高中英语语法系统讲解之九定语从句

定语从句
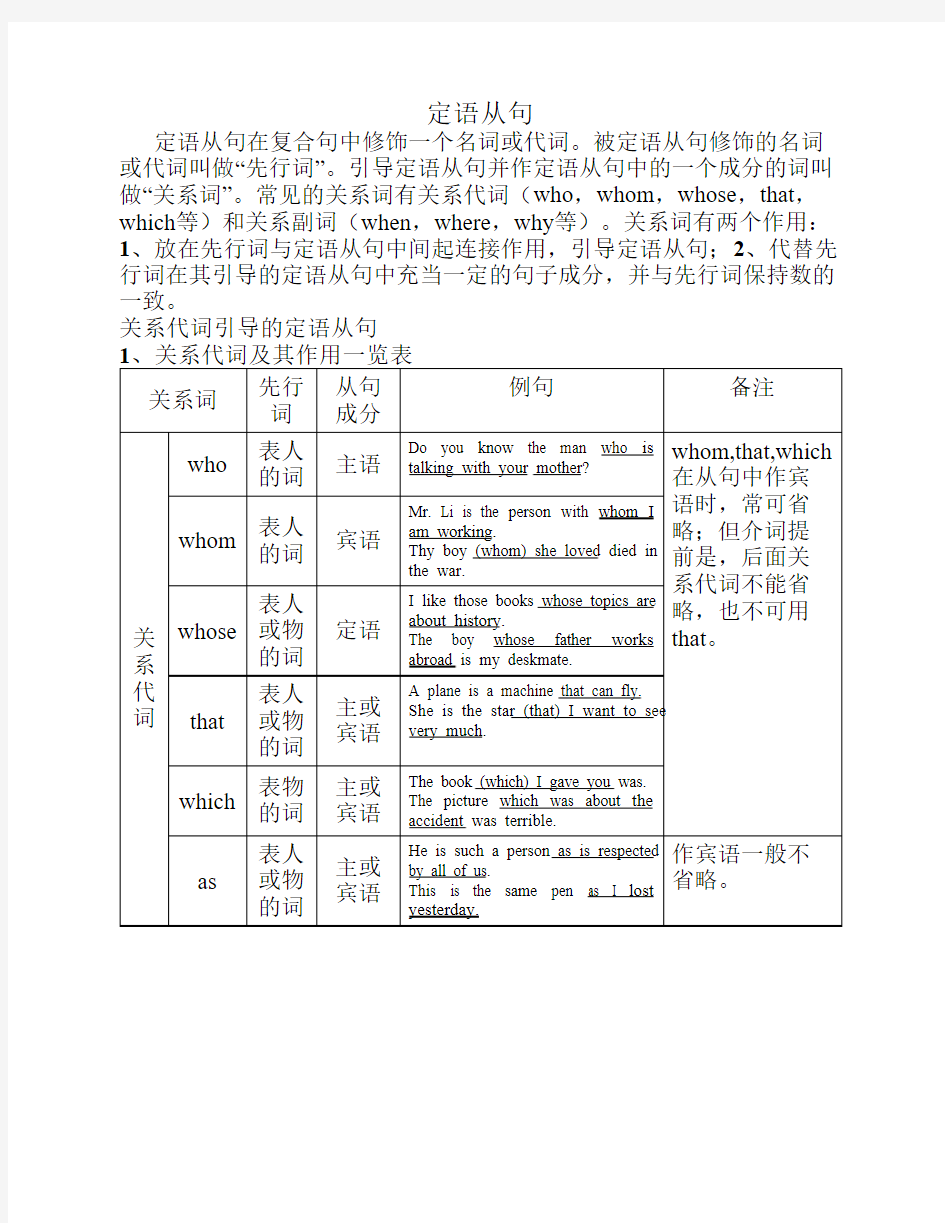
定语从句在复合句中修饰一个名词或代词。被定语从句修饰的名词或代词叫做“先行词”。引导定语从句并作定语从句中的一个成分的词叫做“关系词”。常见的关系词有关系代词(who,whom,whose,that,which等)和关系副词(when,where,why等)。关系词有两个作用:1、放在先行词与定语从句中间起连接作用,引导定语从句;2、代替先行词在其引导的定语从句中充当一定的句子成分,并与先行词保持数的一致。
关系代词引导的定语从句
2、关系代词特殊用法一览表
情况用法说明例句
只用that的情况1、先行词为all,everything,
anything,nothing,little,
much等不定代词时;
2、先行词被all,any,every,
each,much,little,no,
some,few等修饰时;
3、先行词有形容词最高级或序
数词修饰时
4、先行词既指人又指物时;
5、先行词被the only,the very修
饰时;
6、先行词位于以who或which引
导的特殊疑问句式的主句中
时;
7、关系代词在定语从句中作表
语时。
1. He told me everything that he knows.
2. All the books that you offered have
been given out.
3. This is the best film that I have ever
seen.
4. We talked about the person and things
that we remembered.
5. He is the only man that I want to see.
6. Who is the man that is making a
speech?
