这一点对于数字来说最为明显,而英文标点明显要比中文标点细小很多(也许因为英文中,标点的功能没有中文那么复杂,就是说英文中标点符号的能力没有中文那么强大)?所以,很多人在写"参考文献" 时,总是觉得用英文标点+半角很不清楚,间距也太小,其实这点完全不用担心如果你觉得真的太小不好看,就用英文标点+全角吧而在[1] 之后,一般也都有一个空格?更为详细的内容,大家可以从附件中下载国家标准《文后参考文献着录规则GB/T 7714-2005》查看,不过,很长很烦,拿出点耐心看吧?对于英文参考文献,还应注意以下两点:?①作者姓名采用"姓在前名在后"原则,具体格式是:姓,名字的首字母. 如:Malcolm Richard Cowley 应为:Cowley, M.R.,如果有两位作者,第一位作者方式不变,&之后第二位作者名字的首字母放在前面,姓放在后面,如:Frank Norris 与Irving Gordon应为:Norris, F. &I.Gordon.?②书名、报刊名使用斜体字,如:Mastering English Literature,English Weekly.?三、注释?注释是对论文正文中某一特定内容的进一步解释或补充说明注释应置于本页页脚,前面用圈码①、②、③等标识。
参考文献的各种字母的含义

根据GB3469-83《文献类型与文献载体代码》规定,以单字母标识:M——专著(含古籍中的史、志论著)C——论文集N——报纸文章J——期刊文章D——学位论文R——研究报告S——标准P——专利A——专著、论文集中的析出文献Z——其他未说明的文献类型电子文献类型以双字母作为标识:DB——数据库CP——计算机程序EB——电子公告非纸张型载体电子文献,在参考文献标识中同时标明其载体类型:DB/OL——联机网上的数据库DB/MT——磁带数据库M/CD——光盘图书CP/DK——磁盘软件J/OL——网上期刊EB/OL——网上电子公告一、参考文献著录格式1 、期刊作者.题名〔J〕.刊名,出版年,卷(期)∶起止页码2、专著作者.书名〔M〕.版本(第一版不著录).出版地∶出版者,出版年∶起止页码3、论文集作者.题名〔C〕.编者.论文集名,出版地∶出版者,出版年∶起止页码4 、学位论文作者.题名〔D〕.保存地点.保存单位.年份5 、专利文献题名〔P〕.国别.专利文献种类.专利号.出版日期6、标准编号.标准名称〔S〕7、报纸作者.题名〔N〕.报纸名.出版日期(版次)8 、报告作者.题名〔R〕.保存地点.年份9 、电子文献作者.题名〔电子文献及载体类型标识〕.文献出处,日期二、文献类型及其标识1、根据GB3469 规定,各类常用文献标识如下:①期刊〔J〕②专著〔M〕③论文集〔C〕④学位论文〔D〕⑤专利〔P〕⑥标准〔S〕⑦报纸〔N〕⑧技术报告〔R〕2、电子文献载体类型用双字母标识,具体如下:①磁带〔MT〕②磁盘〔DK〕③光盘〔CD〕④联机网络〔OL〕3、电子文献载体类型的参考文献类型标识方法为:〔文献类型标识/载体类型标识〕。
例如:①联机网上数据库〔DB/OL〕②磁带数据库〔DB/MT〕③光盘图书〔M/CD〕④磁盘软件〔CP/DK〕⑤网上期刊〔J/OL〕⑥网上电子公告〔EB/OL〕三、举例1、期刊论文〔1〕周庆荣,张泽廷,朱美文,等.固体溶质在含夹带剂超临界流体中的溶解度〔J〕.化工学报,1995(3):317—323〔2〕Dobbs J M, Wong J M. Modification of supercritical fluid phasebehavior using polor coselvent〔J〕. Ind Eng Chem Res, 1987,26:56〔3〕刘仲能,金文清.合成医药中间体4-甲基咪唑的研究〔J〕.精细化工,2002(2):103-105〔4〕Mesquita A C, Mori M N, Vieira J M, et al .Vinyl acetate polymerization by ionizing radiation〔J〕.Radiation Physics and Chemistry,2002, 63:4652、专著〔1〕蒋挺大.