谓语动词的时态和语态
【语法课件】谓语动词的时态、语态和主谓一致

doing
been doing have been doing
1.一般时态 (1)一般现在时 ①表示经常或习惯性的动作,多用动作动词,且常与表频率的时间状语连用。 We have meals three times a day.我们一日吃三餐。 ②表示客观真理、科学事实及自然现象。 The sun sets in the west.太阳从西方落下。 ③在时间、条件状语从句中常用一般现在时代替一般将来时。 I'll write to her when I have time. 有时间我会写信给她。
②一般将来时的常用结构
·用于“I expect,I'm sure,I think,I wonder+宾语从句”中 ·用于“祈使句+and+陈述句”中 ·与表示时间或条件的状语从句连用
Don't worry about the exam.I'm sure you'll pass. 不要担心这次考试,我确信你会通过的。 If you ask him,he will help you. 如果你请他帮忙,他会帮助你的。
③ 表 示 位 置 转 移 的 动 词 可 用 进 行 时 代 替 将 来 时 。 这 样 的 动 词 有 go , come , start,leave,arrive,begin,return等。 I'm leaving for Beijing next month. 我下个月要去北京。 (2)过去进行时(was/were+现在分词) 过去进行时表示在过去某个时刻或某段时间正在进行的动作或存在的状态。 He was reading an interesting book this time yesterday. 昨天这个时候他在读一本有趣的书。
高考英语谓语动词的时态、被动语态和主谓一致
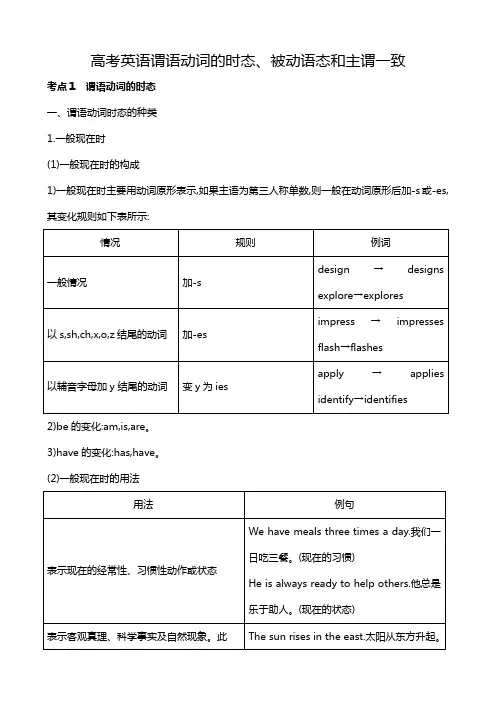
高考英语谓语动词的时态、被动语态和主谓一致考点1 谓语动词的时态一、谓语动词时态的种类1.一般现在时(1)一般现在时的构成1)一般现在时主要用动词原形表示,如果主语为第三人称单数,则一般在动词原形后加-s或-es,其变化规则如下表所示:2)be的变化:am,is,are。
3)have的变化:has,have。
(2)一般现在时的用法2.一般过去时(1)一般过去时的构成1)一般过去时用动词的过去式表示,其规则动词变化方法如下表所示:2)was用于第一、三人称单数,were用于其他情况。
3)注意以元音字母加y结尾的动词:规则变化是直接加-ed,如play→played;不规则变化是把y 改为id,如:pay→paid,say→said。
(2)一般过去时的用法3.一般将来时(1)一般将来时的构成(2)一般将来时的用法4.现在进行时(1)现在进行时的构成:is/am/are+现在分词(2)现在进行时的用法5.过去进行时(1)过去进行时的构成:was/were+现在分词(2)过去进行时的用法6.现在完成时(1)现在完成时的构成:has/have+过去分词(2)现在完成时的用法注意(1)瞬间动词若用于现在完成时且与表示一段时间的时间状语连用,需在谓语动词、时态或句型方面作相应变化。
如:他参军3年了。
(×)He has joined the army for 3 years.(√)He has been in the army for 3 years.(换动词)(√)He joined the army 3 years ago.(换时态)(√)It has been/is 3 years since he joined the army.(换句型)(2)部分瞬间动词(词组)与延续性动词(词组)对应表7.过去将来时(1)过去将来时的构成(2)过去将来时的用法8.将来进行时(1)将来进行时的构成:will/shall be doing(2)将来进行时的用法9.过去完成时(1)过去完成时的构成:had+过去分词(2)过去完成时的用法10.现在完成进行时(1)现在完成进行时的构成:have/has been doing(2)现在完成进行时的用法二、谓语动词时态的呼应1.主将从现2.含宾语从句的句子的时态一致问题(1)宾语从句中的动词时态常受主句谓语动词时态的制约,如果主句谓语动词为一般现在时或一般将来时,宾语从句中的谓语动词可以不受影响。
语法复习-谓语动词的时态+语态(共83张PPT)

现在 过去 将来
一般
进行时
完成时
一般现在时: 现在进行时:
原形(do)
am/is/are doing
第三人称单数形
式(does)
现在完成时: have / has done
一般过去时:
一般过去式 (did)