7. Which is the book that you like best?
只用which who whom 的情况1、在非限制性定语从句中,只
能用which指物;用
who/whom指人;
2、在由“介词+ 关系代词”引导
的定语从句中,用which指
物,whom指人;
3、先行词本身是that时,关系词
用which,先行词为those,
one,he时用who。
1. He has a son, who has gone abroad for
further study.
2. I like the person to whom the teacher is
talking.
3. Those who respect others are usually
respected by others.
温馨提示:“whose + 名词”这一结构在定语从句中既能作主语,又能作宾语,whose的先行词常用来指人,但有时也可以用来指具体事物或抽象概念,这时可以与of which结构互换,词序是“the+名词+ of which”。如Please pass me the book whose cover (the cover of which) is green.
3. 关系副词的用法
由when引导:when指时间,在从句中作时间状语,它所修饰的先行词有time,day,morning,night,week,year等。
如From the time when he was little, he had known what he wanted to be when he grew up.
由where引导:where指地点,在从句中作地点状语,它的先行词有place,spot,street,room,city,country等。如Is this the room where you were living last winter?
Beijing is the place where I was born.
由why引导:why表示原因,常用在先行词reason后面。
如The reason why he said that is quite clear.
I don’t know the reason why she looks unhappy today.
4. 使用关系副词时应注意的几点:
有些先行词虽不表具体的地点,但表达一种“阶段、境地、形势、地步”,也可用where来引导定语从句。如:stage,situation,case,
point等。
如:At that time we had reached a stage where we had more women readers than men readers.
Increasing poverty has led to a situation where some people cannot afford their children’s school fees.
Can you think of a case where you are mistaken by others, but you can’t tell the truth?
It seems that their relation has reached the point where they have to divorce.
先行词虽然是表示时间、地点或原因的名词,但如果关系词在从句中作主语或宾语,则用关系代词that或which引导。
对比:I will never forget the happy days which we spent we spent together.
I will never forget the days when we visited your university.
This is the special school which was set up 10 years ago.
This is the special school where my father has taught for 10 years.
Do you believe the reason that he gave?
Do you know the reason why he killed himself?
在某些表示时间名词后的关系副词可省略。如the time,every time,each time,the moment。
如Do you still remember the day (when) we first met?
5. “介词 + 关系代词”引导的定语从句
“介词+ 关系代词”引导的定语从句中的关系代词只能用which或whom。
先行词表物时用which;先行词表人时用whom。介词的使用取决于句子意义的需要,或句中动词、形容词、副词与介词的搭配,表“所
有”关系或“整体中的一部分”时,用of。
如:I don’t know the time at which (= when) the meeting will begin.
I still remember the day on which (= when) I first came to this school.
This is the subject about which we might argue for a long time.
This is the worker from whom I have learned a great deal.
Is that the boss to whom you have explained your situation?
I bought a dozen of eggs, half of which were broken when I got home.
当介词位于定语从句的末尾时,可用that / which(指物),that / whom / who(指人)作介词的宾语,而且作介词宾语的关系代词往往省略。
如This is the hero (that / who / whom) we are proud of.
This is the pen (that / which) I wrote the letter with.
“复合介词短语+ 关系代词which”引导的定语从句,这种结构引导的定语从句常与先行词用逗号分开,定语从句常用倒装语序。
如He lived in a big house, in front of which stood a big tall tree.
介词 + 关系代词 = 关系副词。如This is the room which we lived in last year.
This is the room in which we lived last year.
This is the room where we lived last year.
6. 关系代词as引导的定语从句
as用作关系代词,引导限制性定语从句,常可与主句中的the same或such 相呼应,其中as为代词,在从句中作主语、宾语、表语。
如We do the same work as they (do).
He is not the same man as he was.
I hope to get such a dictionary as he is using.
We will give you such information as will help you in your work.
as引导非限制性定语从句,在句中作主语、宾语或表语,这个定语从句是说明整个句子的,它可以放在主句之前。如As we all know, he studies very hard.
As is known to all, he is the best student in our class.
常用的这种类似插入语的句式有as is said above,as it is等。
7. 限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句
限制性定语从句是整个句子不可缺少的部分,主句和从句之间不用逗号分开,其引导词可用关系代词that,which,who,whom,whose,as和关系副词when,where,why。这些引导词一般只在从句中作宾语时才可省略。
非限制性定语从句是对主句先行词的补充说明,没有从句,也不影响主句意思的完整。一般不用逗号把主句和从句分开,通常不用关系代词that。
如A dictionary is a book which gives the meaning of words.
I have lost a pen, which I like very much.
Do you remember the teacher who taught us Chinese at middle school?
I have two brothers, who are both students.
温馨提示:as和which引导非限制性定语从句时,都可以指代整个主句内容,二者的区别是: as引导的定语从句位置灵活,可放在句首、句中或句末;which引导的定语从句只能放在主句之后;as意为“正如;
这一点”;which意为“这件事”。
如As is mentioned above, English is easy to learn.
He failed in the examination again, which disappointed his parents.
、非限制性定语从句通常不用that引导。I am fond of the novel, which you bought for me.
、在非限制性定语从句中,指人的关系代词作宾语时,只能用whom,不能用who替换,也不能省略。Lily, whom you met at the party, is my favorite friend.