亮聚糖〔M〕.北京:化学工业出版社,2001.127〔2〕Kortun G.Reflectance Spectroscopy〔M〕.New York: Spring-Verlag,1969 3、论文集〔1〕郭宏,王熊,刘宗林.膜分离技术在大豆分离蛋白生产中综合利用的研究〔C〕.//余立新.第三届全国膜和膜过程学术报告会议论文集.北京:高教出版社,1999.421-425〔2〕Eiben A E, vander Hauw J K.Solving 3-SAT with adaptive genetic algorithms 〔C〕.//Proc 4th IEEE Conf Evolutionary Computation.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1997.81-864、学位论文〔1〕陈金梅.氟石膏生产早强快硬水泥的试验研究(D).西安:西安建筑科学大学,2000〔2 〕Chrisstoffels L A J .Carrier-facilitated transport as a mechanistic tool in supramolecular chemistry〔D〕.The Netherland:Twente University.1988 5、专利文献〔1〕Hasegawa, Toshiyuki, Yoshida,et al.Paper Coating composition〔P〕.EP 0634524.1995-01-18〔2 〕仲前昌夫,佐藤寿昭.感光性树脂〔P 〕.日本,特开平09-26667.1997-01-28〔3〕Yamaguchi K, Hayashi A.Plant growth promotor and productionthereof 〔P〕.Jpn, Jp1290606.1999-11-22〔4〕厦门大学.二烷氨基乙醇羧酸酯的制备方法〔P〕.中国发明专利,CN1073429.1993-06-236、技术标准文献〔1〕ISO 1210-1982,塑料——小试样接触火焰法测定塑料燃烧性〔S〕〔2〕GB 2410-80,透明塑料透光率及雾度实验方法〔S〕7、报纸〔1〕陈志平.减灾设计研究新动态〔N〕.科技日报,1997-12-12(5)8、报告〔1〕中国机械工程学会.密相气力输送技术〔R〕.北京:19969、电子文献〔1〕万锦柔.中国大学学报论文文摘(1983-1993)〔DB/CD〕.北京:中国百科全书出版社,1996------------------------------------------------------------(1) 参考文献的著录应执行GB7714-87《文后参考文献著录规则》及《中国学术期刊(光盘版)检索与评价数据规范》规定,采用顺序编码制,在引文中引用文献出现的先后以阿拉伯数字连续编码,序号置于方括号内。
文献中各符号的意思
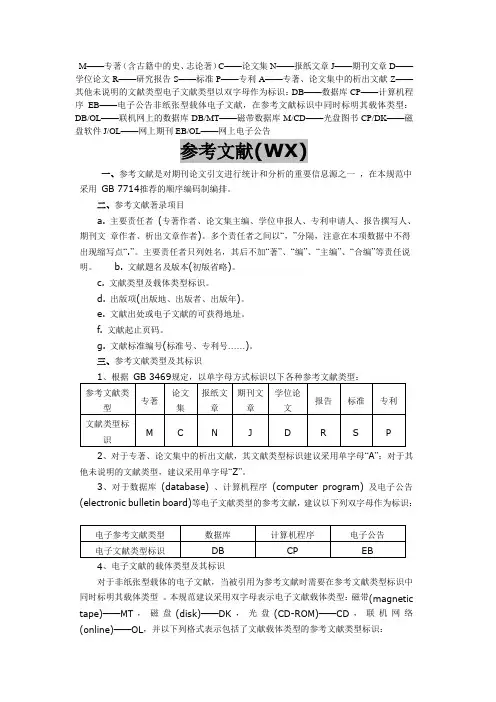
M——专著(含古籍中的史、志论著)C——论文集N——报纸文章J——期刊文章D——学位论文R——研究报告S——标准P——专利A——专著、论文集中的析出文献Z——其他未说明的文献类型电子文献类型以双字母作为标识:DB——数据库CP——计算机程序EB——电子公告非纸张型载体电子文献,在参考文献标识中同时标明其载体类型:DB/OL——联机网上的数据库DB/MT——磁带数据库M/CD——光盘图书CP/DK——磁盘软件J/OL——网上期刊EB/OL——网上电子公告参考文献(WX)一、参考文献是对期刊论文引文进行统计和分析的重要信息源之一,在本规范中采用GB 7714推荐的顺序编码制编排。
二、参考文献著录项目a. 主要责任者(专著作者、论文集主编、学位申报人、专利申请人、报告撰写人、期刊文章作者、析出文章作者)。