过去进行时: 过去完成时: was / were doing had done
一般将来时:
1)will do
drop, fit, nod, dig, forget, regret, rid】 • 4)以 y 结尾的动词,直接加 ing • 5)以ie结尾的动词,把ie改为y ,再加ing
动词的ing形式
• run_____ • swim____ • sit ____
• stop_____ • have_____ • dance_____ • organize____
②③不适合语法填空中填 动词的适当形式。
一般将来时的用法
1. He will graduate from Harvard University next year.
2. I am going to buy a new laptop this winter. 3. The car is going to turn over. 5. I am to take over the job. 6. The conference is about to begin.
过去 将来
现在
将来
现在 过去 将来
一般
进行时
完成时
一般现在时: 现在进行时:
原形(do)
am/is/are doing
第三人称单数形
式(does)
高中英语语法必备之谓语动词的时态和语态详解

⾼中英语语法必备之谓语动词的时态和语态详解⾼中英语动词的时态语态详解在英语中,句⼦不仅有时间状语说明动作发⽣的时间,其谓语动词本⾝也有形式的变化来指⽰时间,这种表明谓语动词发⽣时间的动词形式称为时态。
语态是表现主语和谓语关系的另⼀种动词形式。
⼀动词的时态⼀般说来,发⽣在现在的事情⽤现在的时态进⾏描述;发⽣在过去的事情⽤过去的时态进⾏描述;将要发⽣的事情⽤将来的时态进⾏描述。
英语中的时态共计16种,但常⽤的有11种。
(以动词do 为例)1.⼀般现在时(do/does);2.⼀般过去时(did);3.⼀般将来时( will do/ shall do);4.⼀般过去将来时( would do/should do);5.现在进⾏时( am/is/are doing);6.过去进⾏时(was/were doing);7.将来进⾏时( will/shall be doing);8.现在完成时(have/has done);9.过去完成时( had done);10.将来完成时( will/shall have done);11.现在完成进⾏时( have/has been doing);1.⼀般现在时(1)⼀般现在时是描述现在或经常性的性质、动作或状态的时态常⽤时间状语:sometimes, often, always, usually, seldom,every day / night / week / month / year, in the morning, in the afternoon, in the evening, at night(2)表⽰经常发⽣的动作,习惯性的动作或存在的状态I usually get up at four every morning when it’s still dark.He always goes to work late,which makes his boss angry and disappointed.(3)客观真理,客观存在,科学事实及⾃然现象The sun rises in the east and sets in the west every day.The man who has never been to the Great Wall is not a real man.Trees turn green in spring. Liquid turns into gas when it is hot enough.(4)表⽰格⾔或警句中Pride goes before a fall.Knowledge is power.Practice makes perfect.(5)⼀般现在时表将来表⽰已经计划、安排好了或时间表上所安排,并且⼀定要做的事情。
谓语动词、非谓语动词 vs时态、语态
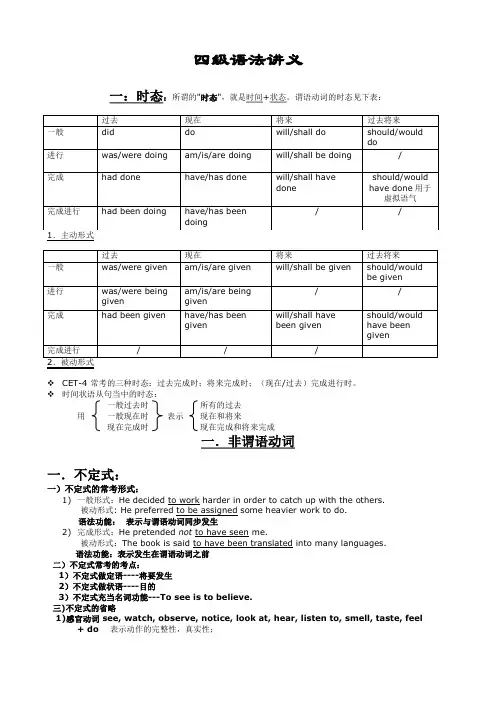
四级语法讲义一:时态:所谓的"时态",就是时间+状态。
谓语动词的时态见下表:1.主动形式2.被动形式CET-4 常考的三种时态:过去完成时;将来完成时;(现在/过去)完成进行时。