、非限制性定语从句不能用why引导,要用for which代替why。
eg: I have told him the reason, for which I missed the early bus.
8. 使用定语从句应注意的问题
关系代词在从句中作主语时,从句的谓语动词用单数还是复数应由先行词决定。
如The man who lives downstairs speaks English fluently.
The students who are in Grade Three are going to climb the hill tomorrow.
引导定语从句的关系副词可以用“介词 + which”代替。
如October 1,1949 was the day on which (=when) the People’s Republic of China was founded
This is the room in which ( = where) Lu Xun once lived.
当定语从句中谓语动词是带介词或副词的动词短语时,动词短语不能拆开。
如The dictionary which you are looking for is on the desk.
The sick man whom she is looking after is her father.
关系代词和关系副词在从句中充当一个成分,因此,使用时要注意避免从句中句子成分的重复出现。如Let me have a look at the dictionary that you bought it yesterday. (×)
Let me have a look at the dictionary that you bought yesterday.
(√)
This is the house where I lived in two years ago. (×)
This is the house (that / which) I lived in two years ago.
(√)
强化训练
1. ---Where did you get to know her?
---It was on the farm we worked.
A. that
B. there
C. which
D. where
2. The book was written in 1946, the education system has witnessed great changes.
A. when
B. during which
C. since the
D. since when
3. Some pre-school children go to a day care center, they learn simple games and songs.
A. then
B. there
C. while
D. where
4. You can only be sure of you have at pressent; you cannot be sure of
something you might get in the future.
A. that ; what
B. what ; /
C. which ; that
D. / ; that
5. Last week, only two people came to look at the house, wanted to buy it.
A. none of them
B. both of them
C. none of whom
D. neither of whom
6. Those successful deaf dancers think that dancing is an activity sight
matters more than hearing.
A. when
B. whose
C. which
D. where
7. Chan’s restaurant on Baker Street, used to be poorly run, is now a
successful business.
A. that
B. which
C. who
D. where
8. He was educated at the local high school, he went on to Beijing
University.
A. after which
B. after that
C. in which
D. in that
9. The course normally attracts 20 students per year, up to half will be
from abroad.
A. in which
B. for whom
C. with which
D. of whom
10. I have never dined with you, sir; and I see no reason .
A. how can I know
B. how I ought to know
C. why shall I know
D. why I
should know
11. ---Do you have anything in mind you’d like for supper?
---Well, is okay with me.
A. that ; anything
B. which ; everything
C. what ; nothing
D. what ;
nothing
12. My uncle and aunt work on a farm, they raise fifty .
A. there ; cattle
B. where ; head of cattle
C. in which ; head of cattle
D.
where ; cattles
13. Amony the winners father is seriously ill in hospital.
A. stand little Tom who
B. stood little Tom whom
C.little Tom stands
whose D.stands little Tom whose
14. The reason he gave for being late was he forgot to use the alarm clock.
A. which ; because
B. why ; because
C. which ; that
D. that ; because
15. While driving through the city, she showed me the building she once
worked as a lift operator.
A. when
B. which
C. by which
D. in which
16. China got 165 gold medals in the Asian Games in Doha, of course,
made the whole nation excited.
A. which
B. what
C. that
D. where
17. The TV set he works well now.
A. has repairing
B. having repaired
C. has been repaired
D. has had
repaired
18. Anyway, that evening, I’ll tell you more about later, ended up staying at
Rachel’s place.
A. when
B. where
C. what
D. which
19. is known to us all is that the old scientist, for life was hard in the
past, still works very hard in his eighties.
A. As ; whom
B. What ; whom
C. It ; whose
D. As ; whose
20. It was in the stone house was built as a school by local villagers the
boy finished his primary school.