多个责任者之间以“,”分隔,注意在本项数据中不得出现缩写点“.”。
主要责任者只列姓名,其后不加“著”、“编”、“主编”、“合编”等责任说明。
b. 文献题名及版本(初版省略)。
c. 文献类型及载体类型标识。
d. 出版项(出版地、出版者、出版年)。
e. 文献出处或电子文献的可获得地址。
f. 文献起止页码。
g. 文献标准编号(标准号、专利号……)。
三、参考文献类型及其标识识2、对于专著、论文集中的析出文献,其文献类型标识建议采用单字母“A”;对于其他未说明的文献类型,建议采用单字母“Z”。
3、对于数据库(database) 、计算机程序(computer program) 及电子公告(electronic bulletin board)等电子文献类型的参考文献,建议以下列双字母作为标识:电子文献类型标识DB CP EB4、电子文献的载体类型及其标识对于非纸张型载体的电子文献,当被引用为参考文献时需要在参考文献类型标识中同时标明其载体类型。
本规范建议采用双字母表示电子文献载体类型:磁带(magnetic tape)——MT,磁盘(disk)——DK,光盘(CD-ROM)——CD,联机网络(online)——OL,并以下列格式表示包括了文献载体类型的参考文献类型标识:[文献类型标识/载体类型标识]如:[DB/OL]——联机网上数据库(database online)[DB/MT]——磁带数据库(database on magnetic tape)[M/CD]——光盘图书(monograph on CD-ROM)[CP/DK]——磁盘软件(computer program on disk)[J/OL]——网上期刊(serial online)[EB/OL]——网上电子公告(electronic bulletin board online)以纸张为载体的传统文献在引作参考文献时不必注明其载体类型。
英语论文参考文献格式

参考文献格式(根据出版社或杂志社的要求适当调整)一、参考文献的类型参考文献(即引文出处)的类型以单字母方式标识,具体如下:M——专著C——论文集N——报纸文章J——期刊文章D——学位论文R——报告S——标准P——专利A——文章对于不属于上述的文献类型,采用字母“Z”标识。
常用的电子文献及载体类型标识:〔DB/OL〕——联机网上数据(database online)〔DB/MT〕——磁带数据库(database on magnetic tape)〔M/CD〕——光盘图书(monograph on CD ROM)〔CP/DK〕——磁盘软件(computer program on disk)〔J/OL〕——网上期刊(serial online)〔EB/OL〕——网上电子公告(electronic bulletin board online)对于英文参考文献,还应注意以下两点:①作者姓名采用“姓在前名在后”原则,具体格式是:姓,名字的首字母.如:Malcolm Richard Cowley应为:Cowley, M.R.,如果有两位作者,第一位作者方式不变,&之后第二位作者名字的首字母放在前面,姓放在后面,如:Frank Norris与Irving Gordon应为:Norris, F. & I.Gordon.;②书名、报刊名使用斜体字,如:Mastering English Literature,English Weekly。