时间状语从句当中的时态:一般过去时所有的过去用一般现在时表示现在和将来现在完成时现在完成和将来完成一.非谓语动词一.不定式:一)不定式的常考形式:1)一般形式:He decided to work harder in order to catch up with the others.被动形式: He preferred to be assigned some heavier work to do.语法功能:表示与谓语动词同步发生2)完成形式:He pretended not to have seen me.被动形式:The book is said to have been translated into many languages.语法功能:表示发生在谓语动词之前二)不定式常考的考点:1)不定式做定语----将要发生2)不定式做状语----目的3)不定式充当名词功能---To see is to believe.三)不定式的省略1)感官动词 see, watch, observe, notice, look at, hear, listen to, smell, taste, feel+ do表示动作的完整性,真实性;+ doing表示动作的连续性,进行性I saw him work in the garden yesterday.昨天我看见他在花园里干活了。
(强调"我看见了"这个事实)I saw him working in the garden yesterday.昨天我见他正在花园里干活。
(强调"我见他正干活"这个动作)感官动词后面接形容词而不是副词:The cake tastes good; It feels comfortable.2) 使役动词 have bid make let 等词后不定式要省略但同1)一样被动以后要还原toI ‘d like to have John do it.I have my package weighed.Paul doesn’t have to be mad e to learn.3) help help sb do help sb to do help do help to do四)有些动词后只跟不定式如:want,wish,hope,manage,promise,refuse,pretend,plan, offer,decide,agree,expect allow sb to do, cause sb to do , permit sb to do, enable sb to doforce sb to do. be more likely to do love to do warn sb to do be able to dobe ambitious to do. begin to do . start to do五) 有的时候to后面要接-ing形式accustom (oneself) to; be accustomed to; face up to; in addition to; look forward to; object to; be reduced to; resign oneself to; be resigned to; resort to; sink to; be used to; be alternative to; be close/closeness to; be dedication/dedicated to; be opposition/opposed to; besimilarity/similar to.三、need/want 后的-ing形式具有被动的意思。
语法:谓语动词两态变化

语法:谓语动词两态变化谓语只能由动词充当,谓语动词有两种方式可以发生形态变化:“时态+语态”两态变化。
A.谓语动词时态变化时态指作谓语的动词在不同时间中所表现出来的不同状态,表现在“时间+状态”的变化。
时间表现在“过去、现在、将来”(过去将来不作讨论)的变化;时间点中的状态表现在“一般、完成、进行”(完成进行不作讨论)的变化。
由此可以通过横、纵两个坐标来组合相应时态:过去现在将来一般一般过去时一般现在时一般将来时进行过去进行时现在进行时将来进行时完成过去完成时现在完成时将来完成时在不同时态中,动词分别以do(原形)、does(第三人称单数)、did(过去式)、done(过去分词)、doing(现在分词)任意一种形式存在,放在具体的时态中分别可以总结为:⑴.“一般”时:谓语变化体现在实义动词本身。
一般过去时→did一般现在时→do, does一般将来时will+do(will无人称和数的变化)⑵.“进行”时:基本结构be doing谓语变化体现在助动词be,实义动词doing不变。
过去进行时→was/were doing现在进行时→am/is/are doing将来进行时→will be doing(will无人称和数的变化)⑶.“完成”时:基本结构have done谓语变化体现在助动词have,实义动词done不变。