A. which ; that
B. that ; where
C. which ; which
D. that ; which
21. The house was blown off is being repaired.
A. whose roof
B. the roof of that
C. of which roof
D. roof of which
22. It’s the third time late this week.
A. that you are
B. you are
C. when you arrived
D. when you have
been
23. Did all the members present agree to the plan?
A. who
B. that
C. wrer
D. /
24. Keep away from such persons will do you no good.
A. as
B. that
C. like
D. who
25. Who has common sense can’t believe such a thing?
A. else
B. which
C. but
D. that
26. Who is the man is reading in the garden?
A. who
B. that
C. whom
D. /
27. That is the town he worked in 1987.
A. where
B. which
C. that
D. in that
28. She doesn’t understand the reason he would like to join them.
A. for that
B. why
C. how
D. which
29. The day will come soon he will see his success.
A. which
B. when
C. on that
D. where
30. They walked together as far as the second crossing they parted.
A. when
B. which
C. why
D. where
31. He is learned, unfortunately I was not.
A. whom
B. that
C. which
D. who
32. He told me to start work, I did not follow.
A. that
B. what
C. this
D. which
33. Anyone agrees may come with me.
A. that
B. who
C. to whom
D. with whom
34. The house colour is red is John’s.
A. whose
B. of which
C. which
D. the
35. Sunday is the day people have a rest.
A. that
B. on which
C. for which
D. at which
36. This is the hotel we stopped to rest.
A. at which
B. that
C. where
D. which
37. Tell me the reason you were wet all over.
A. how
B. why
C. of which
D. for that
38. His father, likes painting, is a teacher.
A. who
B. whom
C. that
D. which
(完整版)初中英语定语从句讲解教师版
初中英语定语从句讲解及练习(教师版) 一.定语从句及相关术语 1.定语从句:修饰一个名词或代词的从句称为定语从句,一般紧跟在它所修饰的先行词后面。 2.关系词:引导定语从句的关联词成为关系词 关系词有关系代词和关系副词。关系代词有that, which, who, whom, whose, as 等; 关系副词有where, when, why等。 关系词常有3个作用:1,引导定语从句。2,代替先行词。3,在定语从句中担当一个成分。 二.关系代词引导的定语从句 1.who指人,在从句中做主语 (1) the boys who are playing football are from class one. (2) yesterday i helped an old man who lost his way. 2. whom指人,在定语从句中充当宾语,常可省略。 (1) mr. liu is the person (whom) you talked about on the bus. (2) mr. ling is just the boy whom i want to see. 注意:关系代词whom在口语和非正式语体中常用who代替,可省略。 (3) the man who/whom you met just now is my friend. 3. which指物,在定语从句中做主语或者宾语,做宾语时可省略 (1) football is a game which is liked by most boys. (2) this is the pen (which) he bought yesterday. 4. that指人时,相当于who 或者whom;指物时,相当于which。在宾语从句中做主语或者宾语,做宾语时可省略。 (5) the number of the people that/who come to visit the city each year rises one million. (6) where is the man that/whom i saw this morning? 5. whose通常指人,也可指物,在定语从句中做定语 (1) he has a friend whose father is a doctor. (2) i once lived in a house whose roof has fallen in. whose指物时,常用以下结构来代替 (3) the classroom whose door is broken will soon be repaired. (4) the classroom the door of which is broken will soon be repaired. (5) do you like the book whose cover is yellow? (6) do you like the book the color of which is yellow? 三.介词+关系代词引导的定语从句 关系代词在定语从句中做介词宾语时,从句常由介词+关系代词引导 (1) the school (that/which) he once studied in is very famous. (2) the school in which he once studied is very famous. (3) tomorrow i will bring here a magazine (that/which) you asked for. (4) tomorrow i will bring here a magazine for which you asked. (5) we'll go to hear the famous singer (whom/that/who) we have often talked about. (6) we'll go to hear the famous singer about whom we have often talked. 注意:1. 含有介词的动词短语一般不拆开使用,如:look for, look after, take care
(完整版)定语从句超详细讲解
定语从句 一学习目标 1.熟练掌握定语从句 二考点解析 ⊙定从的功能—解释说明 This is the factory that/which can produce such machines 这就是能制造这种机器的工厂This is the factory that/which we visited last week 这就是我们上周参观的工厂 ⊙定语从句 定义:一个简单句跟在名词或代词后(先行词)进行修饰限定,就叫做定语从句。这个简单句在主句中充当定语成分。 I bought a cow that looked like a horse. ⊙定语从句怎么考? 语法 22.I live next door to a couple children often make a lot of noise.(2016高考北京卷) A.whose B.why C.where D.which 完形 Balto put his nose to the ground, 52 to find the smell of other dogs that had traveled on the trail. (2016高考北京卷) 阅读&写作 A nurse who understands the healing(治愈) value of silence can use this understanding to assist in the care of patients from their own and from other cultures.(2016高考全国卷D篇) Last year, I spent all my time looking for a job where, without dealing with the public , I could work alone, but still have a team to talk to. (2016高考北京卷阅读A篇) ⊙定从原理:把两个句子合为一个,两个句子有相同的部分,此时可以把其中一个句子作为另一个句子的修饰限定部分。
高中英语语法系统全解【珍藏版】
高中英语语法系统全解 第一章动词时态 在英语中,不同时间发生的动作或存在的状态,要用不同的动词形式来表示,这就叫做动词的时态。一、一般时 一般时包括一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时和一般过去将来时。 A.一般现在时 1.一般现在时的构成 一般现在时主要用动词原形来表示。主语是第三人称单数时,动词后面要加-s 或-es。 They want good jobs. 他们想要好的工作。 The coat matches the dress. 外衣和裙子很相配。 This work does not satisfy me. 这项工作我不满意。 Do you understand? 你懂了吗? 2.一般现在时的用法 ①一般现在时的基本用法 a. 表示现在习惯性的动作或存在状态 He always takes a walk after supper. 晚饭后他总是散散步。 Everyone is in high spirits now. 现在大家都情绪高涨。 b. 表示客观事实或普遍真理 The sun rises in the east and sets in the west. 太阳从东方升起在西方落下。 Sound travels faster through water than it does through air. 声音在水中的传播速度要比在空气中快。
Time and tide wait for no man. 时间不等人。 c. 表示主语的特征、能力和状态 This cloth feels soft. 这布摸上去很软。 I love classical music. 我喜欢古典音乐。 The President still seems able to find time to go fishing. 看来总统仍能有时间去钓鱼。 d. 表示按计划或安排将要发生的动作 The meeting begins at 7:00. 会议七点钟开始。 We leave here at 8:00 sharp. 我们八点整离开这里。 e. 在时间、条件、让步状语从句中表示将来动作 When you come next time, bring me some magazines. 你下次来时,给我带几本杂志。 If time allows, we shall go there tomorrow. 如果时间允许的话,我们明天去那里。 Whether he agrees or not, I will stay at home. 不管他同意与否,我都会待在家里。 ②一般现在时的特殊用法 a. 用于新闻标题或图片说明中 China Declares Manned Spaceflight Successful 中国宣布载人航天飞行圆满成功 Laura Bush Arrives in Moscow 劳拉·布什抵达莫斯科 b. 用于体育运动、表演等实况报道中 Francis slips past, passes the ball to Yao Ming, who jumps, catches and shoots it into the basket.