二、参考文献的格式及举例1.期刊类【格式】[序号]作者.篇名[J].刊名,出版年份,卷号(期号):起止页码.【举例】[1]周融,任志国,杨尚雷,厉星星. 对新形势下毕业设计管理工作的思考与实践[J].电气电子教学学报,2003(6):107-109.[2]夏鲁惠.高等学校毕业设计(论文)教学情况调研报告[J].高等理科教育,2004(1):46-52.[3] Heider, E.R.& D.C.Oliver. The structure of color space in naming and memory of two languages [J]. Foreign Language Teaching and Research, 1999, (3): 62 – 67.2.专著类【格式】[序号]作者.书名[M].出版地:出版社,出版年份:起止页码.【举例】[4]刘国钧,王连成.图书馆史研究[M].北京:高等教育出版社,1979:15-18,31.[5] Gill, R. Mastering English Literature [M]. London: Macmillan, 1985: 42-45 3.报纸类【格式】[序号]作者.篇名[N].报纸名,出版日期(版次).【举例】[6]李大伦.经济全球化的重要性[N].光明日报,1998-12-27(3).[7] French, W. Between Silences: A Voice from China[N]. Atlantic Weekly, 1987-8-15(33).4.论文集【格式】[序号]作者.篇名[C].出版地:出版者,出版年份:起始页码.【举例】[8]伍蠡甫.西方文论选[C].上海:上海译文出版社,1979:12-17.[9] Spivak,G. “Can the Subaltern Speak?”[A]. In C.Nelson & L.Grossberg(eds.). Victory in Limbo: Imigism [C]. Urbana: University of Illinois Press, 1988, pp.271-313.[10] Almarza, G.G. Student foreign language teacher’s knowledge growth [A]. In D.Freeman and J.C.Richards (eds.). Teacher Learning in Language Teaching [C]. New York: Cambridge University Press. 1996. pp.50-78.5.学位论文【格式】[序号]作者.篇名[D].出版地:保存者,出版年份:起始页码.【举例】[11]张筑生.微分半动力系统的不变集[D].北京:北京大学数学系数学研究所, 1983:1-7.6.研究报告【格式】[序号]作者.篇名[R].出版地:出版者,出版年份:起始页码.【举例】[12]冯西桥.核反应堆压力管道与压力容器的LBB分析[R].北京:清华大学核能技术设计研究院, 1997:9-10.7.专利【格式】[序号]专利所有者.题名[P].国别:专利号,发布日期.【举例】[13]姜锡洲.一种温热外敷药制备方案[P].中国专利:881056073, 1989–07–26. 8.标准【格式】[序号]标准编号,标准名称[S].【举例】[14] GB/T 16159—1996,汉语拼音正词法基本规则[S].9.条例【格式】[序号]颁布单位.条例名称.发布日期【举例】[15]中华人民共和国科学技术委员会.科学技术期刊管理办法[Z].1991—06—05 10.电子文献【格式】[序号]主要责任者.电子文献题名.电子文献出处[电子文献及载体类型标识].或可获得地址,发表或更新日期/引用日期.【举例】[16]王明亮.关于中国学术期刊标准化数据库系统工程的进展[EB/OL].http:///pub/wml.txt/980810–2.html, 1998–08–16/1998–10–04.[17]万锦.中国大学学报论文文摘(1983–1993).英文版[DB/CD].北京:中国大百科全书出版社, 1996.11.各种未定义类型的文献【格式】[序号]主要责任者.文献题名[Z].出版地:出版者,出版年.。
【2018最新】参考文献中的字母代表什么word版本 (2页)
【2018最新】参考文献中的字母代表什么word版本
本文部分内容来自网络,本司不为其真实性负责,如有异议或侵权请及时联系,本司将予以删除!