过去完成时→had done(had无人称和数的变化)现在完成时→have/has done将来完成时→will have done(will无人称和数的变化)以下为各时态结构汇总表格,需要识记默写:B.谓语动词语态变化语态的变化可以理解为主语和宾语或表语位置的单词对句子的统治权的争夺,当主语是动词动作的发出者时,句子采用主动语态,当主语是动词动作的被动承受者时,句子采用被动语态。
主动语态中的谓语动词没有结构形态的变化,而被动语态中的谓语动词需要借助助动词be,构成be done的结构。
谓语动词的时间语态及进行语态
should have been studying
would have been studying
谓语动词的时间语态
当所说的事情发生在不同时间时,英语句子的谓语要“变脸”, 出来的样子叫“时间语态”简称“时态”。 时态是英语谓语最大的一种变脸,它一共有8个变化,也叫8个时 态,它们分别是:
20 years by that summer.
感 谢
感 谢
阅阅
读读
2.一般过去时态(V-ed)
当谓语动词发生在”现在以前”时间内,我们就说动作发生 在
“一般过去”时间内。
表达这个时段的时间词可以是yesterday, long time ago,5 years ago, two days early, in 1949,at the end of last year, when you came, he said等 I watched TV last night. They were here only a few minutes ago
6.过去将来时态(should+V)
当谓语动词的动作发生在“从过去看将来”时间时,动词的 动
作发生在“过去将来”时间段内。
当讲一个过去的事件时,事件中又提到一件将要发生的事。 这个事件就发生在“从过去看将来”时间里,比如“昨天他 说他要去国外旅游”。这里的“去”就发生在过去将来时间 里。 He told me he would go to Beijing. I didn't know if he would come.
3. 将来进行时(shall/will + be+ v- ing) You will be making a mistake.
谓语动词的时态和语态:将来时,被动语态
谓语动词的时态和语态:将来时,被动语态谓语动词是句子中的核心动词,它表达了动作、状态或存在。
时态和语态是谓语动词的两个重要方面。
在本文档中,我们将关注将来时和被动语态这两个主题。
将来时态将来时态用来表示将来发生的动作或状态。
在英语中,将来时态有不同的形式:will + 动词原形,be going to + 动词原形,以及一些其他的辅助动词结构。
1. 使用 will + 动词原形来表示将来时态:- 我将去市中心购物。
- I will go shopping in the city center.2. 使用 be going to + 动词原形来表示将来时态:- 我们明天将举办一个重要会议。
- We are going to hold an important meeting tomorrow.3. 其他辅助动词结构用来表示特定的将来动作或状态:- 我明天会正在吃午饭。
- I will be having lunch tomorrow.被动语态被动语态用于强调动作的接受者而不是执行者。
在被动语态中,谓语动词以一种形式变为动作的接受者。
被动语态的形式为:be + 过去分词。
1. 将主动语态转换为被动语态:- 主动语态:他吃了这个苹果。
- 被动语态:This apple has been eaten by him.2. 如果主动语态中有物主代词,需要将其作为被动语态的主语,并使用对应的被动语态动词形式:- 主动语态:我们修理了这辆车。
- 被动语态:This car was repaired by us.被动语态可以用来强调行为的接受者,或者在不知道或不关心动作执行者时使用。
总结谓语动词的时态和语态在句子中起着重要的作用。
将来时态用于表示将来发生的动作或状态,可以使用 will + 动词原形、be going to + 动词原形或其他辅助动词结构。
被动语态用于强调动作的接受者,可以通过将主动语态动词转换为 be + 过去分词的形式来表达。
高中英语谓语动词时态和语态最全课件
• 还有几种特殊的形式也表示将来时态:
• 1.be going to+do表示:
• 主观上已经决定、打算、准备要做的事。 例如:I am going to buy a new car. 我打 算买辆新车。
• 某种迹象表明很可能发生的事情。例如: Dark clouds are gathering. It is going to rain.乌云密布,要下雨了。
there by air.