定语从句讲解关系代词的用法
Un itl 《 school life 》 Grammar (1) 定语从句(AttributiveClause) I根据初中所学知识,请用红笔标出下列表格中的定语 定语从句的定义及其作用: 定语从句是又称形容词性从句,在句子中起定语作用,修饰一个名词或代词,有时也可修饰一个句子.受定语从句修饰的词叫先行词.定语从句的作用和作定语的形容词、介词词组、分词词组相似,有时可以相互转换,例如:金发女孩可译作abl on degirl, agirlwithbl on dehair 或agirlwhohasblo ndehair。定语从句通常由关系代词 that/which/who/whom/which/as 或关系副词when/where/why 引导,这些词既指代主句中要说明的名词或代词,又充当从句中的某个句子成分。定语从句可分为:限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句。 定语从句一般都紧跟在它所修饰名词后面,所以如果在名词或代词后面出现一个从句,根据它与前面名词或代词的逻辑关系来判断是否是定语从句。 川定语从句的必备三要素 1先行词(名词或代词) | relativepr on. (assub.,obj.,pred.) 2关系词 (that 指人或物/which 指物/who(m)指人/whose) 3关系词在从 句中充当成分ativeadv. (asadverbial) (whe n/where/why) 找出下列句中的定语从句;分析定语从句三要素 1.Youaretherightmanwhomwearelookingfor. 2.I ' vespentallthemoneythatwasgivenbymyparents. 3.Iwillneverforgettheday whenljoinedtheparty.
(完整版)高中英语定语从句讲解及练习
高中英语定语从句讲解及练习 定语从句是高中重点知识,也是高考常考点,大家也不容易掌握,这篇文章主要教你关系代词引导的定语从句 关系副词引导的定语从句判断关系代词与关系副词限制性和非限制性定语从句等内容,有例题讲解定语从句在句中做定语,修饰一个名词或代词,被修饰的名词词组或代词即先行词。定语从句通常出现在先行词之后,由关系词(关系代词或关系副词)引出。 关系代词有:who, whom, whose, that, which等。 关系副词有:when, where, why等。 18.1 关系代词引导的定语从句 关系代词所代替的先行词是人或物的名词或代词,并在句中充当主语、宾语、定语等成分。关系代词在定语从句中作主语时,从句谓语动词的人称和数要和先行词保持一致。 1)who, whom, that 这些词代替的先行词是人的名词或代词,在从句中作主语和宾语。例如: Is he the man who/that wants to see you? 他就是你想见的人吗?(who/that在从句中作主语) He is the man whom/ that I saw yesterday. 他就是我昨天见的那个人。(whom/that在从句中作宾语) 2)whose 用来指人或物,(只用作定语, 若指物,它还可以同of which互换)。例如: They rushed over to help the man whose car had broken down.那人车坏了,大家都跑过去帮忙。 Please pass me the book whose (of which)cover is green.请递给我那本绿皮的书。 3)which, that所代替的先行词是事物的名词或代词,在从句中可作主语、宾语等。例如: A prosperity which / that had never been seen before appears in the countryside. 农村出现了前所未有的繁荣。(which / that在句中作宾语) The package (which / that)you are carrying is about to come unwrapped. 你拿的包快散了。(which / that在句中作宾语) 18.2 关系副词引导的定语从句 关系副词可代替的先行词是时间、地点或理由的名词,在从句中作状语。 1)关系副词when, where, why的含义相当于\"介词+ which\"结构,因此常常和\"介词+ which\"结构交替使用。例如: There are occasions when (on which)one must yield.任何人都有不得不屈服的时候。 Beijing is the place where(in which)I was born.北京是我的出生地。 Is this the reason why (for which)he refused our offer?这就是他拒绝我们帮助他的理由吗? 2)that代替关系副词,可以用于表示时间、地点、方式、理由的名词后取代when, where, why和\"介+which\"引导的定语从句,在口语中that常被省略。例如: His father died the year (that / when / in which)he was born.他父亲在他出生那年逝世了。 He is unlikely to find the place (that / where / in which)he lived forty years ago. 他不大可能找到他四十年前居住过的地方。 18.3 判断关系代词与关系副词 方法一:用关系代词,还是关系副词完全取决于从句中的谓语动词。及物动词后面无宾语,就必须要求用关系代词;而不及物动词则要求用关系副词。例如: This is the mountain village where I stayed last year. 这是我去年呆过的山村。 I'll never forget the days when I worked together with you.我永远不会忘记与你共事的日子。 判断改错: (错)This is the mountain village where I visited last year. (错)I will never forget the days when I spent in the countryside. (对)This is the mountain village (which)I visited last year. (对)I'll never forget the days (which)I spent in the countryside. 习惯上总把表地点或时间的名词与关系副词where, when联系在一起。此两题错在关系词的误用上。 方法二:准确判断先行词在定语从句中的成分(主、谓、宾、定、状),也能正确选择出关系代词/关
人教版高中英语【必修二】[语法讲解
人教版高中英语必修二 知识点梳理 重点题型(常考知识点)巩固练习 限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句 概念引入: He is a person who never gives up. 他是个永远不服输的人。 I found him in the woods, where has a well-known tree. (我是在树林里找到他的,那里有一棵很有名的树。) Our guide,(who was a Frenchman, ) was an excellent cook. 我们的导游是个很优秀的厨师,他是个法国人 She was not on the train which arrived just now。 她没在刚刚到达的那辆车上 语法点拨 什么是定语从句? 修饰主语、宾语、表语的句子就叫做定语从句。引导定语从句的关系词有: 关系代词:who, whom, whose, which, that 关系副词:when, where, why 我们把下面两个句子组合成一个复合句: 1. This is our school. It is beautiful. →This is our school which is beautiful. 2. This is our school. We study in our school. →This is our school which we study in. →This is our school in which we study. →This is our school where we study. 3. Do you know the room? It is made of amber. →Do you know the room which is made of amber? 4. I have read the newspaper. It carries the important news. →I have read the newspaper which carries the important news. 从上述定语从句的组合我们可以看出: 先行词和关系词的关系:关系代词实际上是先行词的复指;关系词whose 实际上是先行词的所有格。 1. A plane is a machine that can fly. the machine = that 2. The boy who broke the window is called Wangkai. the boy =who 3. The boy whose parents are working outside was brought up by his grandfather. the boy’s =whose 【高一英语语法(二)定语从句(二)356521限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句】