== 本文为word格式,下载后可随意编辑修改! ==
参考文献中的字母代表什么
国家期刊出版格式要求在中图分类号的下面应标出文献标识
码,规定如下:
作者可从下列a、b、c、d、e中选用一种标识码来揭示文章的性质:
a—理论与应用研究学术论文(包括综述报告);
b—实用性成果报告(科学技术)、理论学习与社会实践总结(科技);
c—业务指导与技术管理的文章(包括特约评论);
d—一般性通讯、报导、专访等;
e—文件、资料、人物、书刊、知识介绍等。
注:英文的文献标识码应与中文对应。
[参考文献类型标识码]
m——专著 monograph ; c——-论文集collection ;
n——报纸文章 news; j——期刊文章 journal; d——学位论文 degree;
r——报告 report; s——标准 standard; p——专利 patent;
a——专著、论文集中的析出文献 article; z——其它末说明文献
(1)文献类型标识:专著[m];期刊[j];论文集[c];学位论文[d]; 标准[s];报告[r];专利[p];报纸[n];。
论文参考文献的各种字母的含义及写法
DB/OL——联机网上的数据库
DB/MT——磁带数据库
M/CD——光盘图书
CP/DK——磁盘软件
J/OL——网上期刊
EB/OL——网上电子公告
示例:
文中:“宫、商、角、徵、羽,杂比曰音,单出曰声。”[1](《史记·乐书》:第1180页)
文未:[1] 汉·司马迁. 史记 [M]. 北京:中华书局, 1974.
2)参考文献的类型
根据GB3469-83《文献类型与文献载体代码》规定,以单字母标识:
〔3〕Yamaguchi K, Hayashi A.Plant growth promotor and productionthereof 〔P〕.Jpn, Jp1290606.
1999-11-22
〔4〕厦门大学.二烷氨基乙醇羧酸酯的制备方法〔P〕.中国发明专利,CN1073429.1993-06-23
〔1〕蒋挺大.亮聚糖〔M〕.北京:化学工业出版社,2001.127
〔2〕Kortun G. Reflectance Spectroscopy〔M〕. New York: Spring-Verlag,1969
3、论文集
〔1〕郭宏,王熊,刘宗林.膜分离技术在大豆分离蛋白生产中综合利用的研究〔C〕.//余立新.第三届全国膜和膜过程学术报告会议论文集.北京:高教出版社,1999.421-425
[序号]标准编号,标准名称[S].
[8] GB/T16159-1996,汉语拼音正词法基本规则[S].
f.专利
[序号]专利所有者.专利题名[P].专利国别:专利号,出版日期.
[9] 姜锡洲.一种温热外敷药制备方案[P].中国专利:881056073,1989-07-26.
期刊参考文献格式
最佳答案论文参考文献格式规范一、参考文献的类型参考文献(即引文出处)的类型以单字母方式标识,具体如下:[M]——专著,著作[C]——论文集(一般指会议发表的论文续集,及一些专题论文集,如《***大学研究生学术论文集》。
[N]——报纸文章[J]——期刊文章:发表在期刊上的论文,尽管有时我们看到的是从网上下载的(如知网),但它也是发表在期刊上的,你看到的电子期刊仅是其电子版。
[D]——学位论文:不区分硕士还是博士论文[R]——报告:一般在标题中会有“关于****的报告”字样。
[S]——标准[P]——专利[A]——文章:很少用,主要是不属于以上类型的文章。
[Z]——对于不属于上述的文献类型,可用字母“Z”标识,但这种情况非常少见。
常用的电子文献及载体类型标识:[DB/OL] ——联机网上数据(database online)[DB/MT] ——磁带数据库(database on magnetic tape)[M/CD] ——光盘图书(monograph on CD ROM)[CP/DK] ——磁盘软件(computer program on disk)[J/OL] ——网上期刊(serial online)[EB/OL] ——网上电子公告(electronic bulletin board online)很显然,标识的就是该资源的英文缩写,/前面表示类型,/后面表示资源的载体,如OL表示在线资源。