Exercise 2
用现在进行时翻译下列句子。 V.
1. 我星期五动身去北京。 leave / go2ຫໍສະໝຸດ 我的朋友今晚过来。come
3. 下周五我们乘飞机去上海。 fly
4. 下课后我们打算在操场踢足球。 play
1.我星期五动身去北京。 leave / go I’m leaving for Beijing this Friday. 2. 我的朋友今晚过来。 come My friends are coming over this evening. 3. 下周五我们乘飞机去上海。 fly We are flying to Shanghai next Friday. 4. 下课后我们打算在操场踢足球。 play After class we are playing football on the
• 2.be to+动词原型表示:
• 约定、计划或按职责、义务要求即将发生 的动作。例如:
• We are to meet at the train station at four this afternoon. 我们计划今天下午四点在 火车站见面
• The sports meet is to take place on Sunday morning.运动会将在周日上午举 行。
(完整版)2019 谓语动词的时态和语态
谓语动词的时态和语态一.谓语的概念谓语动词指在句子中充当谓语的动词,有行为动词,系动词,情态动词和助动词等几种,其中行为动词又包括及物动词和不及物动词。
谓语成分就是用来说明主语的动作或状态的,一般由动词或动词短语承担。
如果句子中没有动词充当谓语的时候,就使用“be"动词。
Tom’s garden is beautiful。
My aunt always looks young。
He cannot swim。
Some women are washing clothes by the river。
I have got a new job.We will visit the Great Wall tomorrow.The rabbit was shot dead。
They will be invited to attend the meeting.The child opened his eyes, looking at his mother for a while.No one can avoid being influenced by advertisements。
谓语动词的时态时态是英语谓语动词的一种形式,表示动作发生的时间和所处的状态.英语中的时态是通过动词形式本身的变化来实现的。
英语有16种时态,但中学阶段较常用的有十种:一般现在时,一般过去时,一般将来时,过去将来时,现在进行时,过去进行时,将来进行时,过去完成时,现在完成时和现在完成进行时。
一般现在时(the simple present tense )1. 经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频腮度的时间状语连用。
时间状语:every…, sometimes, on Sunday sI leave home for school at 7 every morning. He sometimes stays in bed until lunch time。
- 1、下载文档前请自行甄别文档内容的完整性,平台不提供额外的编辑、内容补充、找答案等附加服务。
- 2、"仅部分预览"的文档,不可在线预览部分如存在完整性等问题,可反馈申请退款(可完整预览的文档不适用该条件!)。
- 3、如文档侵犯您的权益,请联系客服反馈,我们会尽快为您处理(人工客服工作时间:9:00-18:30)。
动词的时态和语态英语的时态是一种动词形式.不同的时态用以表示不同的时间与方式. 英语动词有16种时态,常用的有8种:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、过去将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时。
但高中学生需要了解13种,除了以上8种,还须掌握以下5种:将来进行时(一般将来进行时、过去将来进行时)、一般将来完成时、完成进行时(现在完成进行时、过去完成进行时)。
下面分别介绍。
【注】构成时态的助动词be (is, am, are), have (has), shall, will 等需根据主语的变化来选.一.一般现在时1).表示经常性或习惯性的动作或状态. 常与表示频度的时间状语连用.如:often, usually, always, sometimes, now, seldom, now and then, every day, occasionally等.I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning.We have meals three times a day.He is always ready to help others.2).表示客观事实、普遍真理、谚语、格言、警句。
Guangzhou is situated/lies in the south of China. Everything is much lighter on the moon. There are four seasons in a year: spring, summer, autumn and winter.The sun rises in the east and sets in the west. The earth goes around the sun.Light travels faster than sound. Practice makes perfect.Pride goes before a fall.骄者必败。
Actions speak louder than words.注意:此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。
Columbus proved that the earth is round.The day before yesterday I was told that in time of danger one’s mind works fast.3).表示主语目前的特征、性格或说话时的感觉或状态。
Ann writes good English but does not speak well.He works very hard. He is very happy. I’m glad to see you again. You see what I mean.4). 在时间状语从句、条件状语从句或让步状语从句中,用一般现在时表将来。