高一英语定语从句讲解精华版
定语从句 一、基本概念: 定语: 定语从句: Do you know the man who spoke at the meeting just now That is the house where he lived ten years ago. 引导词:关系词 关系代词有:that, who, whom, whose, which; 在从句中充当: 关系副词有:when, where, why. 在从句充当: 先行词: 定语从句中引关系词的作用: 二、关系词的用法: (一)关系代词的用法: 1. He is the man lives next door. The train has just left is for Shenzhen. 2. The man ________ we have just seen is a famous writer. Where is the book ___________I bought last week (二)关系副词的用法: 1. I still remember the time ________I first became a college student. Do you know the date __________Lincoln was born
(三) 使用关系副词应注意下列几点: 1.这三个关系副词在意义上都相当于一定的介词+which结构: when = on (in, at, during…) + which; where = in (at, on…) + which; why = for which. 如: I was in Beijing on the day when (=on which) he arrived. The office where (=in which) he works is on the third floor. This is the chief reason why (=for which) we did it. 2.当先行词是表时间的time, day等和表地点的place, house等时,一定要注意分析从句的结构,如果缺少主语或宾语时,关系词应该用which或that, 缺少时间状语或地点状语时,才能用when或where,试比较: I’ll never forget the day _________ my hometown was liberated. I’ll never forget the days____________we spent together last summer. His father works in a factory____________radio parts are made. His father works in a factory______________makes radio parts. 三.限制性定语从句与非限制性定语从句 1.限制性定语从句 This is the telegram which he refers to. Is there anything (that) I can do for you 2.非限制性定语从句 This note was left by Tom, who was here a moment ago. As a boy, he was always making things, most of which were electric.
(完整word版)英语定语从句用法详解
英语定语从句用法详解 在复合句中,修饰名词或代词的从句叫定语从句,被修饰的名词或代词叫先行词,引导定语从句的有关系代词who, whom, whose, which, that等和关系副词where, when, why等,关系代词和关系副词在定语从句中担任句子成份。 1.由who引导的定语从句中,who用作主语,如:This is the boy who often helps me. 2.由whom引导的定语从句中,whom用作宾语,如:The man whom you are waiting for has gone home. 3.由whose引导的定语从句中,whose用作定语,如:Do you know the girl whose skirt is white? 4.由which引导的定语从句中,which用作主语或谓语动词的宾语或介词的宾语,如: The room in which there is a machine is a work shop. The river which is in front of my house is very clean. This is the pen which you want. 注意: (1)whom, which用作介词宾语时,介词可放在whom、which之前,也可放在从句原来的位置上;但在含有介词的动词固定词组中,介词只能放在原来的位置上。如:He is the very person whom we must take good care of. (2)引导非限制性定语从句时,必须用关系代词which,不用that,如:I have lost my bag, which I like very much. (3)关系代词在句中作主语时,从句的谓语动词的人称和数必须和先行词保持一致。 5.由that引导的定语从句中,that可以指人或物,在从句中作主语或谓语动词的宾语,但不能放在介词后面作介词宾语,如: The book that I bought yesterday was written by Lu Xun. 注意在下面几种情况下必须用that引导定语从句。 (1)先行词是不定代词all, few, little, much, something, nothing, anything等,如: All that we have to do is to practise English. (2)先行词被序数词或形容词最高级所修饰,如 The first letter that I got from him will be kept. (3)先行词被all, any, every, each, few, little, no, some等修饰,如 I've eaten up all the food that you gave me. (4)先行词被the only, the very, the same, the last修饰时如 He is the only person that I want to talk with. (5)先行词既有人又有物时,如: They talked about persons and things that they met. (6)当句中已有who时,为避免重复,如:Who is the man that is giving us the class? 6.由when, where, why引导的定语从句,如: I don't know the reason why he was late. This is the place where we have lived for 5 years. I'll never forget the day when I met Mr Li for the first time. 注意:先行词是表示地点时,如果从句的谓语动词是及物的,就用that(which),如果从句的谓语动词是不及物的,就用where引导。This is the house Which /that he has lived in for 15 years.(Where he has lived for 15 year.)