二、参考文献的格式及举例1.期刊类【格式】[序号]作者.篇名[J].刊名,出版年份,卷号(期号)起止页码.【举例】[1] 周融,任志国,杨尚雷,厉星星.对新形势下毕业设计管理工作的思考与实践[J].电气电子教学学报,2003(6):107-109.[2] 夏鲁惠.高等学校毕业设计(论文)教学情况调研报告[J].高等理科教育,2004(1):46-52.[3] Heider, E.R. D.C.Oliver. The structure of color space in naming and memory of two languages [J]. Foreign Language Teaching and Research, 1999, (3): 62 – 67. 2.专著类【格式】[序号]作者.书名[M].出版地:出版社,出版年份:起止页码.【举例】[4] 刘国钧,王连成.图书馆史研究[M].北京:高等教育出版社,1979:15-18,31.[5] Gill, R. Mastering English Literature [M]. London: Macmillan, 1985: 42-45. 3.报纸类【格式】[序号]作者.篇名[N].报纸名,出版日期(版次).【举例】[6] 李大伦.经济全球化的重要性[N]. 光明日报,1998-12-27(3).[7] French, W. Between Silences: A Voice from China[N]. Atlantic Weekly, 1987-8-15(33).4.论文集【格式】[序号]作者.篇名[C].出版地:出版者,出版年份:起始页码.【举例】[8] 伍蠡甫.西方文论选[C]. 上海:上海译文出版社,1979:12-17.[9] Spivak,G. “Can the Subaltern Speak?”[A]. In C.Nelson L. Grossberg(eds.). Victory in Limbo: Imigism [C]. Urbana: University of Illinois Press, 1988, pp.271-313.[10] Almarza, G.G. Student foreign language teacher’s knowledge growth [A]. InD.Freeman and J.C.Richards (eds.). Teacher Learning in Language Teaching [C]. New York: Cambridge University Press. 1996. pp.50-78.5.学位论文【格式】[序号]作者.篇名[D].出版地:保存者,出版年份:起始页码.【举例】[11] 张筑生.微分半动力系统的不变集[D].北京:北京大学数学系数学研究所, 1983:1-7. 6.研究报告【格式】[序号]作者.篇名[R].出版地:出版者,出版年份:起始页码.【举例】[12] 冯西桥.核反应堆压力管道与压力容器的LBB分析[R].北京:清华大学核能技术设计研究院, 1997:9-10.7.专利【格式】[序号]专利所有者.题名[P].国别:专利号,发布日期.【举例】[13] 姜锡洲.一种温热外敷药制备方案[P].中国专利:881056073, 1989–07–26.8.标准【格式】[序号]标准编号,标准名称[S].【举例】[14] GB/T 16159—1996, 汉语拼音正词法基本规则 [S].9.条例【格式】[序号]颁布单位.条例名称.发布日期【举例】[15] 中华人民共和国科学技术委员会.科学技术期刊管理办法[Z].1991—06—0510.电子文献【格式】[序号]主要责任者.电子文献题名.电子文献出处[电子文献及载体类型标识].或可获得地址,发表或更新日期/引用日期.【举例】[16] 王明亮.关于中国学术期刊标准化数据库系统工程的进展[EB/OL]. http: //–2.html, 1998–08–16/1998–10–04.[17] 万锦.中国大学学报论文文摘(1983–1993).英文版 [DB/CD]. 北京: 中国大百科全书出版社, 1996.11.各种未定义类型的文献【格式】[序号] 主要责任者.文献题名[Z].出版地:出版者, 出版年.特别说明:凡出现在“参考文献”项中的标点符号都失去了其原有意义,且其中所有标点必须是半角,如果你的输入法中有半角/全解转换,则换到半角状态就可以了,如果你的输入法中没有这一转换功能,直接关闭中文输入法,在英文输入状态下输入即可.其实,很多输入法(如目前比较流行的搜狐输入法)都提供了四种组合:(1)中文标点+全角:这时输入的标点是这样的,。