这时主句是将来时或祈使句.When he arrives, he’ll tell us all about the match. Tell him the news as soon as he comes.When I graduate, I’ll go to countryside.What are you going to be when you grow up. We’re to go outing if it’s fine tomorrow. I’ll not go unless I’m invited.Even if she doesn’t come this Saturday, I’ll go fishing by myself.注意:make sure, take care, mind, it doesn’t matter, I don’t care 后跟从句时, 从句中用一般现在时表将来.We must take care that no one sees us.Our staff will do their best to make sure you enjoy your visit.It doesn’t matter where we go on holiday.5).表示按时刻表拟定(如火车、飞机、轮船等定点的驶进驶出,起飞降落。
)或安排好将要发生的事情。
这时句中都带有一个表示将来的时间状语。
能用于此种用法的少量动词有:begin, come, leave, go ,arrive, take off, start , stop, return, open, close等。
The train leaves at 10 a.m. the plane for Canada departs/takes off at 9:15 a.m.The film starts at 9:30 p.m. The new term starts at the beginning of September.The program ends at 11:10 pm When does the train stop at Jinan?6).在某些以here,there开头的句子中用一般现在时表示正在发生的动作或存在的状态。
Here comes the bus!=the bus is coming here!There goes the thief!=the thief is going there!7).用于文章标题,小说、戏剧、电影等的剧本或图片的文字说明中。
Hundreds of people die in the earthquake. (新闻标题)When the curtain rises, Juliet is sitting at her desk.Mary, _____ here— everybody else, stay where you are.A. comeB. comesC. to comeD. coming二.一般过去时1).表示过去某一时间发生的动作或存在的状态。
常常与过去的时间状语连用。
yesterday, last night, just now, at that time, 3 years ago, in1949, the other day, then…等等He graduated from No.1 Middle School in 1978.I went to the movies/cinema last night. Marry worked in the company for five years. Whenever the Browns went during their visit, they were given a warm welcome2).表示过去经常或反复发生的动作,往往与often, usually, always, would, used to连用。
He often asked a lot of strange questions when he was a boy.She used to walk dogs along the river in the morning.Often at night she would hear a long low whistle and a sound of metallic noise.3).用于一些常用结构,表示刚刚,刚才…Oh, it’s you. I didn’t recognize you at first. I didn’t know you were here.Sorry, I forgot to bring my money. You look young. I thought you were 30. Sorry, but I didn’t mean to hurt you.Edward, you play so well. But I you played the piano.A. didn't knowB. hadn't knownC. don't knowD. haven't known4).在时间、条件、让步状语从句中用一般过去时代替过去将来时。
这时主句中是过去将来时或表示将来意义的动词。
She said he would give me a gift when she came again.They planed to go outing if it was fine the next day.He promised to buy me a computer if he got a raiseHelen had left her keys in the office so she had to wait until her husband came home.三.一般将来时1).表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态。
I will/shall do it again tomorrow. Tom will be here next week.He will be six years old next month. We shall know more and more as time goes on.2).表示事物固有的属性或必然趋。
Fish will die without water.Oil will float on water.一般将来时常与时间状语tomorrow, soon, next week, in (the )future, in three days等连用。
注意:won’t可用来表示“不能,没法”,表示主语不具备某种功能.The door won’t open. This machine won’t work.What’s the matter with the pen? The ink won’t come out.除了用shall/will(美语中,一般不论人称都用will)表示将来时之外,还有5种表达将来时的方法。
①be going to do (1)表示按照计划或安排“打算做…”(2)有迹象表明,注定要,必定要发生某事。
He is going to watch TV this evening.Look, dark clouds are gathering .It’s going to rain注意:be going to表示现在打算在最近或将来要做某事,这种打算往往经过事先考虑,甚至已做了某种准备。