高中定语从句详细讲解精编版
高中定语从句详细讲解 精编版 -CAL-FENGHAI-(2020YEAR-YICAI)_JINGBIAN
高中定语从句详细讲解 (一)定义及相关术语 1.定语从句:修饰某一名词或代词的从句叫定语从句。定语从句一般紧跟在它所修饰的先行词之后。 2.先行词:被定语从句修饰的词叫先行词。 3.关系词:引导定语从句的词叫关系词。 关系词有关系代词和关系副词。关系代词有that, which, who, whom, whose, as等;关系副词有when, where, why等。 关系词通常有下列三个作用:A、引导定语从句;B、代替先行词;C、在定语从句中担当一个成分。例如: The man who is shaking hands with my father is a policeman. 该句中,who is shaking hands with my father 是定语从句,修饰先行词the man,“who”是引导定语从句的关系词,代替先行词the man,在定语从句中作主语。 (二)关系代词引导的定语从句 1.who 指人,在定语从句中作主语。 The boys who are playing football are from Class One. 正在踢足球的男孩是一班的。 Those who want to go to the museum must be at the school gate at 7 tomorrow morning. 想去博物馆的人必须在明晨7点到大门口集合。Yesterday I helped an old man who had lost his way. 昨天我帮助了一位迷路的老人。 That is the teacher who teaches us physics. 那就是教我们物理的老师。 2.whom 指人,在定语从句中做宾语,常可省略。 Mr Liu is the person ( whom ) you talked about on the bus. 刘先生就是你们在公共汽车上谈论的那个人。 Li Ming is just the boy ( whom ) I want to see. 李明正是我想要见的男孩。 The professor ( whom ) you are waiting for has come. 你正在等的教授已经来了。 The girl ( whom ) the teacher often praises is our monitor. 老师经常表扬的那个女孩是我们的班长。 注意:关系代词whom 在口语或非正式文体中常可用who 来代替,也可省略。 The man ( whom / who )you met just now is my old friend. 3.Which 指物,在定语从句中做主语或宾语,做宾语时常可省略。 Football is a game which is liked by most boys. 足球是大多数男孩所喜欢的运动。 The factory which makes computers is far away from here. 制造计算机的那家公司离这儿很远。 He likes to read books which are written by foreign writers. 他喜欢外国作家写的书。
高中英语语法大全(详细)
第一主题英语语法系统全解(一) 第1章动词时态 2-4楼 第2章被动语态 5-7 楼 第3章虚拟语气 9-11 楼 第4章情态动词 12-16楼 第5章动词不定式 17-20 楼 第6章动词的ing形式 21-24楼 第7章过去分词 25-27楼 第8章独立主格结构 28-30楼 第9章名词性从句 31-33楼 第10章定语从句 35-40楼 第11章状语从句(一) 40-45楼 第11章状语从句(二) 第12章直接引语和间接引语 第13章倒装 第14章强调 第15章省略 第16章主谓一致 动词时态--一般时 第一章动词时态(一) 在英语中,不同时间发生的动作或存在的状态,要用不同的动词形式来表示,这就叫做动词的时态。 一、一般时 一般时包括一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时和一般过去将来时。
A.一般现在时 1.一般现在时的构成 一般现在时主要用动词原形来表示。主语是第三人称单数时,动词后面要加-s或-es。 “我’为开头做称呼的是第一人称 ‘你’怎么怎么样是第二人称 ‘他她它’是第三人称 第三人称就是第三人称转述。 例:小兰对妈妈说:“我要出去玩了” 第三人称:小兰对妈妈说,她要出去玩了。 第三人称,就是说是叙述性质的,没有人的语言,是旁白在记叙! 以我的角度说,就是第一人称; 以和你说的角度说,就是第二人称; 站在事情外说事情,他怎么怎么样,那就是第三人称了 They want good jobs. 他们想要好的工作。 The coat matches the dress. 外衣和裙子很相配。 This work does not satisfy me. 这项工作我不满意。 Do you understand? 你懂了吗? 2.一般现在时的用法 ①一般现在时的基本用法 a. 表示现在习惯性的动作或存在状态 He always takes a walk after supper. 晚饭后他总是散散步。 Everyone is in high spirits now. 现在大家都情绪高涨。 b. 表示客观事实或普遍真理 The sun rises in the east and sets in the west.