论文参考文献中J含义
论文参考文献中 J、 M 等是什么意思国家期刊出版格式要求在中图分类号的下面应标出文献标识码,规定如下:作者可从下列A、B、C、D、E 中选用一种标识码来揭示文章的性质:A—理论与应用研究学术论文(包括综述报告);B—实用性成果报告(科学技术)、理论学习与社会实践总结(科技);C—业务指导与技术管理的文章(包括特约评论);D—一般性通讯、报导、专访等;E—文件、资料、人物、书刊、知识介绍等。
注:英文的文献标识码应与中文对应。
[参考文献类型标识码]M——专著Monograph ;C——-论文集Collection ;N --- 报纸文章News ;J ----- 期刊文章Journal ; D ---- 学位论文Degree ;R --- 报告Report ;S ----- 标准Sta ndard ;P ---- 专利Pate nt ;A——专著、论文集中的析出文献Article;Z——其它末说明文献(1)文献类型标识:专著[M];期刊[J];论文集[c];学位论文[D];标准[S];报告[R];专利[P];报纸[N];(2)电子文献类型标识:数据库[DB];计算机程序[CP];电子公告[EB]; (3)电子文献的载体类型及其标识:联机网上数据库[DB/OL];参考文献(即引文出处)的类型以单字母方式标识:M 专著,C 论文集,N 报纸文章,J 期刊文章,D 学位论文,R 报告,S 标准,P――专利;对于不属于上述的文献类型,采用字母“Z”识。
参考文献的格式要求很多,一般来说参考文献的格式都要符合国标GB7714 - 87《文后参考文献著录规则》,但实际中很多出版社和期刊对论文的要求也不尽相同。
发现周围的很多人对论文参考文献的规范格式不是很清楚,所以把规范格式贴出来。
参考文献著录格式及示例1专著著录格式[序号]著者.书名.版本(第一版不写).出版地:出版者,出版年.起止页码例:[1]孙家广,杨长青.计算机图形学.北京:清华大学出版社,1995.26〜28Sun Jiaguang, Yang Changqing. Computer graphics [M] .Beijing: Tsinghua UniversityPress,1995.26~28(in Chinese)例:[2]Skolink M I. Radar handbook [M] . New York: McGraw-Hill, 19902期刊著录格式[序号]作者.题名[ J] .刊名,出版年份,卷号(期号):起止页码例::3]李旭东,宗光华,毕树生,等.生物工程微操作机器人视觉系统的研究[J] .北京航空航天大学学报,2002,28(3) : 249 〜252Li Xudong, Zong Guanghua, Bi Shusheng, et al. Research on global vision system for bioengineering-oriented micromanipulation robot system [J] . Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2002,28(3):249 〜252(in Chinese)3论文集著录格式[序号]作者.题名[ A] .见(英文用In) :主编.论文集名[ C] .出版地:出版者,出版年.起止页码例:[4]张佐光,张晓宏,仲伟虹,等.多相混杂纤维复合材料拉伸行为分析[A] •见:张为民编.第九届全国复合材料学术会议论文集(下册)[C].北京:世界图书出版公司,1996.410〜416例:[5]Odoni A R. The flow management problem in air traffic control [A] . In: Odoni A R, Szego G,eds. Flow Cont⑹ of Congested Networks [C] . Berlin: Springer-Verlag,1987.269 〜2984学位论文著录格式[序号]作者.题名[ D] .保存地点:保存单位,年例:[6]金宏.导航系统的精度及容错性能的研究[D] .北京:北京航空航天大学自动控制系,19985科技报告著录格式[序号]作者.题名[R].