高中英语语法全英详解
必修一 语法点一:Be+v.ing表将来use the present continuous tense for future plans In English, we have lots of ways of talking about the future. The most common ways of talking about the future we encounter use ‘will’ or ‘be going to’ followed by an infinitive(动词原形), and we tend to use ‘be going to’ most often for talking about future plans. Sometimes, we also use the present continuous tense to talk about future plans. Ex. ①we are going to Mexico next Sunday. ②Are you coming to the cinema? ③He is leaving for London in two hours. ④We are spending next winter in Australia. Only some verbs can be used in this situation, such as: go, arrive, come, leave, start, stay, return, play, have, work, wear, spend, see, meet, etc. 扩展: What’s the difference between using ‘be going to’ and the present continuous to talk about future plans? Let’s look at some more examples: “I’m going to play football on Saturday” You have made a plan in your head but possibly not taken any real action to confirm it. Also, playing football on Saturday is probably not a regular event for you. “I’m playing football on Saturday” You have made a plan and taken some real action to confirm it (e.g. called your friends or booked a place to play). In this case, it’s likely that playing football on Saturdays is a common activity for you. 语法点二:Direct speech and indirect speech(直接引语和间接引语) Let's first define the terms, then look at how to talk about what someone said, and how to convert speech from direct to indirect or vice-versa. You can answer the question What did he say? in two ways: by repeating the words spoken (direct speech) by reporting the words spoken (indirect or reported speech). Direct speech repeats, or quotes, the exact words spoken. When we use direct speech in writing, we place the words spoken between quotation marks (" ") and there is no change in these words. Reported or indirect speech is usually used to talk about the past, so we normally change the tense of the words spoken. We use reporting verbs like 'say', 'tell', 'ask', and we may use the word 'that' to introduce the reported words. Quotation marks are not used. 1、declarative sentence陈述句 ①Change in pronoun: The pronoun (subject) of the reported speech is changed according to the pronoun of reporting verb or object (person) of reporting verb (first part of sentence). Sometimes the pronoun may not change. In following example the pronoun of reported speech is “I” which will be changed in indirect speech into the pronoun (Subject) of reporting verb that is “he”. He said, “I like it very much.”→He said that he liked it very much. ②Change in tense: If the first part of sentence (reporting verb part) belongs to past tense the tense of reported speech will change. If the first part of sentence (reporting verb part) belongs to present or
英语定语从句用法详解(初中)
英语定语从句用法详解(初中) 在复合句中,修饰名词或代词的从句叫定语从句,被修饰的名词或代词叫先行词,引导定语从句的有关系代词 who, whom, whose, which, that等和关系副词where, when, why 等,关系代词和关系副词在定语从句中担任句子成份。 1.由who引导的定语从句中, who用作主语,如: This is the boy who often helps me. 2.由whom引导的定语从句中,whom用作宾语,如:The man whom you are waiting for has gone home. 3.由whose引导的定语从句中, whose用作定语,如: Do you know the girl whose skirt is white? 4.由which引导的定语从句中,which用作主语或谓语动词的宾语或介词的宾语,如: The room in which there is a machine is a work shop. The river which is in front of my house is very clean. This is the pen which you want. 注意: (1)whom, which用作介词宾语时,介词可放在 whom、which之前,也可放在从句原来的位置上;但在含有介词的动词固定词组中,介词只能放在原来的位置上。如: He is the very person whom we must take good care of. (2)引导非限制性定语从句时,必须用关系代词which,不用that,如:I have lost my bag, which I like very much. (3)关系代词在句中作主语时,从句的谓语动词的人称和数必须和先行词保持一致。 5.由that引导的定语从句中,that可以指人或物,在从句中作主语或谓语动词的宾语,但不能放在介词后面作介词宾语,如: The book that I bought yesterday was written by Lu Xun. 注意在下面几种情况下必须用 that引导定语从句。 (1)先行词是不定代词all, few, little, much, something, nothing, anything等,如: All that we have to do is to practise English. (2)先行词被序数词或形容词最高级所修饰,如 The first letter that I got from him will be kept. (3)先行词被all, any, every, each, few, little, no, some等修饰,如 I've eaten up all the food that you gave me. (4)先行词被the only, the very, the same, the last修饰时如 He is the only person that I want to talk with. (5)先行词既有人又有物时,如: They talked about persons and things that they met. (6)当句中已有who时,为避免重复,如: Who is the man that is giving us the class? 6.由when, where, why引导的定语从句,如: I don't know the reason why he was late. This is the place where we have lived for 5 years. I'll never forget the day when I met Mr Li for the first time. 注意:先行词是表示地点时,如果从句的谓语动词是及物的,就用 that(which),如果从句的谓语动词是不及物的,就用where引导。This is the house Which /that he has lived in for 15 years.(Where he has lived for 15 year.)