报告题名及编号,出版年例:[7]Kyungmoon Nho. Automatic landing system design using fuzzy logic[R].AIAA-98-4484,19986国际或国家标准著录格式[序号]标准编号,标准名称[S]例:[8]GB/T 16159 -1996 ,汉语拼音正词法基本规则[S]7专利著录格式[序号]专利所有者.专利题名[P].专利国别:专利号,出版日期例::9]姜锡洲.一种温热外敷药制备方案[P]•中国专利:881056073 , 1989-07-068电子文献著录格式[序号]作者.题名[电子文献/载体类型标识].电子文献的出处或可获得地址,发表或更新日期/引用日期例:[10]王明亮. 关于中国学术期刊标准化数据系统工程的进展[EB/OL]•ttp:///pub/wm1.txt...8-16/1998-10-04说明:①参考文献应是公开出版物,按在论著中出现的先后用阿拉伯数字连续排序.②参考文献中外国人名书写时一律姓前,名后,姓用全称,名可缩写为首字母(大写),不加缩写点(见例2).③参考文献中作者为3人或少于3人应全部列出,3人以上只列出前3人,后加"等"或"et al"(见例3).④在著录中文参考文献时应提供英文著录,见例1、例3.⑤参考文献类型及其标识见表1 ,电子参考文献类型及其标识见表2.⑥电子文献的载体类型及其标识为:磁带一一MT, 磁盘一一DK,光盘一一CD,联机网络——OL.表1 参考文献类型及文献类型标识参考文献类型专著论文集报纸文章期刊文章学位论文报告标准专利文献类型标识M C N J D R S P表2 电子参考文献类型及其标识电子参考文献类型数据库计算机程序电子公告电子文献类型标识DB CPEB科技期刊论文的参考文献1参考文献的功能与作用(1)参考文献是科技论文的重要组成部分,它不仅能为作者的论点提供有力的论据,而且可以精练文字节约篇幅,增加论文的信息量,具有很高的信息价值。
- 1、下载文档前请自行甄别文档内容的完整性,平台不提供额外的编辑、内容补充、找答案等附加服务。
- 2、"仅部分预览"的文档,不可在线预览部分如存在完整性等问题,可反馈申请退款(可完整预览的文档不适用该条件!)。
- 3、如文档侵犯您的权益,请联系客服反馈,我们会尽快为您处理(人工客服工作时间:9:00-18:30)。
J——期刊文章
N——报纸文章
M——专著
更多请看下面:
参考文献(即引文出处)的类型以单字母方式标识,具体如下:
M——专著C——论文集N——报纸文章J——期刊文章D——学位论文R——报告S——标准P——专利A——文章
对于不属于上述的文献类型,采用字母“Z”标识。
常用的电子文献及载体类型标识:
〔DB/OL〕——联机网上数据(database online)
〔DB/MT〕——磁带数据库(database on magnetic tape)
〔M/CD〕——光盘图书(monograph on CDROM)
〔CP/DK〕——磁盘软件(computer program on disk)
〔J/OL〕——网上期刊(serial online)
〔EB/OL〕——网上电子公告(electronic bulletin board online)
参考文献著录格式
1 期刊作者.题名[J].刊名,出版年,卷(期):起止页码
2 专著作者.书名[M].版本(第一版不著录).出版地:出版者,出版年.起止页码
3 论文集作者.题名[C].//编者.论文集名.出版地:出版者,出版年.
起止页码
4 学位论文作者.题名[D].保存地点:保存单位,年份
5 专利文献题名[P].国别,专利文献种类,专利号.出版日期
6 标准标准编号,标准名称[S]
7 报纸作者.题名[N].报纸名,出版日期(版次)
8 报告作者.题名[R].保存地点:年份
9 电子文献作者.题名[电子文献及载体类型标识].文献出处,日期
二、文献类型及其标识
1.根据GB3469 规定
①期刊[J]
②专著[M]
③论文集[C]
④学位论文[D]
⑤专利[P]
⑥标准[S]
⑦报纸[N]
⑧技术报告[R]
2.电子文献载体类型用双字母标识,例如:
①磁带[MT]②磁盘[DK]③光盘[CD]④联机网络[OL]
3.电子文献载体类型的参考文献类型标识方法为:[文献类型标识/载体类型标识
例如:①联机网上数据库[DB/OL]②磁带数据库[DB/MT]③光盘图书[M/CD]④磁盘软件[CP/DK]⑤网上期刊[J/OL]⑥网上电子公告[EB/OL]。
